What is the cerebellar peduncle made of?
The middle cerebellar peduncle (brachium pontis) consists almost entirely of crossed afferent fibers from the pontine nuclei that transmit impulses from the cerebral cortex to the intermediate and lateral zones of the cerebellum (corticopontocerebellar tract).
What are the three cerebellar peduncles?
There are three on each side: the inferior cerebellar peduncle (#4025, #6172), the middle cerebellar peduncle (brachium pontis) (#8361, #6553), and the superior cerebellar peduncle (brachium conjunctivum) (#6554). The middle and inferior cerebellar peduncles contain most of the cerebellar afferents.
What is cerebral peduncle?
The cerebral peduncles ('crus cerebri') are a large collection of fiber bundles in the ventral midbrain, which originate in the cerebral cortex. Many of these fibers connect either with nuclei in the pons and ultimately the cerebellum or the spinal cord.
What is the importance of the cerebral peduncles?
These cerebral peduncles are the main highway for signals that need to be transported from the cortex to other parts of the central nervous system (CNS), and are especially important for body coordination.
What does a peduncle mean?
a stalkpe·dun·cle ˈpē-ˌdəŋ-kəl pi-ˈdəŋ- : a stalk bearing a flower or flower cluster or a fructification. : a narrow part by which some larger part or the whole body of an organism is attached : stalk, pedicel. 3. : a narrow stalk by which a tumor or polyp is attached.
What is the function of the middle cerebellar peduncles?
Function. The middle cerebellar peduncle conveys information from the cerebrum and the pons to the cerebellum.
How many peduncles are in the cerebellum?
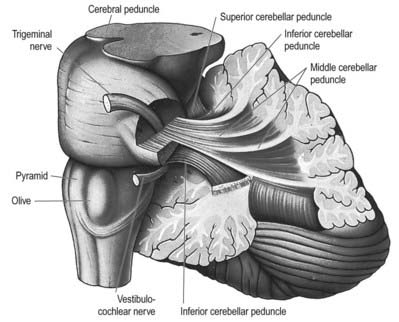
Bilaterally, three cerebellar peduncles connect the cerebellum to the brainstem. The peduncles are named for the directions they take in connecting to the brainstem (synonyms are shown below parenthetically). Caudal cerebellar peduncle (restiform body) connects the cerebellum to the medulla oblongata.
How many peduncles are in the brain?
There are six cerebellar peduncles in total, three on each side: Superior cerebellar peduncle is a paired structure of white matter that connects the cerebellum to the mid-brain.
What are the 3 cerebellar peduncles and state their functions?
These peduncles are superior, middle and inferior. Superior cerebellum connects cerebellum to the midbrain, middle to the pons and inferior to the medulla oblongata. Superior cerebellar peduncle (brachium conjunctivum) ascends upward from the anterior cerebellar notch to the tectum of the midbrain.
How many peduncles are in the cerebellum?
three cerebellar pedunclesCerebellar peduncles are the structure connecting the cerebellum to the brain stem and the cerebrum. There exist three cerebellar peduncles.
What is the role of the three peduncles near the anterior aspect of the cerebellum?
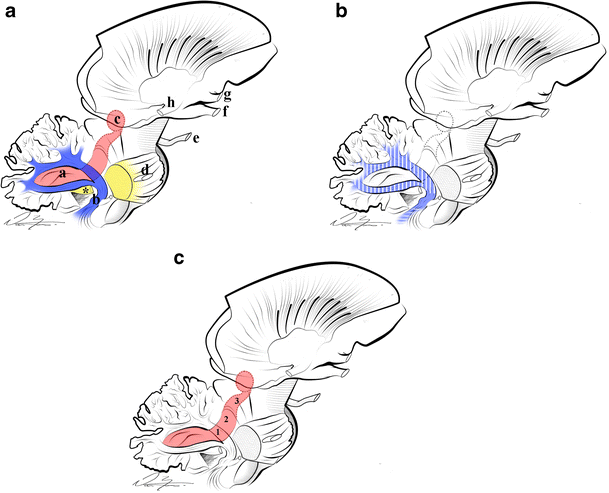
Cerebellar peduncles. Three fiber bundles carry the input and output of the cerebellum. The inferior cerebellar peduncle (also called the restiform body) primarily contains afferent fibers from the medulla, as well as efferents to the vestibular nuclei.
How many cerebral peduncles are there?
There are six cerebellar peduncles in total, three on each side: Superior cerebellar peduncle is a paired structure of white matter that connects the cerebellum to the mid-brain.
What is the middle peduncle?
Middle cerebellar peduncles connect the cerebellum to the pons and are composed entirely of centripetal fibers. Inferior cerebellar peduncle is a thick rope-like strand that occupies the upper part of the posterior district of the medulla oblongata.
Where do the superior peduncles enter the brain?
