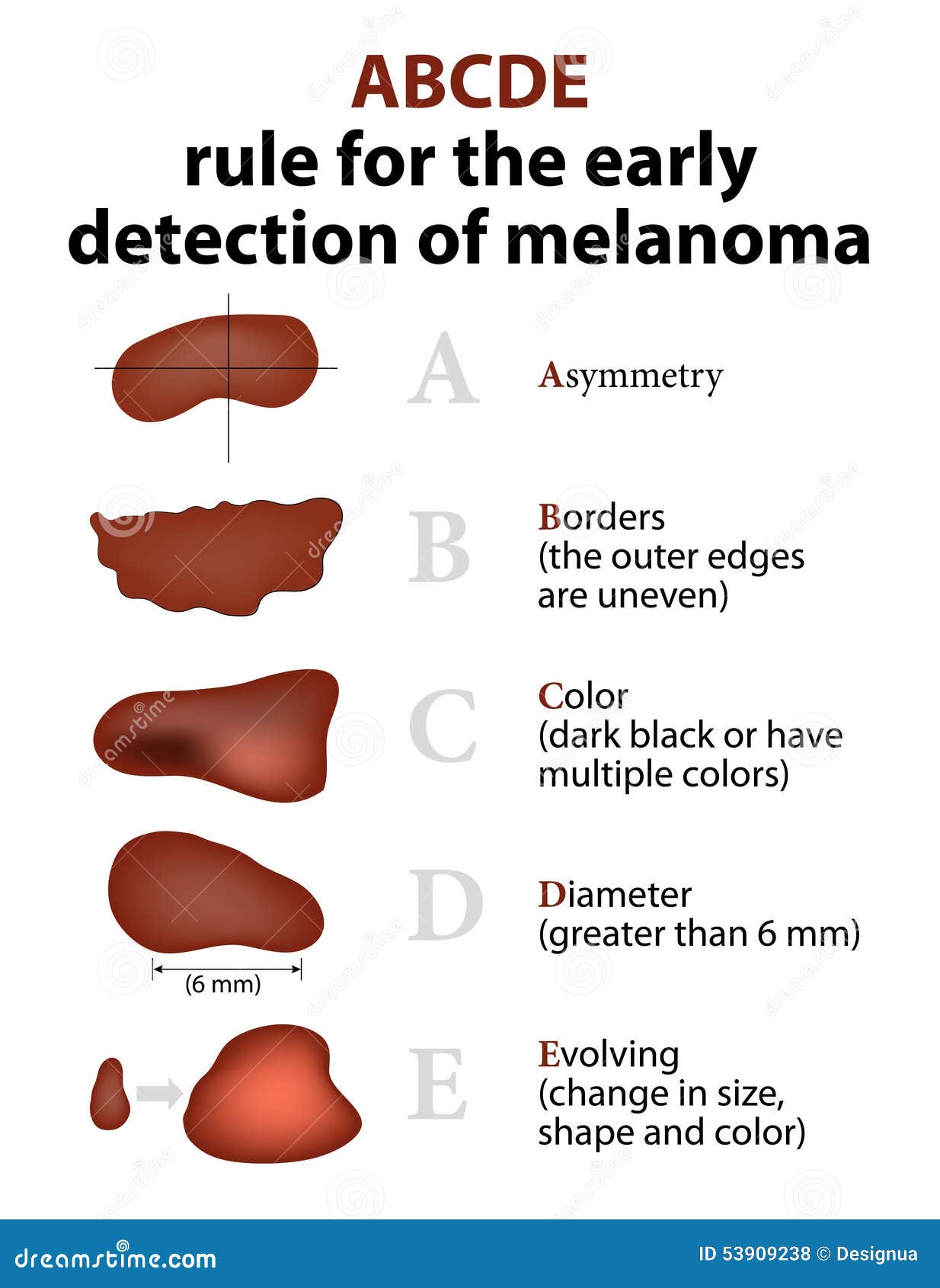
What are the ABCDE rules for melanoma?
The ABCDE’s of Melanoma Detection
- A: This stands for asymmetry. Some doctors say that if you could fold the mole in two, the halves would not be identical. ...
- B: This letter refers to the border. ...
- C: Color is denoted by this letter. ...
- D: This letter refers to the diameter. ...
- E: This stands for evolving. ...
