How do you calculate bacterial growth?
- Get a counting chamber. These tools have a chamber, slide, and microscope built in, so they are easy to set up and use. ...
- Get a pour plate or a spread plate. These are the containers you will observe the bacteria in.
- Culture is the term used to describe an organism grown artificially for an experiment.
- Broth is a liquid medium that the culture grows in.
What are the phases of the bacterial growth curve?
The bacterial growth curve represents the number of live cells in a bacterial population over a period of time. There are four distinct phases of the growth curve: lag, exponential (log), stationary, and death. The initial phase is the lag phase where bacteria are metabolically active but not dividing. The exponential or log phase is a time of ...
What are the four stages in the microbial growth curve?
Key Takeaways: Bacterial Growth Curve
- The bacterial growth curve represents the number of live cells in a bacterial population over a period of time.
- There are four distinct phases of the growth curve: lag, exponential (log), stationary, and death.
- The initial phase is the lag phase where bacteria are metabolically active but not dividing.
What factors affect bacterial growth?
pH:
- pH affects the ionic properties of bacterial cell so it affects the growth of bacteria.
- Most of the bacteria grow at neutral pH (60.5-7.5). However there are certain bacteria that grow best at acidic or basic pH.
- relationship between pH and bacterial growth is given in figure below.

What are the four stages of the bacterial growth curve?
For this reason, graphs that show the growth of bacterial cultures are plotted as the logarithm of the number of cells. Bacterial colonies progress through four phases of growth: the lag phase, the log phase, the stationary phase, and the death phase.
Why is the bacterial growth curve important?
The study of bacterial growth curves is important when aiming to utilize or inoculate known numbers of the bacterial isolate, for example to enhance plant growth, increase biodegradation of toxic organics, or produce antibiotics or other natural products at an industrial scale.
What is bacterial growth curve quizlet?
A typical bacterial growth curve shows four distinct phases: lag phase, log phase, stationary phase, and death phase. Bacterial growth cannot be sustained in this closed system because nutrients become depleted and waste products accumulate, inhibiting further growth.
How do you describe a growth curve?
A growth curve is a graphical representation that shows the course of a phenomenon over time. An example of a growth curve might be a chart showing a country's population increase over time.
How does bacterial growth happen?
Bacteria replicate by binary fission, a process by which one bacterium splits into two. Therefore, bacteria increase their numbers by geometric progression whereby their population doubles every generation time. Generation time is the time it takes for a population of bacteria to double in number.
What feature of the growth graph relates to the growth rate K?
The straight line indicates that there is a constant growth rate. This growth rate is defined as k. "The growth constant k refers to the number of generations per time period, which remain constant."
What is the log phase in bacterial growth?
Log phase, also referred to as the exponential phase or logarithmic phase, is one of the phases observed in a bacterial growth curve. The striking feature of this phase is the property of cell doubling through binary fission. The count of bacteria (new) that appear each time is proportionate to the current population.
Do bacteria grow exponentially?
Hence, bacterial growth is one of nature's most dramatic examples of exponential growth. Bacterial growth is also an extremely useful adaptation. Because its rate of division is highly sensitive to local conditions, the organism can change quickly and exploit new resources as they become available.
What are the characteristics of a growth curve?
A graph in which the number of organisms in a population is plotted against time. Such curves are amazingly similar for populations of almost all organisms from bacteria to human beings and are considered characteristic of populations. Growth curves typically have a sigmoid or S-shaped curve.
How do you measure bacterial growth?
The easiest way to measure bacterial growth is to put your sample on a clear glass plate under a microscope and count how many bacteria cells there are. Alternatively, you can measure turbidity, which is the amount of bacteria in your sample.
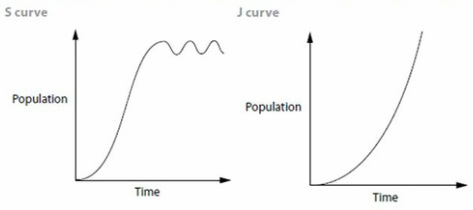
What are two types of growth curves?
