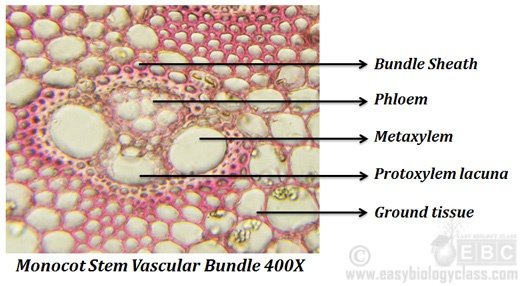
How are vascular tissues arranged in a monocot stem a dicot stem?
Monocot stems have scattered vascular bundles. Dicot stems have their vascular bundles in a ring arrangement. Monocot stems have most of their vascular bundles near the outside edge of the stem. The bundles are surrounded by large parenchyma in the cortex region.
How is vascular tissue arranged in stems?
Organization of the vascular tissue. Vascular tissue is organized into discrete strands called vascular bundles, each containing xylem and phloem. In stems, the vascular tissue is organized into many discrete vascular bundles. In the roots, the vascular tissue is organized within a single central vascular cylinder.
How is the arrangement of vascular bundles in dicot and monocot stem?
In monocots stem, the vascular bundles are scattered across the stem without any definite arrangement. On the other hand, in dicots stem, the vascular bundles are arranged in the form of one or two broken circular rings, following that they have a definite shape.
How does the vascular tissue arrangement differ in monocots and dicots?
The main difference between monocot stem and dicot stem is that monocot stem contains scattered vascular bundles across the stem whereas dicot stem contains vascular bundles arranged in the form of one or two rings.
How are vascular tissues of plants arranged?
The vascular tissue in plants is arranged in long, discrete strands called vascular bundles. These bundles include both xylem and phloem, as well as supporting and protective cells. In stems and roots, the xylem typically lies closer to the interior of the stem with phloem towards the exterior of the stem.
How are the vascular bundles arranged in the following specimens in dicot stem?
Dicot stem In dicot stems, the vascular bundles are arranged in a ring. Like dicot roots, dicot stems are protected by an outer layer of dermal tissue called the epidermis. Then, also similar to dicot roots, dicot stems have a layer of ground tissue called the cortex beneath the epidermis.
How are the vascular bundles arranged in a monocot leaf?
Monocot leaf First, they tend to be more oblong or linear in shape, and their vascular bundles are organized into veins that originate at the base of the leaf and run parallel to one another. In other words, they have a striate venation pattern.
How many vascular bundles are in a monocot stem?
Difference # Vascular Bundle of Monocot Stem: 2.
What is the vascular tissue arrangement in the dicot root?
In dicot roots, the vascular structures are located in the middle of the root. The arrangement of xylem and phloem is different in dicots than it is in monocots. The xylem is all located in the middle of the dicot root, and bundles of phloem are arranged around it, separated from it by vascular cambium.
What is the main difference between monocot stem and dicot stem?
Difference Between Monocot and Dicot StemDicotMonocotThe dicot stem is solid in most of the cases.The monocot stem is usually hollow at the centre.The hypodermis is formed of collenchyma fibres which are often green in colour.The hypodermis is made of sclerenchyma fibres and they are not green.13 more rows•Nov 19, 2020
What are the different structure of a monocot stem?
Anatomy of monocot stem The Monocot Stem has Vascular Bundles near the outside edge of Stem. Vascular Bundles are scattered in Parenchymatous ground Tissue. There is no pith region in Monocots. Dicot Stems have bundles in a ring surrounding Parenchyma cells in a pith region.
What are three differences between monocot and dicot stems?
Comparison ChartPropertiesMonocot StemDicot StemIntrastelar ground tissuePericycleAbsentPresent outer to the vascular bundlePithAbsentDicot stem contains pith made of parenchyma cellsMedullary raysAbsentPresent between the vascular bundle20 more rows
What is the structure of vascular tissue?
Vascular tissue is comprised of the xylem and the phloem, the main transport systems of plants. They typically occur together in vascular bundles in all plant organs, traversing roots, stems, and leaves. Xylem is responsible for the transport of water and dissolved ions from the roots upwards through the plant.
What are vascular bundles and where do they appear within the stem?
A vascular bundle is a part of the transport system in vascular plants. The transport itself happens in the stem, which exists in two forms: xylem and phloem. Both these tissues are present in a vascular bundle, which in addition will include supporting and protective tissues.
What is the function of stems in vascular plants?
A stem is one of two main structural axes of a vascular plant, the other being the root. It supports leaves, flowers and fruits, transports water and dissolved substances between the roots and the shoots in the xylem and phloem, stores nutrients, and produces new living tissue.
What tissues are present in the stem of the plant?
The stem has three tissue systems: dermal, vascular, and ground tissue. Dermal tissue is the outer covering of the plant. It contains epidermal cells, stomata, guard cells, and trichomes. Vascular tissue is made up of xylem and phloem tissues and conducts water, minerals, and photosynthetic products.