See more

What is the function of the medulla in the brain?
Your medulla oblongata is the bottom-most part of your brain. Its location means it's where your brain and spinal cord connect, making it a key conduit for nerve signals to and from your body. It also helps control vital processes like your heartbeat, breathing and blood pressure.
What are the 3 main centers in the medulla?
The medulla contains the cardiac, respiratory, vomiting and vasomotor centers, and therefore deals with the autonomic functions of breathing, heart rate and blood pressure as well as the sleep–wake cycle.
What is the ventral medulla?
left cerebral hemisphere of the human brain. The medulla is divided into two main parts: the ventral medulla (the frontal portion) and the dorsal medulla (the rear portion; also known as the tegmentum). The ventral medulla contains a pair of triangular structures called pyramids, within which lie the pyramidal tracts.
What is the most caudal part of the brainstem?
The medulla oblongata (or simply the medulla) is the most caudal part of the brainstem between the pons superiorly and spinal cord inferiorly. It is the transition from the spinal cord to the brain.
What happens if there is damage to the medulla?
It plays an essential role in passing messages between your spinal cord and brain. It's also essential for regulating your cardiovascular and respiratory systems. If your medulla oblongata becomes damaged, it can lead to respiratory failure, paralysis, or loss of sensation.
What actions are controlled by the medulla?
The medulla oblongata is the rod-shaped part of the brain which is seen below the cerebrum, located near the cerebellum of the brain. It controls involuntary actions like heartbeat and breathing.
Is medulla rostral or caudal?
The rostral medulla is continuous with the pons superiorly, with which it forms the pontomedullary junction. The caudal medulla continues onto the spinal cord inferiorly, just above the origin of the first pair of the cervical spinal nerves. The medulla oblongata has many important features and functions.
What does medulla mean in medical terms?
1 plural medullae. a : bone marrow. b : medulla oblongata. 2a : the inner or deep part of an organ or structure the adrenal medulla. b : myelin sheath.
What is the caudal pons?
The caudal pontine tegmentum contains the rostral tip of the solitary nucleus (nucleus solitarius). This is a sensory nucleus that extends into the dorsolateral aspect of the medulla oblongata, where it lies ventral and lateral to the dorsal nucleus of the vagus nerve.
What does caudal mean in the brain?
Toward the back of the brainCaudal: Toward the back of the brain or the bottom of the spinal cord.
What is the caudal part of the brain?
The hindbrain is the most caudal part of the brain and it includes the cerebellum, pons, and medulla oblongata.
Is the medulla the most caudal part of the brain?
The Medulla Oblongata (Myelencephalon) In essence, the brain stem connects the cerebrum to the rest of the body; it does this through joining the brain to the cerebellum and spinal cord. The most caudal structure, communicating directly with the spinal cord, is the medulla oblongata.
What centers does the medulla oblongata contain?
The medulla oblongata contains the cardiac, respiratory, vomiting, and vasomotor centers and deals with breathing, heart rate and blood pressure.
How many centers are in the medulla oblongata?
There are three groups of nuclei in the medulla. The first includes nuclei and processing centers controlling visceral functions. The coordination of complex autonomic reflexes is within the medulla.
Where are the 3 main parts of the brain located?
The brain has three main parts:The cerebrum fills up most of your skull. It is involved in remembering, problem solving, thinking, and feeling. ... The cerebellum sits at the back of your head, under the cerebrum. It controls coordination and balance.The brain stem sits beneath your cerebrum in front of your cerebellum.
What are the 3 components of the brainstem?
AnatomyMidbrain: The top part of the brainstem is crucial for regulating eye movements.Pons: The middle portion of the brainstem coordinates facial movements, hearing and balance.Medulla oblongata: The bottom part of the brainstem helps regulate your breathing, heart rhythms, blood pressure and swallowing.
What is the caudal medulla?
The caudal medulla continues onto the spinal cord inferiorly, just above the origin of the first pair of the cervical spinal nerves . The medulla oblongata has many important features and functions. It is a conduit for many ascending and descending nerve tracts that carry the information between the brain and spinal cord.
Where is the medulla located?
Medulla oblongata. Medulla oblongata is the terminal part of the brainstem . It sits in the posterior cranial fossa, below the tentorium cerebelli. The rostral medulla is continuous with the pons superiorly, with which it forms the pontomedullary junction.
What are the dorsal and ventral surfaces of the Medulla oblongata?
The ventral and dorsal surfaces of the medulla oblongata are marked by unique protuberances and fissures that are formed by the presence of different nuclei and their associated tracts. Let’s learn about the distinctive features of each surface in a structured and easy-to-understand manner.