There are two types of growth curves: the j shaped growth curve and the s-shaped growth curve. Both the types of growth curves fit population growth models that have different environmental pressures.
What is the growth curve of bacteria?
The bacterial growth curve represents the number of live cells in a bacterial population over a period of time. There are four distinct phases of the growth curve: lag, exponential (log), stationary, and death. The initial phase is the lag phase where bacteria are metabolically active but not dividing.
What is a growth curve?
bacterial growth curve A curve on a graph that shows the changes in size of a bacterial population over time in a culture. The bacteria are cultured in sterile nutrient medium and incubated at the optimum temperature for growth. Samples are removed at intervals and the number of viable bacteria is counted.
Why is the growth curve important?
Also, why is the bacterial growth curve important? The study of bacterial growth curves is important when aiming to utilize or inoculate known numbers of the bacterial isolate, for example to enhance plant growth, increase biodegradation of toxic organics , or produce antibiotics or other natural products at an industrial scale.
What factors influence the rate of growth of bacteria?
Environmental factors influence rate of bacterial growth such as acidity (pH), temperature, water activity, macro and micro nutrients, oxygen levels, and toxins. Conditions tend to be relatively consistent between bacteria with the exception of extremophiles.
How to study the dynamics of bacterial growth?
The dynamics of the bacterial growth can be studied by plotting the cell growth (absorbance) versus the incubation time or log of cell number versus time. The curve thus obtained is a sigmoid curve and is known as a standard growth curve. The increase in the cell mass of the organism is measured by using the Spectrophotometer.
What happens in the stationary phase of a bacterial population?
As the bacterial population continues to grow, all the nutrients in the growth medium are used up by the microorganism for their rapid multiplication. This result in the accumulation of waste materials, toxic metabolites and inhibitory compounds such as antibiotics in the medium.
How long does it take for a bacteria to double in number?
The time taken by the bacteria to double in number during a specified time period is known as the generation time. The generation time tends to vary with different organisms. E.coli divides in every 20 minutes, hence its generation time is 20 minutes, and for Staphylococcus aureus it is 30 minutes. 3.
What happens to bacteria during the death phase?
The depletion of nutrients and the subsequent accumulation of metabolic waste products and other toxic materials in the media will facilitates the bacterium to move on to the Death phase. During this, the bacterium completely loses its ability to reproduce.
Why do bacteria cells die?
The number of bacterial cells declines in death phase , as the metabolic waste products and lack of nutrients both prevents division of bacterial cells, and causes cell death... the Y axis of the graph represents number of living bacterial cells, and therefore will decline during death phase. see more.
How do bacteria divide?
Bacteria are unicellular (single cell) organisms. When the bacteria reach a certain size, they divide by binary fission, in which the one cell divides into two, two into four and continue the process in a geometric fashion. The bacterium is then known to be in an actively growing phase.
What is the principle of growth?
Principle: The increase in the cell size and cell mass during the development of an organism is termed as growth. It is the unique characteristics of all organisms. The organism must require certain basic parameters for their energy generation and cellular biosynthesis.
What is the growth curve of bacteria?
Bacterial growth curve. The term growth is more commonly used to refer to growth in the size of a population. Population growth is often studied by analyzing the growth of microbes in liquid (broth) culture. When microorganisms are cultivated in broth, they usually are grown in a batch culture; that is, they are incubated in a closed culture vessel ...
How to get a growth curve of a species of bacteria?
The bacterial growth curve of a particular species of bacteria can be obtained by the following steps; The growth curve of a population of a particular species can be obtained by growing a pure culture of the organism in a liquid medium at a constant temperature.
How many phases of growth are there in bacteria?
In the laboratory, they are grown in a closed system or batch culture system in a predictable pattern where no foods are added, and no wastes are removed, resulting in a growth curve consist of four distinct phases of growth: the lag phase, the exponential or log phase, the stationary phase, and the death or decline phase. Additionally, this growth curve can generate the generation time for a distinct organism – the number of times it takes for the population to double.