The superior cerebellar peduncles (brachia conjunctiva) emerge from the cerebellum and ascend to form the lateral portion of the roof of the fourth ventricle, where they enter the brainstem below the inferior colliculi. They are bridged by the superior medullary velum. The superior cerebellar peduncles represent the main output route from the cerebellum, and as such, most of their fibers are efferent. A relatively small afferent contribution is present. The efferent pathways include the cerebellorubral, dentatothalamic, and fastigioreticular tracts. All of them emerge from cerebellar nuclei; the cerebellorubral fibers from the globose and emboliform nuclei, the dentatothalamic fibers from the dentate nucleus, and the fastigioreticular fibers from the fastigial nucleus. They emerge together from the various nuclei to ascend in the roof of the fourth ventricle and proceed anteriorly to the midbrain tegmental area medial to the lateral lemniscus. The cerebellorubral fibers cross over at this point to enter the contralateral red nucleus. The dentatothalamic fibers also cross over and ascend to synapse in the ventral intermediate (VI) and ventral anterior (VA) nuclei of the thalamus. The fastigioreticular fibers enter the reticular formation of the midbrain, pons, and medulla oblongata. Afferent pathways include the anterior spinocerebellar and tectocerebellar tracts. The fibers of the anterior spinocerebellar tract originate in Clarke's column of the spinal cord and cross in the anterior white commissure to the lateral funiculus, where they ascend to upper pontine levels before crossing back to enter the cerebellum through the superior peduncle. They terminate in the hind limb region of the cerebellar cortex. The tectocerebellar tracts emerge from the superior and inferior colliculi on both sides, terminating in the intermediate vermis (culmen, declive, folium, tuber, pyramid) and the lobulus simplex. The function of the tectocerebellar tract is not known, but it is widely believed to mediate visual and auditory reflexes.
Where do tectocerebellar tracts end?
They terminate in the hind limb region of the cerebellar cortex. The tectocerebellar tracts emerge from the superior and inferior colliculi on both sides, terminating in the intermediate vermis (culmen, declive, folium, tuber, pyramid) and the lobulus simplex.
Where do the fibers of the anterior spinocerebellar tract originate?
The fibers of the anterior spinocerebellar tract originate in Clarke's column of the spinal cord and cross in the anterior white commissure to the lateral funiculus, where they ascend to upper pontine levels before crossing back to enter the cerebellum through the superior peduncle.
Which ventricle has a diamond?
The peduncles form the lateral border of the fourth ventricle, and form a distinctive diamond – the middle peduncle forming the central corners of the diamond, while the superior and inferior peduncles form the superior and inferior edges, respectively.
Which part of the thalamus is the dentatothalamic fiber?
The dentatothalamic fibers also cross over and ascend to synapse in the ventral intermediate (VI) and ventral anterior (VA) nuclei of the thalamus. The fastigioreticular fibers enter the reticular formation of the midbrain, pons, and medulla oblongata.
What is the name of the nerve that allows communication between the cerebellum and the other parts of the nervous system?
Cerebellar Peduncle. A cerebellar peduncle is a nerve tract that permits communication between the cerebellum and the other parts of the central nervous system. Three pairs of cerebellar peduncles conduct this communication.
Which part of the brain sends impulses to the midbrain?
Continued From Above... After integrating and analyzing the information from these two sources, the cerebellum sends impulses through the superior peduncles to the midbrain. In response, motor impulses are transmitted down through the pons, medulla oblongata, and spinal cord to stimulate or inhibit skeletal muscles at appropriate times and cause movements of body parts into the desired positions. This activity makes rapid and complex muscular movements possible.
What are the functions of the cerebral peduncle?
The cerebral peduncles help refine our movements.
How do cerebral peduncles help us?
The cerebral peduncles help refine our movements. If body movement impulses came straight from the cortex, the movements would seem erratic and clumsy. The peduncles adjust the commands by taking into account where the body parts currently are located before directing the movement, and they sometimes slow down the movement. When there is an injury to cerebral peduncles, the symptoms of the injury show up in the part of the body related to the injured peduncle.
What is the meaning of the term "peduncle"?
The term ‘cerebral’ means it is related to the brain. A ‘peduncle’ is a stem-like connector. The cerebral peduncles are connected to the pons, which is a part of the frontal brain stem that looks like a swelling.
What is the connection between the cerebral peduncle and the frontal brain?
The term ‘cerebral’ means it is related to the brain. A ‘peduncle’ is a stem-like connector. The cerebral peduncles are connected to the pons , which is a part of the frontal brain stem that looks like a swelling. Many other nerve bundles also connect to the pons. Cerebral peduncles help transport nerve impulses from the higher part of the brain ...
Where are the cerebral peduncles located?
The cerebral peduncles are located on either side of the midbrain and are the frontmost part of the midbrain, and act as the connectors between the rest ...