What is the cranial enlargement of the cuneate nucleus?
It also features a large cranial enlargement, the cuneate tuber cle, which is formed by the cuneate nucleus, a relay nucleus for the cuneate fasciculus. Lateral to each cuneate nucleus is another prominence called the trigeminal tubercle, which is formed by the spinal nucleus of trigeminal nerve (CN V) .
Where is the respiratory center located?
The respiratory center is a complex group of nuclei located within the pons and medulla oblongata. It consists of three parts: the dorsal respiratory group, ventral respiratory group and pneumotaxic center. The former two are found within the dorsal and ventral medulla, respectively, while the latter lies within the rostral pons.
Which part of the cranial nerve is located directly lateral to the sulcus?
The one that is located immediately lateral to the sulcus is formed by the gracile fasciculus that ascends from the spinal cord. The cranial part of the gracile fasciculus contains the gracile nucleus, a relay nucleus that synapses with the fibers of the gracile fasciculus.
What is the ventral surface of the medulla?
Ventral surface. Along the midline of the ventral surface of the medulla is the anterior median fissure. This is a continuation of the anterior median fissure of the spinal cord. On either side of the fissure is a vertical protuberance known as the medullary pyramid, formed by the fibers of the corticospinal tract .
Where is the medulla located?
Your medulla oblongata is located at about the same level or slightly above this hole. The top of your medulla creates the floor of the fourth ventricle of your brain. Ventricles are cavities filled with cerebral spinal fluid that help provide your brain with nutrients.
Where is the Medulla Oblongata located?
Your medulla oblongata is located at the base of your brain, where the brain stem connects the brain to your spinal cord. It plays an essential role in passing messages between your spinal cord and brain. It’s also essential for regulating your cardiovascular and respiratory systems.
What happens if your medulla is damaged?
If your medulla is damaged, your brain and spinal cord won’t be able to effectively transmit information to one another.
What is the medulla oblongata?
Your medulla oblongata looks like a rounded bulge at the end of your brain stem, or the part of your brain that connects with your spinal cord. It also lies in front of the part of your brain called the cerebellum.
What is the condition that affects the back portion of the brain?
Dejerine Syndrome. Dejerine syndrome or medial medullary syndrome is a rare condition that affects less than 1% of people who have strokes that affect the back portion of their brain. Symptoms include: weakness of the arm and leg on the opposite side of the brain damage.
What is the brain responsible for?
Along with being the site of conscious thought, your brain also controls most of your body’s involuntary actions. It tells your glands when to release hormones, regulates your breathing, and tells your heart how fast to beat.
What is the cerebellum?
Your cerebellum looks like a tiny brain joined onto the back of your brain. In fact, its name literally translates to “little brain” from Latin.
What is the most caudal part of the brainstem?
The medulla oblongata (or simply the medulla) is the most caudal part of the brainstem between the pons superiorly and spinal cord inferiorly. It is the transition from the spinal cord to the brain. The medulla contains the vital autonomic cardiovascular and respiratory centers controlling heart rate, blood pressure, and breathing.
Which part of the brain is the medulla?
The myelencephalon portion of the rhombencephalon (or hindbrain) becomes the medulla.
What is the dorsal surface of the medulla?
Superiorly the dorsal surface of the medulla is slightly depressed, forming the diamond-shaped rhomboid fossa which is the floor of the fourth ventricle. The superior dorsal aspect of the medulla is occupied by the inferior cerebellar peduncle situated between the lower part of the fourth ventricle. The inferior dorsal and lateral aspect of the medulla is surrounded by the cisterna magna (posterior cerebellomedullary cistern), and lateral cerebellomedullary cistern 2,3.
Which part of the medulla contains the posterior median sulcus?
The dorsal aspect of the medulla contains the posterior median sulcus (most dorsal medial sulcus) and the more lateral posterolateral sulcus. Between these sulci are the fasciculus gracilis and nuclei forming the gracilis tubercle medially and the fasciculus cuneatus and nuclei forming the cuneate tubercle laterally 2,3.
How big is the medulla?
The medulla is approximately 3 cm in length and 2 cm in greatest diameter 2. The caudal border of the medulla is the 1 st cervical spinal nerves. The superior broad part of the medulla joins the pons 2,3.
Which cistern is surrounded by the inferior dorsal and lateral aspect of the medul?