Do you know the ABCs of melanoma?
The ABCDEs of melanoma The first five letters of the alphabet are a guide to help you recognize the warning signs of melanoma. A is for Asymmetry. Most melanomas are asymmetrical. If you draw a line through the middle of the lesion, the two halves don’t match, so it looks different from a round to oval and symmetrical common mole. B is for Border.
Is melanoma considered skin cancer?
Melanoma is a type of skin cancer that develops when melanocytes (the cells that give the skin its tan or brown color) start to grow out of control. Cancer starts when cells in the body begin to grow out of control. Cells in nearly any part of the body can become cancer, and can then spread to other areas of the body.
What is the "ABCD" test of moles for melanoma?
The ABCD’s of melanoma are as follows: Asymmetry, Border irregularity, Color variability, and Diameter larger than a pencil eraser. Asymmetry: Most early melanomas are asymmetrical: a line through the middle would not create matching halves. Common moles are round and symmetrical.
What is the meaning of D in the ABCD rule of determining skin cancer?
A – Asymmetry: Different from one side to the next. B – Border irregularity: Melanoma lesions usually have irregular borders that are difficult to define. C – Color: Variation and/or change. D – Diameter: More than 6 mm (end of a pen tip) and/or change in diameter.
What does ABCD mean in examination of pigmented areas?
The ABCD (asymmetry, border irregularity, color variegation, diameter >6 mm) acronym was created in 1985 to help primary care physicians and laypersons recognize early melanomas that might be confused with benign pigmented lesions.
What is the ABCD rule?
One easy way to remember common characteristics of melanoma is to think alphabetically – the ABCDEs of melanoma. ABCDE stands for asymmetry, border, color, diameter and evolving. These are the characteristics of skin damage that doctors look for when diagnosing and classifying melanomas.
How do you use ABCDE rule?
The ABCDE Rule of Skin CancerA Is for Asymmetry. Normal moles or freckles are typically symmetrical. ... B Is for Border. Moles, spots, or “beauty marks" are typically round and of no cause for concern. ... C Is for Color. Normal moles and spots are usually one color. ... D Is for Diameter. ... E Is for Evolution. ... Example.
What does the B stand for in the melanoma ABCD acronym?
The ABCDE rule for skin cancer is a handy acronym that can help you identify potential skin cancers. The letters stand for “Asymmetrical, Border, Color, Diameter, Evolving.”
What do the Abcdef of melanoma stand for?
The 'ABCDE' of melanoma is an acronym designed to help the public and clinicians identify features in a skin lesion that may suggest an early or in situ melanoma (superficial spreading melanoma, lentigo maligna melanoma, or acral lentiginous melanoma). Asymmetry. Border irregularity. Colour variability/Change. ...
What are the Abcde indicators of a mole or lesion that warn of melanoma whose cure rate is nearly 100 percent with early detection and treatment?
ABCDE stands for asymmetry, irregular border, color variations (especially red, white, and blue tones in a brown or black lesion), diameter greater than 6 mm, and elevated surface. Lesions may itch, bleed, ulcerate, or develop satellites.
How do you describe a melanoma lesion?
The lesions of superficial spreading melanoma are dark brown or black. In the initial phase they have a slowly spreading irregular outline. Some areas may be a lighter shade. Vertical growth occurs later, penetrating into the dermis and causing some parts of the lesion to become raised.
What does ABCDE stand for in melanoma?
The American Academy of Dermatology suggests learning the ABCDE rule to recognize the warning signs of melanoma. The ABCDE rule says “A” stands for asymmetry. “If a mole does not look the same on both sides, then you need to see a Dermatologist immediately,” said Dr. Howington. “B” stands for border irregularity.
What does C stand for in skin cancer?
Border irregularity is when the edges of a mole are ragged, notched or blurred. “C” stands for color. “If the color of a mole differs from one area to another, then you should get a skin cancer screening immediately,” said Dr. Howington. “D” stands for diameter.
How to prevent skin cancer?
You can also prevent skin cancer by wearing protective clothing, using “broad-spectrum” sunscreen, avoiding tanning beds, and exercising caution around water, sand and snow because these elements intensify the sun’s heat. Sunscreen should be applied every two hours or after swimming or sweating.
What does ABCDE stand for in melanoma?
