
What element is 1s22s22p63s23p64s23d104p5?
Apr 28, 2016 · The electron configuration of phosphorus is 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p3. Phosphorus has an atomic number of 15, so it has 15 electrons. What is the Valency of phosphorus?
What is electronic configuration of phosphorus?
Feb 05, 2012 · This answer is: 👍Helpful (0)👎Not Helpful (0) Add a Comment. Study guides. Chemistry. 20 cards. To name a monatomic anion change the suffix of the element's name to. The electron geometry of ...
What is the noble gas electronic configuration for phosphorus?
Therefore the Phosphorus electron configuration will be 1s 2 2s 2 2p 6 3s 2 3p 3. Video: Phosphorus Electron Configuration Notation The configuration notation provides an easy way for scientists to write and communicate how electrons are arranged around the nucleus of an atom.
What are unabbreviated and abbreviated electron configurations?
Nov 13, 2020 · Phosphorus is a chemical element with atomic number 15 which means there are 15 protons and 15 electrons in the atomic structure. The chemical symbol for Phosphorus is P. Electron Configuration and Oxidation States of Phosphorus. Electron configuration of Phosphorus is [Ne] 3s2 3p3. Possible oxidation states are +3,5/-3. Electron Configuration
See more
Electron configuration of Phosphorus is [Ne] 3s2 3p3. Possible oxidation states are +3,5/-3 . As an element, phosphorus exists in two major forms—white phosphorus and red phosphorus—but because it is highly reactive, phosphorus is never found as a free element on Earth.
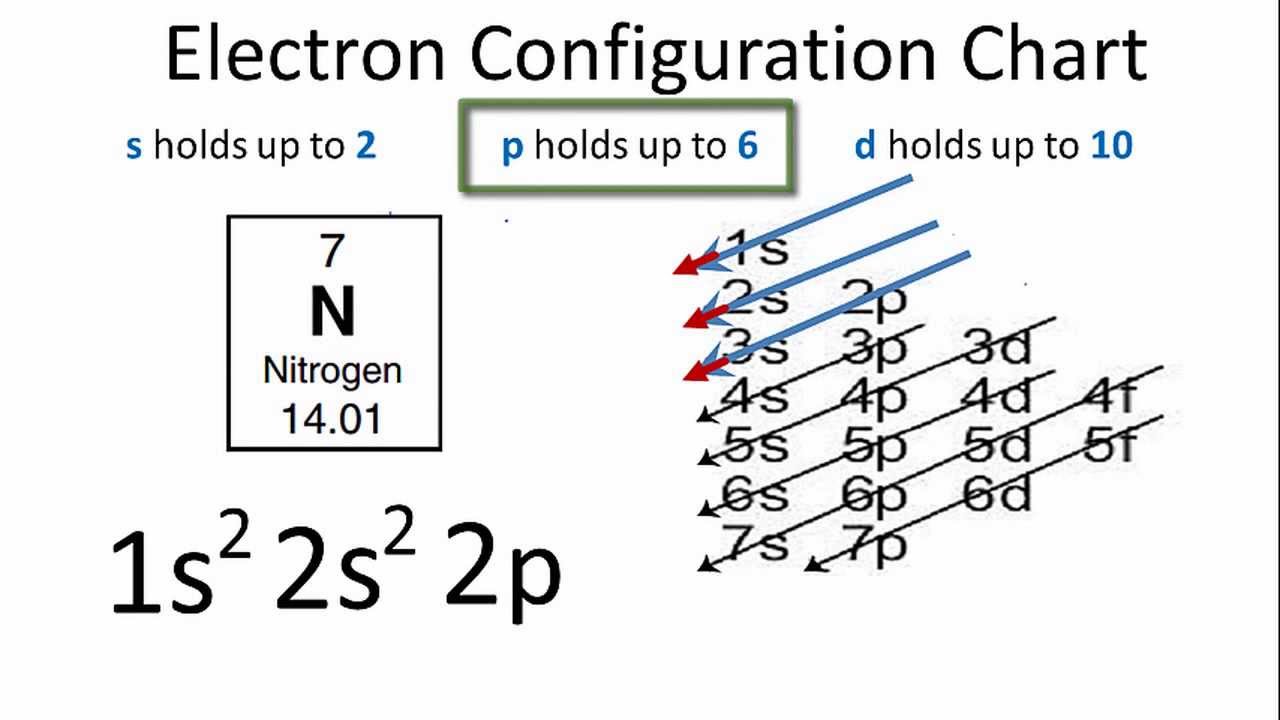
How do you write electron configuration of Phosphorus?
What is 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p6 4s2 3d3?
What is a abbreviated electron configuration?
Which element has the electron configuration 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p6 4s2 3d6?
What element is 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p6 4s2 3d8?
| A | B |
|---|---|
| 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p6 4s2 3d8 | Ni |
| 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p2 | Si |
| 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s1 | Na |
| 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p6 4s2 3d1 | Sc |
What element has the electron configuration 1s22s22p63s2?
What is the abbreviated electron configuration of nobelium?
How do you write the electron configuration?
What is the abbreviated electron configuration of lawrencium?
What does 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p6 mean?
What element has an electron configuration of 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p6 4s2 and which block is it in?
What is the electron configuration of aluminum AL )?
Electron Configuration
The periodic table is a tabular display of the chemical elements organized on the basis of their atomic numbers, electron configurations, and chemical properties. The electron configuration is the distribution of electrons of an atom or molecule (or other physical structure) in atomic or molecular orbitals.