The inferior dorsal and lateral aspect of the medulla is surrounded by the cisterna magna (posterior cerebellomedullary cistern), and lateral cerebellomedullary cistern 2,3. The median aperture ( foramen of Magendie) and the more superior lateral apertures ( foramina of Luschka) open at the level of the pons, with the canals projecting to ...
Which artery supplies the lateral aspect of the medulla?
posterior inferior cerebellar artery (PICA) supplies the lateral aspect of the medulla 2,3. anterior spinal artery supplies the entire medial aspect 2,3. direct branches of the distal vertebral artery supplies an area between the other two main arteries 2,3.
Which part of the medulla is the most ventral and most caudal?
Pyramidal decussation of the motor pathway: This is the most ventral and most caudal part of the medulla, which is where the majority of the motor fibers from the motor cortex in the cerebrum decussate in the medulla and form the lateral corticospinal tract in the spinal cord. Some of the fibers that don’t cross the midline become the anterior corticospinal tract.
What is the function of the medulla?
The cardiovascular-respiratory function of the medulla: Multiple studies show that the cardiovascular system and the respiratory system unite as one regulating system within a specific part of the medulla. The rostral ventral lateral medulla (RVLM) has been found to have the excitatory neurons that carry information to the pre-sympathetic neurons in the spinal cord, which maintain baseline arterial pressure. Within the RVLM, there is also the ventral respiratory column, which is known to be the center of control of respiratory rhythm and pattern. The ventral respiratory column divides into multiple sub-nuclei that establish connections with the presynaptic fibers in the RVLM and regulate the oscillating respiratory pattern that allows us to perfuse our tissues with oxygen. The caudal ventrolateral medulla contains synaptic input from tonic inhibitory baroreflex control. Together both the caudal and the rostral part of the ventral medulla have been known to be an essential location for input and convergence for controlling respiration with cardiovascular regulation. [2]
What is the medulla oblongata?
The medulla oblongata is the connection between the brainstem and the spinal cord, carrying multiple important functional centers. It is comprised of the cardiovascular-respiratory regulation system, descending motor tracts, ascending sensory tracts, and origin of cranial nerves IX, X, XI, and XII. Motor neurons cross from the left motor cortex to the right side of the spinal cord in the medulla. The medulla is the most caudal aspect of the brainstem, approximately at the level of the foramen magnum. Anterior to the medulla oblongata is the median fissure, which connects with the median fissure of the spinal cord. The posterior surface of the medulla can divide into two parts, the inferior part, which has median sulcus continuous with the spinal cord, and the superior part, which forms the lower floor of the fourth ventricle. The medulla, including the pons and the midbrain, is divided into three laminae, from dorsal to ventral, called the tectum, tegmentum, and basis, respectively. The tectum of the medulla involves the inferior medullary velum, which is the most inferior posterior part of the fourth ventricle. The tegmentum consists of the inferior olivary nucleus and the cranial nerve nuclei of IX, X, XI, XII. The basis, most ventral layer, has the pyramid decussation at the medulla.[1]
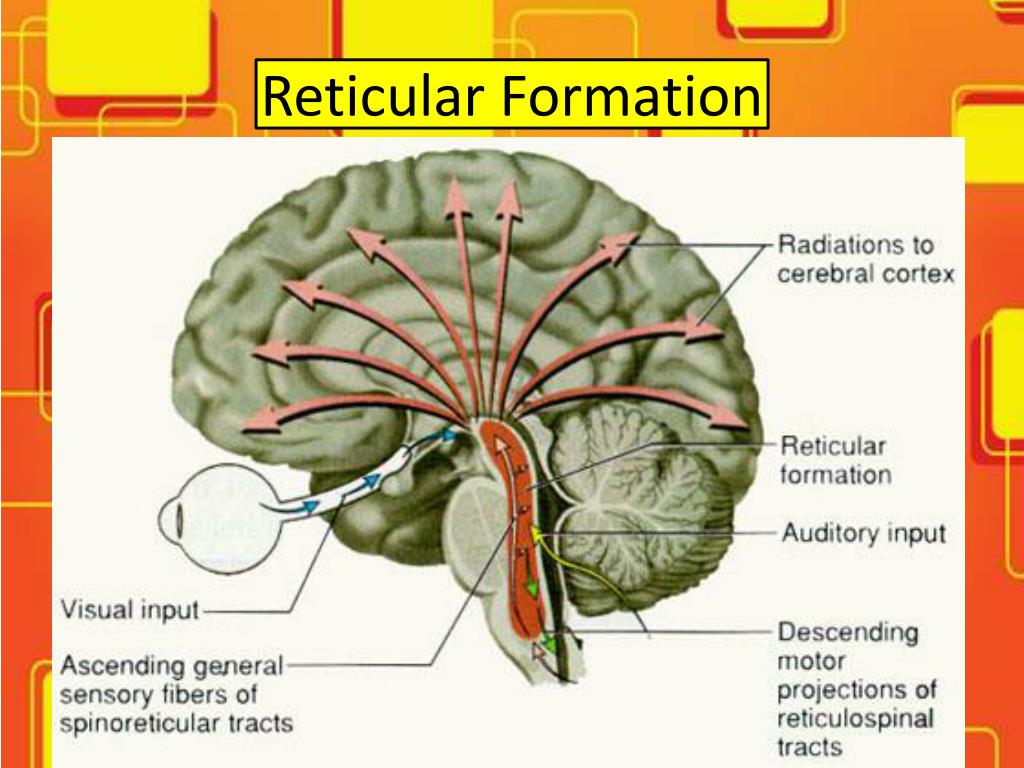
What is the reticular system?
