
How to increase joint fluid?
How to Lubricate Your Joints
- Move Your Joints. Movement pumps more lubrication into your joints and releases more water into your lubricating synovial fluid.
- Feed Your Joints. According to the Academy of Nutrition & Dietetics, one of the most effective natural anti-inflammatories is omega-3 fatty acids.
- Supplement Your Joints. ...
What is normal synovial fluid?
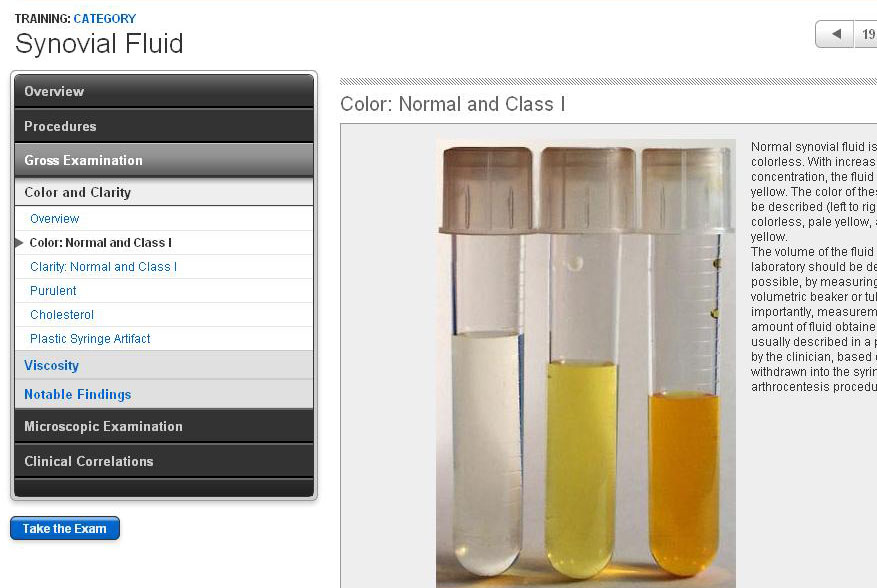
Normal synovial fluid is straw-colored, clear, and slightly sticky or stringy. Abnormal synovial fluid may be cloudy and thicker or thinner than normal fluid. Cloudiness could mean there are crystals, excess white blood cells, or microorganisms in the fluid. If you have gout, the fluid will contain crystals.
What are the functions of synovial fluid?
Synovial fluid has three functions inside the joint:
- It allows the ends of the bones to move without friction and lubricates the joint.
- It contains nutrients needed for the cartilage at the ends of the bones and carries away waste.
- It acts as a shock absorber.
How do you interpret synovial fluid results?
Synovial fluid should be viscous, meaning that it is thick and sticky. Synovial fluid that is an abnormal color can indicate inflammation. Synovial fluid is usually clear and colorless, but abnormal fluid can appear cloudy and colored. This suggests that microscopic or chemical changes have occurred.

Is synovial fluid yellow?
Normal synovial fluid is clear in color, transparent in clarity, and highly viscous. Therefore, fluid that is yellow/green, opaque, and very thin is more likely to represent a septic joint.
What color is synovial joint fluid?
Synovial fluid is normally a thick, straw-colored liquid found in small amounts in joints. After the skin around the joint is cleaned, the health care provider inserts a sterile needle through the skin and into the joint space.
What color is normal joint fluid?
What do the test results mean? Normal synovial fluid is straw-colored, clear, and slightly sticky or stringy. Abnormal synovial fluid may be cloudy and thicker or thinner than normal fluid. Cloudiness could mean there are crystals, excess white blood cells, or microorganisms in the fluid.
Is synovial fluid white?
Whitish-creamy synovial fluid.
What does infected synovial fluid look like?
Normal synovial fluid is clear and colorless or straw-colored. Abnormal fluid may look cloudy, opaque, and/or differently colored. For example, cloudy fluid may indicate an infection, and pink or reddish fluid may indicate the presence of blood.
What does normal synovial fluid look like?
Normal synovial fluid is clear and colorless (right). Center and left tubes contain abnormal synovial fluid that is turbid and contains flocculent debris. Turbidity is caused by the presence of cells, fibrin, bacteria, or, on rare occasions, crystals.
What does gout fluid look like?
Slightly cloudy fluid may be caused by inflammation, gout, or pseudogout. A deep, dark red color may be caused by bleeding in the joint. Milky white may be caused by infection or inflammation or a condition such as gout.
What does red synovial fluid mean?