Oxidation States
Oxidation states are typically represented by integers which may be positive, zero, or negative. Most elements have more than one possible oxidation state. For example, carbon has nine possible integer oxidation states from −4 to +4.
What is the electron configuration of phosphorus?
Electron configuration of Phosphorus is [Ne] 3s2 3p3. Possible oxidation states are +3,5/-3. As an element, phosphorus exists in two major forms—white phosphorus and red phosphorus—but because it is highly reactive, phosphorus is never found as a free element on Earth. The most prevalent compounds of phosphorus are derivatives of phosphate, ...
How many electrons are in a neutral atom of phosphorus?
Therefore, the number of electrons in neutral atom of Phosphorus is 15. Each electron is influenced by the electric fields produced by the positive nuclear charge and the other (Z – 1) negative electrons in the atom.
Why is phosphorus needed?
Phosphate is needed to replace the phosphorus that plants remove from the soil, and its annual demand is rising nearly twice as fast as the growth of the human population. The predominant source of phosphorus in modern times is phosphate rock (as opposed to the guano that preceded it).
How many protons does phosphorus have?
Phosphorus is a chemical element with atomic number 15 which means there are 15 protons in its nucleus. Total number of protons in the nucleus is called the atomic number of the atom and is given the symbol Z. The total electrical charge of the nucleus is therefore +Ze, where e (elementary charge) equals to 1,602 x 10-19 coulombs.
What is the difference between neutrons and atomic numbers?
Neutron number plus atomic number equals atomic mass number: N+Z=A. The difference between the neutron number and the atomic number is known as the neutron excess: D = N – Z = A – 2Z.
Is phosphorus a free element?
As an element, phosphorus exists in two major forms—white phosphorus and red phosphorus—but because it is highly reactive, phosphorus is never found as a free element on Earth. The most prevalent compounds of phosphorus are derivatives of phosphate, a tetrahedral anion. Phosphate is the conjugate base of phosphoric acid, ...
What is the most common compound of phosphorus?
Most Common Compound of Phosphorus. Phosphoric acid is a weak acid with the chemical formula H3PO4. Food-grade phosphoric acid is used to acidify foods and beverages such as various colas and jams, providing a tangy or sour taste.
How are atoms determined?
The chemical properties of the atom are determined by the number of protons, in fact, by number and arrangement of electrons. The configuration of these electrons follows from the principles of quantum mechanics. The number of electrons in each element’s electron shells, particularly the outermost valence shell, is the primary factor in determining its chemical bonding behavior. In the periodic table, the elements are listed in order of increasing atomic number Z.
How are the chemical properties of a solid, liquid, gas, and plasma determined?
The chemical properties of the atom are determined by the number of protons, in fact, by number and arrangement of electrons. The configuration of these electrons follows from the principles of quantum mechanics. The number of electrons in each element’s electron shells, particularly the outermost valence shell, is the primary factor in determining its chemical bonding behavior. In the periodic table, the elements are listed in order of increasing atomic number Z.
How are atomic nuclei determined?
Properties of atomic nuclei (atomic mass, nuclear cross-sections) are determined by the number of protons and number of neutrons (neutron number). It must be noted, especially nuclear cross-sections may vary by many orders from nuclide with the neutron number N to nuclide with the neutron number N+1. For example, actinides with odd neutron number are usually fissile (fissionable with slow neutrons) while actinides with even neutron number are usually not fissile (but are fissionable with fast neutrons). Heavy nuclei with an even number of protons and an even number of neutrons are (due to Pauli exclusion principle) very stable thanks to the occurrence of ‘paired spin’. On the other hand, nuclei with an odd number of protons and neutrons are mostly unstable.
How to determine the stability of an isotope?
To determine the stability of an isotope you can use the ratio neutron/proton (N/Z). Also to help understand this concept there is a chart of the nuclides, known as a Segre chart. This chart shows a plot of the known nuclides as a function of their atomic and neutron numbers. It can be observed from the chart that there are more neutrons than protons in nuclides with Z greater than about 20 (Calcium). These extra neutrons are necessary for stability of the heavier nuclei. The excess neutrons act somewhat like nuclear glue. Only two stable nuclides have fewer neutrons than protons: hydrogen-1 and helium-3.
What is the symbol for electronegativity?
Electronegativity, symbol χ, is a chemical property that describes the tendency of an atom to attract electrons towards this atom. For this purposes, a dimensionless quantity the Pauling scale, symbol χ, is the most commonly used.
What is the boiling point of a substance?
The boiling point of a substance is the temperature at which this phase change (boiling or vaporization) occurs. The temperature at which vaporization (boiling) starts to occur for a given pressure is also known as the saturation temperature and at this conditions a mixture of vapor and liquid can exist together. The liquid can be said to be saturated with thermal energy. Any addition of thermal energy results in a phase transition. At the boiling point the two phases of a substance, liquid and vapor, have identical free energies and therefore are equally likely to exist. Below the boiling point, the liquid is the more stable state of the two, whereas above the gaseous form is preferred. The pressure at which vaporization (boiling) starts to occur for a given temperature is called the saturation pressure. When considered as the temperature of the reverse change from vapor to liquid, it is referred to as the condensation point.
What is thermal expansion?
Thermal expansion is generally the tendency of matter to change its dimensions in response to a change in temperature. It is usually expressed as a fractional change in length or volume per unit temperature change. Thermal expansion is common for solids, liquids and for gases. Unlike gases or liquids, solid materials tend to keep their shape when undergoing thermal expansion. A linear expansion coefficient is usually employed in describing the expansion of a solid, while a volume expansion coefficient is more useful for a liquid or a gas.