ABCDE stands for asymmetry, border, color, diameter and evolving. These are the characteristics of skin damage that doctors look for when diagnosing and classifying melanomas.
What to do if you have melanoma?
If you notice any of the s igns and symptoms of melanoma or you have a suspicious mole or lesion, make an appointment to see your doctor . You may want to have annual skin checks with a dermatologist as well so you can catch skin cancer before it becomes life threatening.
What is the difference between melanoma and non-cancerous moles?
Border – Melanoma often has borders that aren’t well defined or are irregular in shape, whereas non-cancerous moles usually have smooth, well-defined borders.
Does melanoma change over time?
Evolution – Melanoma will often change characteristics, such as size, shape or color. Unlike most benign moles, melanoma tends to change over time. If you have a mole or skin growth, watch it for signs of changes.
Can skin cancer be cured?
Skin cancer is common, and when it’s caught early, most skin cancer – including melanoma – can be cured. If you see something on your skin, don’t panic. Most skin lesions and moles are not cancerous, but it’s always best to get checked out to be sure. Learn more about moles and different types of skin cancer.
What to do if you notice any of the ABCDE traits?
Make an appointment to see a Water’s Edge Dermatology provider if you notice any of the ABCDE traits. Your practitioner will examine any mole that has one or more of these traits and all new growths.
How to tell if you have a melanoma?
Make sure you are doing regular skin checks. Look for moles and other spots on your skin and apply the ABCDE rules listed below. During a skin self-exam, keep in mind that moles are typically uniform in color, round or oval and have a well-defined border. Though melanomas can vary greatly in appearance, most tend to have one or more of these ABCDE traits, and some have several.
What are the signs of melanoma?
A common warning sign of melanoma is change. Melanoma often begins in or near an existing mole. A change in the shape, color or size of a mole can be a warning sign of melanoma. Also be aware if a mole becomes painful or begins to bleed or itch.
Where does melanoma start?
Melanoma is tricky. It can start on the surface of the skin, under a nail or even in the eye. Once it gets started growing, it can grow deep into the skin and spread through the body. That’s what makes it so dangerous.
What is the ABCDE rule for skin cancer?
Updated on July 15, 2020. The ABCDE Rule of skin cancer is an easy-to-remember system for determining whether a mole or growth may be cancerous. They describe the physical condition and/or progression of any skin abnormality that would suggest the development of a malignancy. 1:50.
What does the type of cell involved in a patient's treatment plan mean?
The type of cell involved helps your healthcare provider determine both the treatment options and the likely outcome (prognosis).
What is skin cancer?
The Basics About Skin Cancer. By definition, skin cancer is the abnormal growth of skin cells. Two types of skin cancer, basal cell carcinoma and squamous cell carcinoma, develop primarily on areas of sun-exposed skin, including the scalp, face, lips, ears, neck, chest, arms, and hands. 1 It is also common on the legs of women.
Can cancer cause skin bleeds?
This is particularly true if there is any blemish or growth that changes rapidly or bleeds easily. While not all skin changes are caused by cancer, the advantages of early diagnosis greatly outweigh the inconvenience (and even cost) of a doctor’s visit. Check it out today.
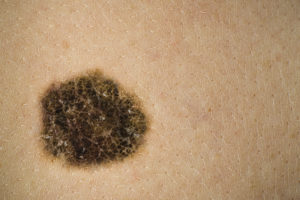
Is melanoma an ABCDE?
The following photo is an example of melanoma that meets most of the ABCDE criteria. However, every case of skin cancer is unique, and a different individual's malignancy could look quite different.
Why is ABCDE important?
That is why learning the ABCDE rule for skin cancer is so important. This system provides an easy way to recognize moles and growths that might be cancerous. Although most of your “suspicious” moles turn out to be normal noncancerous moles, it is much better to be safe than sorry. To not see, or simply ignore an early melanoma can be devastating.
When should you show your mole to your doctor?
If your mole or growth has one or more of the ABCDE’s, you should show it to your doctor as soon as possible!
Is it safe to ignore melanoma?
Although most of your “suspicious” moles turn out to be normal noncancerous moles, it is much better to be safe than sorry. To not see, or simply ignore an early melanoma can be devastating. Because melanoma can disguise itself as a strange looking mole, be sure to review the ABCDE rule for skin cancer to properly identify abnormal growths.