Cloudy synovial fluid may indicate the presence of microbes, white blood cells, or crystals. Reddish synovial fluid may indicate the presence of blood, but an increased number of red blood cells may also be present in cloudy synovial fluid.
Why does synovial fluid leak?
This can happen as a result of injury, infection, or arthritis: Injuries to joints can rupture blood vessels or lymph vessels, causing blood or lymph to build up under the skin.
What does yellow fluid drained from knee mean?
A doctor may also learn things just by looking at the aspirated fluid—for example, pink or red fluid indicates the presence of blood and suggests an injury, and opaque, yellowish fluid suggests septic arthritis.
How would you describe synovial fluid?
Synovial fluid, also known as joint fluid, is a thick liquid located between your joints. The fluid cushions the ends of bones and reduces friction when you move your joints. A synovial fluid analysis is a group of tests that checks for disorders that affect the joints.
What is synovial fluid made of?
Synovial fluid is produced as an ultrafiltrate of blood plasma and is primarily composed of hyaluronan, lubricin, proteinase, collagenases, and prostaglandins. [1] Synovial fluid production is from fibroblast like type B synovial cells.
Can synovial fluid leak from a joint?
When effusion happens in a joint — commonly the knee — excess fluid can pool in a part of the joint called the synovial cavity. It then leaks out into the soft tissue around the joint.
Is there blood in synovial fluid?
Cloudy synovial fluid may indicate the presence of microbes, white blood cells, or crystals. Reddish synovial fluid may indicate the presence of blood, but an increased number of red blood cells may also be present in cloudy synovial fluid.
What is synovial fluid made of?
Synovial fluid is produced as an ultrafiltrate of blood plasma and is primarily composed of hyaluronan, lubricin, proteinase, collagenases, and prostaglandins. [1] Synovial fluid production is from fibroblast like type B synovial cells.
Does synovial fluid remove waste?
In addition, synovial fluid delivers nutrients to the cartilage and removes waste from the cartilage.
Q1. What is the Main Function of Synovial Fluid?
Ans: The synovial fluids are produced by the synovium. It is the composition of water, inorganic salts, hyaluronic acid, lubricin, aggrecans, and m...
Q2. How Can I Increase My Synovial Fluid Naturally?
Ans: A person who needs to increase their synovial fluid between bones can take green leaves, bright-coloured fruits and vegetables, nuts, seeds, a...
Q3. Does Synovial Fluid Replace Itself?
Ans: Synovial fluids is a cartilage substance, they can pour out through the holes. The permanent loss of the synovial fluids may result in increas...
Why is the test done?
Taking a sample of the fluid can help diagnose the exact problem causing the inflammation. If the cause of the joint swelling is known, a synovial fluid analysis or joint aspiration may not be necessary.
What is synovial fluid analysis?
Synovial fluid analysis is also known as joint fluid analysis. It helps diagnose the cause of joint inflammation. Each of the joints in the human body contains synovial fluid. This fluid is a thick liquid that lubricates the joint and allows for ease of movement.
What does it mean when your fluid is red?
Less stringiness in the fluid could signal inflammation. Excess fluid in the joint could be a predictor of osteoarthritis. Reddish-colored fluid could mean blood is present. Blood in the fluid could point to a bleeding injury in the joint or a more serious bleeding problem throughout the body, such as hemophilia.
What does it mean when synovial fluid is cloudy?
Cloudiness could mean there are crystals, excess white blood cells, or microorganisms in the fluid.
What does a lab technician look for in a fluid?
A lab technician will look at the color and thickness of the fluid and assess red and white blood cells under a microscope. The technician will also look for crystals or signs of bacteria and measure: lactic dehydrogenase (an enzyme that increases in cases of inflammation and tissue damage)
What is the main place of inflammation in the body?
In joint diseases like arthritis, the synovium of the joint is the main place where inflammation occurs. Limited mobility in the joint, or pain and stiffness with movement, are often the first signs of joint disorders. Joint inflammation is more common as you age.
What is it called when you take fluid out of a joint?
This process of removing fluid from a joint is called arthrocentesis. Your doctor will send the fluid sample to the laboratory for examination.
What is the test for mucin clot?
Another test known as the mucin clot test (acetic acid is added to synovial fluid) estimates the production of hyaluronate. Poor mucin clot formation is associated with inflammatory types of arthritis. Blood tests or other laboratory tests can also be ordered with the intent of supporting the evidence derived from the synovial fluid analysis.
What is the procedure to draw synovial fluid from the affected joint?