What fibers run through the cerebral peduncles?
Important fiber tracts that run through the cerebral peduncles are the corticospinal, corticopontine, and corticobulbar tracts . Damage to the cerebral peduncles results in unrefined motor skills, imbalance, and lack of proprioception.
What are the three areas of the brain that give rise to the cerebral peduncle?
Mainly, the three common areas that give rise to the cerebral peduncles are the cerebral cortex, the spinal cord and the cerebellum. The cerebral peduncle, by most classifications, is everything in the midbrain except the tectum. The region includes the tegmentum, crus cerebri and pretectum.
Which nerve wraps around the lowest part of the cerebral peduncle?
Cranial nerve 3 ( oculomotor nerve) appears ventrally between the two cerebral peduncles in the interpeduncular fossa. Cranial nerve 4 ( trochlear nerve) wraps around the lowest part of the cerebral peduncle.
What is the obtuse section of the brain?
Obtuse section (perpendicular to the brainstem) through superior colliculus showing path of oculomotor nerve (Crus cerebri labeled at lower left.) The cerebral peduncles are the two stalks that attach the cerebrum to the brainstem. They are structures at the front of the midbrain which arise from the ventral pons and contain the large ascending ...
What is Cerebral Peduncle?
The Cerebral Peduncle is also known as Cerebral Crus. The term cerebral stands for brain and Peduncle is a stem-like a connector. It is that part of the midbrain, which arises from the front part of the pon. It is a mass of neuron fibers positioned at the base of the brain. The large ascending and descending nerve tracts stretch from the cerebrum to the pons. They are the chief connectors between the spinal cord and midbrain.
Why is the cerebral peduncle important?
It helps to refine your body movements and transmit the information updates to the brain . In case of any medical damage in the cerebral peduncle, there is a loss in proprioception and acceptance of commands by the body.
What are the three types of nerves that run along the cerebral peduncle?
The fiber bands that run along the cerebral peduncle are divided into three; corticospinal, corticobulbar and corticopontine. The descending motor fibers arise from the internal capsule (cerebral hemisphere) and end in the midbrain. The outer and inner third of cerebral peduncle is made of corticopontine fibers traits. They act as cortical input for the pontine nuclei. The middle of the cerebral peduncle is formed of corticobulbar. The internal capsule consists of corticospinal in the cerebral peduncle.
What happens when a peduncle is damaged?
In case of damaged cerebral peduncles, the sense of proprioception fails and leads to clumsiness and graceless feelings. Each human brain is united by the interpeduncular fossa that comprises of cranial nerves. There is two pair of cranial nerves (3 and 4) that originates from the cerebral.
What is the role of the cerebral peduncle in the brain?
Cerebral Peduncle controls the motor skills of the body and transmits the data to the brain. The brain then gets information on how to control the body movements accordingly.
What is the midbrain?
The midbrain is subsequently the highway between the two parts of the brain. Midbrain divides the brain into three main structures; Corpora quadrigemina, Cerebral Peduncle and the cerebral aqueduct. In this article, we will discuss the structure and functions of Cerebral Peduncle.
What is the red nucleus?
Additionally, there is something called the red nucleus that communicates cerebellum with the cerebral peduncle. It fine-tunes the communication and the motor movements commonly known as proprioception. Proprioception is the sense of self-environment which allows you to feel your own body parts with blindfolds.
What is inferior cerebellar peduncle?
Inferior cerebellar peduncle. Scheme showing the connections of the several parts of the brain. (Inferior peduncle labeled at bottom right.) Section of the medulla oblongata at about the middle of the olive. (Inferior peduncle labeled at upper right. The upper part of the posterior district of the medulla oblongata is occupied by ...
Which peduncle carries sensory input?
The inferior cerebellar pe duncle carries many types of input and output fibers that are mainly concerned with integrating proprioceptive sensory input with motor vestibular functions such as balance and posture maintenance.
What connects the spinal cord and medulla oblongata with the cerebellum?
Each cerebellar inferior peduncle connects the spinal cord and medulla oblongata with the cerebellum, and comprises the juxtarestiform body and restiform body. Important fibers running through the inferior cerebellar peduncle include the dorsal spinocerebellar tract and axons from the inferior olivary nucleus, among others.
Where does the posterior spinocerebellar tract originate?
This tract originates at the ipsilateral Clarke's nucleus (T1-L1) and travels upward to reach the inferior cerebellar peduncle and synapses within the spinocerebellum (also known as the paleocerebellum).
Which peduncle connects the spinal cord and medulla?
Each cerebellar inferior peduncle connect s the spinal cord and medulla oblongata with ...
Where is the vestibular nucleus located?
This peduncle also carries information leaving cerebellum: from the Purkinje cells to the vestibular nuclei in the dorsal brainstem located at the junction between the pons and medulla oblongata .