What happens to bacteria during the stationary phase?
During the stationary phase, the bacterial cells also produce secondary metabolites or metabolites produced after active growth, such as antibiotics.
What is the lag phase of a population?
From this curve, it can be seen that there is an initial period of what appears to be no growth (the lag phase), followed by rapid growth (the exponential or logarithmic phase), then a leveling off ( stationary phase), and finally a decline in the viable population (death or decline phase).
What causes bacteria to die?
The depletion of essential nutrients and the accumulation of toxic wastes; such as acids are the main reasons for the Death or Decline phase of growing bacterial cells. It is thought to be under specific conditions the dead cells might be revived, this condition is known as viable but nonculturable (VBNC).
What happens to the population of bacteria during the inoculum phase?
During this phase, the bacterial cells start to increase their size and physiologically they are becoming very active and are synthesizing new protoplasm.
How long does it take for bacteria to grow?
All bacterial growth will produce a graph like this, but the actual times can vary a lot. We already know E. coli has a generation time of 20 minutes, while Staph. aureus needs 30. The spirochete that causes the STD syphilis has a generation time of 33 hours. And these are at optimal conditions. In reality, environmental limitations and competition for resources is going to make the doubling time even longer.
What is the first phase of bacteria?
The first phase is called the lag phase. This phase is characterized by very little to no bacterial growth. During this time, the bacteria are adjusting to the environment, growing in size, synthesizing biochemicals, and storing up nutrients. The length of the lag phase depends on the environmental conditions the bacteria are in and the overall health of the cells.
What is the second phase of Staph. aureus?
The second phase should look familiar. This is the log phase, characterized by the bacterial cells doubling at a constant, exponential rate. During this time, our Staph. aureus is hitting its stride, doubling in number every 30 minutes. You can see how the population can increase very rapidly.
How long does it take for E. coli to split?
In reality, it takes about 20 minutes for one E. coli cell to split into two. To put it another way, every 20 minutes, the population of E. coli can double. If you started with a single E. coli cell and let it grow unchecked for 36 hours, you would end up with enough cells to fully cover the surface of the Earth.
What is the term for the reproduction of bacteria?
Bacterial growth refers to the reproduction of bacteria, and generation time is the period of this process. Learn more about these topics through an example of E. coli. Discover also the curves, stages, and phases of bacterial growth. Updated: 10/08/2021
How to calculate population growth during exponential phase?
In order to calculate population growth during the exponential phase, simply multiply the original starting population number by 2 raised to the power representing the number of generation times that have elapsed.
How do bacteria reproduce?
Bacteria reproduce by splitting themselves in half, making one cell into two. Every species of bacteria has its own generation time, the time it takes for one cell to become two. Generation times can vary depending on the species of bacteria and the environmental conditions.
What is the significance of a bacterial growth curve?
When a broth culture is inoculated with a small bacterial inoculum, the population size of the bacteria increases showing a classical pattern. When plotted on a graph , a distinct curve is obtained referred to as the bacterial growth curve.
What can scientists learn from the slope and shape of growth curves produced from bacteria grown with industrial waste products?
Similarly, the slope and shape of growth curves produced from bacteria grown with mixtures of industrial waste products can inform scientists whether the bacteria can metabolize the particular substance, and how many potential energy sources for the bacteria can be found in the waste mixture.
What is the curve of a broth culture?
When plotted on a graph, a distinct curve is obtained referred to as the bacterial growth curve.
Why is bacterial growth kinetics important?
Growth kinetics is also useful for assessing whether particular strains of bacteria are adapted to metabolize certain substrates, such as industrial waste or oil pollution.
What is the lag phase of bacterial growth?
It takes some time to multiply. The time between inoculation and beginning of multiplication is known as lag phase.
Why does bacterial growth stop after log phase?