Sterile technique must be followed when obtaining synovial fluid for analysis. Precautions are taken so that bacteria are not introduced into the joint. A sterile needle is used to draw joint fluid from the affected joint, but first, the skin is sterilized using a topical agent, e.g., Betadine (povidone-iodine). A local anesthetic is also used.
Why is my joint fluid yellow?
Normal joint fluid is viscous and appears clear to light yellow. Cloudy joint fluid is abnormal and suggestive of inflammation or infection. Bloody joint fluid is also abnormal and may be caused by trauma to the joint.
What is joint fluid?
Joint fluid, also referred to as synovial fluid, can be aspirated from a joint using a needle and syringe. The procedure can be performed in a healthcare provider's examination room and the fluid is then sent to a laboratory for analysis. Joint fluid analysis is also commonly referred to by other names, including:
What is used to remove fluid from a joint?
A local anesthetic is also used. After the fluid is withdrawn from the joint, the doctor may inject medicine (usually a corticosteroid) into the joint using the same injection site. A bandage is applied after the needle has been removed.
What is the purpose of a microscope to examine a joint?
Microscopic Examination. Joint fluid is examined under a microscope for the presence of blood cells, crystals, and bacteria. Normal joint fluid has none or few blood cells. Large numbers of red blood cells indicate bleeding in the joint. Large numbers of white blood cells can occur with infection, inflammatory arthritis, gout, or pseudogout .
Where is Anita Chandrasekaran?
Anita Chandrasekaran, MD, MPH, is board-certified in internal medicine and rheumatology and currently works as a rheumatologist at Hartford Healthcare Medical Group in Connecticut.
What can a doctor do to help diagnose joint conditions?
A doctor can perform a synovial fluid analysis to help diagnose joint conditions.
Why do doctors use synovial fluid analysis?
Doctors use synovial fluid analysis, or synovial joint analysis, to help diagnose the cause of joint pain and to rule out infection. Common causes of joint pain include rheumatoid arthritis (RA), osteoarthritis, and gout. The test can also help rule out some serious conditions that may require immediate treatment.
Why do doctors analyze synovial fluid?
When a person has painful or swollen joints, a doctor can extract and analyze a sample of their synovial fluid to help determine the cause of these symptoms. Synovial joint analysis can help a doctor diagnose and monitor the following: infections. inflammatory conditions, such as gout or RA.
What does it mean when your synovial fluid is viscous?
Synovial fluid should be viscous, meaning that it is thick and sticky.
What is the synovial fluid in the joints?
Many joints contain small amounts of synovial fluid, which helps keep the joint lubricated and able to move smoothly. Most joints, including the knees and hips, are synovial joints.
What are the signs of a medical condition?
Signs of a medical condition may include the abnormal appearance of synovial fluid, changes in its chemical makeup, or the presence of crystals.
What does it mean when your white blood count is high?
an abnormally high white blood cell count, which could indicate gout, RA, or septic arthritis. an abnormally high red blood cell count, which could indicate a bleeding disorder. the presence of crystals, which can signify gout or pseudogout.
What is the concentration of hyaluronic acid in synovial fluid?
Hyaluronic acid is synthesized by fibroblast-like synovial lining cells, and it appears in high concentrations in synovial fluid, at around 3 g/L, compared with a plasma concentration of 30 µg/L. Lubricin, a glycoprotein that assists articular lubrication, is another constituent of synovial fluid that is generated by the lining cells. It is now believed that hyaluronan functions in fluid-film lubrication, whereas lubricin is the true boundary lubricant in synovial fluid (see following). Because the volume of synovial fluid is determined by the amount of hyaluronan, water retention seems to be the major function of this large molecule. 234,238
What makes synovial fluid viscous?
Synovial fluid contains hyaluronic acid, which makes it very viscous. A small amount (pinch) of hyaluronidase powder should be added to all joint fluids to make them less viscous (liquefy them) before cell counts are performed by automated methods or manual methods or cytocentrifuge slides are prepared.
What is the function of synovial fluid?
Synovial Fluid. Synovial fluid, present in very small quantities in normal synovial joints, has two functions: lubrication and nutrition.62,63 Synovial fluid is a combination of a filtrate of plasma that enters the joint space from the subsynovial capillaries and hyaluronic acid, which is secreted by the synoviocytes.
What is synovial fluid?
Synovial fluid is both a lubricant for joint surfaces (lubricin for boundary cartilage-to-cartilage lubrication and hyaluronate for synovium-on-synovium lubrication) and a source of nourishment for the avascular articular cartilage. It also contributes to joint stability by forming a hydraulic “adhesive seal” between the two articulating bones.