Reticular formation: This is a net-like system found in the tegmentum of the midbrain, pons, and medulla, as well as the subthalamus and thalamus. This system is a complex organization divided into four regions. The 4th zone is the only one in the medulla between the medial and lateral columns. This zone plays a role in autonomic regulation of respiration, heart rate, and blood pressure. [9]
Where is the medial lemniscus located?
The medial lemniscus pathway is located in between the two inferior olivary nuclei and is dorsal to the pyramidal motor pathway. It travels through the rest of the medulla up to the level of the pons and midbrain. [10]
Which organ contains multiple nuclei and tracts that have information from the spinal cord as well as the higher cortex?
The medulla includes multiple nuclei and tracts that have information from the spinal cord as well as the higher cortex. Each nucleus in the medulla or tract passing through will have a separate explanation below.
What is the trigeminal nucleus?
Spinal trigeminal Nucleus: This brainstem nucleus is in the lateral medulla. It further subdivides into the trigeminal nucleus pars oralis, pars interpolaris, and pars caudalis, named rostral to caudal, respectively. The caudal portion predominantly receives nociceptive afferents from the face. The other nuclei incorporate sensory information from the sensory branches of the trigeminal cranial nerve (V) of the ipsilateral side of the face. The sensation of temperature, pain, and a deep or crude touch of the ipsilateral face are sent to this nucleus as well. It is the first central synapse and relay in the orofacial pain nerve fibers, which later reach the ventral posteromedial nucleus of the thalamus. [6][7]
What is the function of the medulla?
The medulla contains the cardiac, respiratory, vomiting and vasomotor centers, and therefore deals with the autonomic functions of breathing, heart rate and blood pressure as well as the sleep wake cycle. During embryonic development, the medulla oblongata develops from the myelencephalon.
What is the posterior part of the medulla?
The posterior part of the medulla between the posterior median sulcus and the posterolateral sulcus contains tracts that enter it from the posterior funiculus of the spinal cord. These are the gracile fasciculus, lying medially next to the midline, and the cuneate fasciculus, lying laterally. These fasciculi end in rounded elevations known as the gracile and the cuneate tubercles. They are caused by masses of gray matter known as the gracile nucleus and the cuneate nucleus. The soma (cell bodies) in these nuclei are the second-order neurons of the posterior column-medial lemniscus pathway, and their axons, called the internal arcuate fibers or fasciculi, decussate from one side of the medulla to the other to form the medial lemniscus .
What is the region between the anterolateral and posterolateral sulcus in the upper part of?
The region between the anterolateral and posterolateral sulcus in the upper part of the medulla is marked by a pair of swellings known as olivary bodies (also called olives ). They are caused by the largest nuclei of the olivary bodies, the inferior olivary nuclei .
What is the medulla oblongata?
FMA. 62004. Anatomical terms of neuroanatomy. The medulla oblongata or simply medulla is a long stem-like structure which makes up the lower part of the brainstem. It is anterior and partially inferior to the cerebellum.
What is the bulb in the medulla?
The bulb is an archaic term for the medulla oblongata. In modern clinical usage, the word bulbar (as in bulbar palsy) is retained for terms that relate to the medulla oblongata, particularly in reference to medical conditions. The word bulbar can refer to the nerves and tracts connected to the medulla, and also by association to those muscles innervated, such as those of the tongue, pharynx and larynx .
How many parts does the Medulla have?
The medulla can be thought of as being in two parts:
Which view of the Medulla oblongata and Pons?
Anteroinferior view of the medulla oblongata and pons.