After log phase, the bacterial growth almost stops completely due to lack of essential nutrients, lack of water oxygen, change in pH of the medium, etc. and accumulation of their own toxic metabolic wastes. It is during this phase that the culture is at its greatest population density. However, Death rate of bacteria exceeds the rate ...
What happens to the bacterial population during every generation?
The bacterial population doubles during every generation. They multiply at their maximum rate. The bacterial cells are small and uniformly stained. The microbes are sensitive to adverse conditions, such as antibiotics and other antimicrobial agents. Growth rate is the greatest during the log phase.
What are the phases of bacteria growth?
Bacterial growth in batch culture can be modeled with four different phases: lag phase, exponential or log phase, stationary phase, and death phase.
What happens during the lag phase of the bacterial growth cycle?
o During the lag phase of the bacterial growth cycle, synthesis of RNA, enzymes and other molecules occurs.
What happens to bacteria during the death phase?
At death phase, bacteria run out of nutrients and die.
What happens to the population doubling rate if growth is not limited?
o If growth is not limited, doubling will continue at a constant rate so both the number of cells and the rate of population increase doubles with each consecutive time period.
Why can't exponential growth continue?
o Exponential growth cannot continue indefinitely, however, because the medium is soon depleted of nutrients and enriched with wastes.
What happens when cells enter exponential growth?
This is when cells divide by binary fission and the doubling of each generation creates the exponential growth for which the phase is named.
What is the stationary phase of cell culture?
During the stationary phase of cell culture, it is generally considered to be the products of the cells that are of interest and that makes this an important part of bioprocessing. Additional supplements may be added to keep the cells alive but stressed enough to continue producing rather than reproducing. In cases where cell culture may last days, weeks, or months, like the production of monoclonal antibodies via hybridoma cells, or the production of ethanol and CO 2 via yeast fermentation, the stationary phase is where the magic happens.
What is the lag phase of a cell?
Lag Phase. This initial cell growth phase is generally characterized by metabolic activity but not growth. The cells utilize media to synthesize the small molecules necessary for replication. This stage is where the cells start to increase in size but not necessarily in number.
How long does a cell culture last?
In cases where cell culture may last days, weeks, or months, like the production of monoclonal antibodies via hybridoma cells, or the production of ethanol and CO 2 via yeast fermentation, the stationary phase is where the magic happens.
Why is stopping cell culture important?
If the number of cells produced is the final product then stopping cell culture at the end of the log phase is important. This is especially true in industrial microbiology where cost and time affect the bottom line and may mean the difference between profits or losses.
Is it counterintuitive to stop a culture during the lag phase?
Stopping a culture during the lag phase may seem counterintuitive but if the primary interest is learning about the first metabolic activity cells experience, this may in fact be the prime time to finish.

Lag Phase
Exponential Or Logarithmic (log) Phase
- During this phase, the microorganisms are in a rapidly growing and dividing state. Their metabolic activity increases and the organism begin the DNA replication by binary fission at a constant rate. The growth medium is exploited at the maximal rate, the culture reaches the maximum growth rate and the number of bacteria increases logarithmically (e...
Stationary Phase
- As the bacterial population continues to grow, all the nutrients in the growth medium are used up by the microorganism for their rapid multiplication. This result in the accumulation of waste materials, toxic metabolites and inhibitory compounds such as antibiotics in the medium. This shifts the conditions of the medium such as pH and temperature, thereby creating an unfavoura…
Decline Or Death Phase
- The depletion of nutrients and the subsequent accumulation of metabolic waste products and other toxic materials in the media will facilitates the bacterium to move on to the Death phase. During this, the bacterium completely loses its ability to reproduce. Individual bacteria begin to die due to the unfavourable conditions and the death is rapid and at uniform rate. The number of de…
Calculation
- The generation time can be calculated from the growth curve(Fig 3). Fig 3: Calculation of generation time The exactly doubled points from the absorbance readings were taken and, the points were extrapolated to meet the respective time axis. Generation Time = (Time in minutes to obtain the absorbance 0.4) – (Time in minutes to obtain the absorbance 0.2) = 90-60 = 30 minut…