How is synovial fluid cleared?
Synovial fluid is cleared through lymphatics in the synovium, assisted by joint movement. In contrast to ultrafiltration, lymphatic clearance of solutes is independent of molecular size. In addition, constituents of synovial fluid, such as regulatory peptides, may be degraded locally by enzymes, and low-molecular-weight metabolites may diffuse along concentration gradients into plasma. The kinetics of delivery and removal of a protein must be determined (e.g., using albumin as a reference solute) to assess the significance of its concentration in the joint. 237
What are the elements that are absent from synovial fluid?
Notably absent from synovial fluid are elements of the coagulation pathway (fibrinogen, prothrombin, factors V and VII, tissue thromboplastin, and antithrombin). 65 As a result, normal synovial fluid is resistant to clotting.
Where is synovial fluid found?
Synovial fluid is normally present in very small amounts in the synovial cavity surrounding joints. When fluid is present in amounts large enough to aspirate, there is a disease process in the joint. Figure 15.19 demonstrates placement of the needle for synovial fluid collection from a knee. Normally this fluid is straw colored and clear.
What is synovial fluid?
Synovial fluid is the thick liquid that lubricates your joints and keeps them moving smoothly. It’s on all of your joints, including in your knees, shoulders, hips, hands, and feet. Joint conditions like arthritis, gout, infections, and bleeding disorders can change how your synovial fluid looks and feels. A sample of this fluid taken ...
What is synovial fluid analysis?
What Is a Synovial Fluid Analysis? A synovial joint fluid analysis is a group of tests your doctor can use to diagnose problems with your joints. Joint conditions like arthritis, gout, infections, and bleeding disorders can change how your synovial fluid looks and feels.
How to numb a joint?
First, your doctor will give you a local anesthetic to numb your joint. Then, they'll put a needle in and take some fluid out. How much depends on the size of the joint and how many tests you're going to have.
What is the disease that breaks down joints over time?
An infection like septic arthritis. Bleeding disorders like hemophilia or von Willebrand disease. A disease that break down joints over time, like osteoarthritis. Your doctor might also use this test to see if your treatment for your joint condition is working.
How to check fluids?
Check your fluid's color and thickness. Measure chemicals like glucose, protein, and uric acid. See how many red and white blood cells and crystals your fluid has. Test for bacteria, viruses, or other germs.
What does it mean when your white blood count is high?
A high white blood cell count could mean you have an infection or another medical condition.
Can a synovial fluid test help you?
If you have joint symptoms like: Synovial fluid analysis can also help your doctor figure out if you have: Your doctor might also use this test to see if your treatment for your joint condition is working. If your doctor thinks you need this test, ask them how to prepare.
Overview
- Joint fluid, also referred to as synovial fluid, can be aspirated from a joint using a needle and syringe. The procedure can be performed in a doctor's examination room and the fluid is then sent to a laboratory for analysis. Joint fluid analysis is also commonly referred to by other names, including:
Treatment
- Removal of joint fluid has a dual purposediagnostic and therapeutic. While finding the cause of joint swelling is the goal, the removal of fluid may also help to relieve pain and pressure on the joint. After the fluid is withdrawn from the joint, the doctor may inject medicine (usually a corticosteroid) into the joint using the same injection site. A bandage is applied after the needle …
Symptoms
- Once the joint fluid arrives at the laboratory for analysis, it is observed by the human eye for color and clarity. Normal joint fluid is viscous and appears clear to light yellow. Cloudy joint fluid is abnormal and suggestive of inflammation or infection. Bloody joint fluid is also abnormal and may be caused by trauma to the joint.
Diagnosis
- Joint fluid is examined under a microscope for the presence of blood cells, crystals, and bacteria. Normal joint fluid has none or few blood cells. Large numbers of red blood cells indicate bleeding in the joint. Large numbers of white blood cells can occur with infection, inflammatory arthritis, gout, or pseudogout. Joint fluid can also be tested for glucose, protein, and lactic dehydrogenas…
Causes
- Crystals are an abnormal finding. Uric acid crystals are indicative of gout while CPPD crystals occur with pseudogout. Bacteria is also abnormal. A culture can identify the source of a bacterial infection.
Pathophysiology
- Joint fluid is observed in a plain tube after one hour for the formation of a fibrin clot. The quality of clot is graded, but any clot suggests that there is a problem with the synovial membrane. Another test known as the mucin clot test (acetic acid is added to synovial fluid) estimates the production of hyaluronate. Poor mucin clot formation is associated with inflammatory types of a…