
What are the three types of bone marrow?
- Types of the bone marrow
- Red bone marrow
- Yellow bone marrow
- Blood supply
- Innervation
What is bone marrow, and what does it do?
Bone marrow definition can be stated that it is the soft blood-forming tissue that fills the bone cavities. This tissue contains fat and immature blood cells and is responsible for producing mature blood cells, white blood cells, that helps fight diseases and build immunity, helps to form red blood cells and platelets. And any diseases or drugs that affect the human body and the human bone ...
What is the main purpose of bone marrow?
What’s the function of red bone marrow?
- Red blood cells. These are the cells that work to carry oxygen-rich blood to the cells of the body. ...
- Platelets. Platelets help your blood clot. This prevents uncontrolled bleeding.
- White blood cells. There are several types of white blood cells. They all work to help your body fight off infections. ...
What is the combining form for bone marrow?
What is the root word for bone marrow? Myelo- is a combining form used like a prefix meaning “marrow” or “of the spinal cord.” It is often used in medical terms. Marrow is a soft, fatty, vascular tissue in the interior cavities of bones that is a major site of blood cell production.

What is the composition and function of bone marrow?
Bone marrow is a spongy organ that fills the center of various bones of your body. It is where stem cells produce red and white blood cells and platelets. Without bone marrow, you couldn't move oxygen through your body or fight infections, and blood wouldn't clot.
What are the 3 components of bone marrow?
It is composed of hematopoietic cells, marrow adipose tissue, and supportive stromal cells. In adult humans, bone marrow is primarily located in the ribs, vertebrae, sternum, and bones of the pelvis.
Is eating bone marrow good for you?
Bone marrow is full of collagen, which improves the health and strength of bones and skin. It is also rich in glucosamine, a compound that helps against osteoarthritis, relieves joint pain, and reduces inflammation in the joints.
Where is bone marrow made?
Bone marrow is a spongy substance found in the center of the bones. It manufactures bone marrow stem cells and other substances, which in turn produce blood cells. Each type of blood cell made by the bone marrow has an important job. Red blood cells carry oxygen to tissues in the body.
What cells are in bone marrow?
Hematopoietic stem cells in the bone marrow give rise to two main types of cells: myeloid and lymphoid lineages. These include monocytes, macrophages, neutrophils, basophils, eosinophils, erythrocytes, dendritic cells, and megakaryocytes, or platelets, as well as T cells, B cells, and natural killer (NK) cells.
How do you eat bone marrow?
Bone marrow is loaded with good saturated fats, minerals and proteins like collagen. It can be eaten straight out of the bone, spread on bread or even used on tacos. The marrow bones can also be simmered with vegetables to make a nutritious bone broth.
Is bone marrow high in cholesterol?
Cholesterol is influenced by diet, and bovine marrow from grass-fed animals contains an average cholesterol content of 119.6 mg/ 100 g, while marrow from grain-fed animals contains an average of 150.6 mg/100 g (Kunsman et al., 2010) .
Is bone marrow fat or protein?
Bones, marrow, and connective tissue are all largely made up of the protein collagen, which turns into gelatin when cooked. Gelatin has a unique profile of amino acids and is particularly high in the amino acid glycine (3). Bone broth contains many vitamins and minerals, which can be an important part of your diet.
What is the best bone marrow to eat?
Bone marrow is of course present in all bones, but beef or veal bones are predominantly used due to their size. The long, straight femur bones are used as, being the biggest, these contain the most marrow and are the most easily accessible.
Can a person live without bone marrow?
Without bone marrow, our bodies could not produce the white cells we need to fight infection, the red blood cells we need to carry oxygen, and the platelets we need to stop bleeding. Some illnesses and treatments can destroy the bone marrow.
What two bones make blood cells?
Some bones in the fingers are classified as long bones, even though they are short in length. This is due to the shape of the bones, not their size. Long bones contain yellow bone marrow and red bone marrow, which produce blood cells.
What does bone marrow taste like?
Bone marrow has a rich, buttery, semi-sweet flavor with a delicately creamy texture. When roasted, the marrow takes on slightly nutty, umami notes.
How often should you eat bone marrow?
For best results we do suggest drinking bone broth every day, but if your budget or lifestyle doesn't allow that, aim for 3+ times a week. If you have specific goals, like building muscle or improving gut health, you may want to drink more broth.
Is bone marrow a Superfood?
It has a soft, sponge-like texture and a rich, buttery and meaty flavor. It's a true superfood that contains the types of nutrients that can sustain our bodies and support healing processes.
Can I eat raw bone marrow?
Raw Bone Marrow has become extremely popular amongst the Carnivore and Ancestral eating communities. Raw Bone Marrow is surprisingly palatable, clean tasting, easily digested and pairs well with a sprinkle of Kosher salt.
Whats bone marrow taste like?
Bone marrow has a rich, buttery, semi-sweet flavor with a delicately creamy texture. When roasted, the marrow takes on slightly nutty, umami notes.
1. Is the Bone Marrow Transplant Procedure Expensive?
Ans. In India, the bone marrow transplant cost ranges from 15, 00,000 to 40, 00,000. The actual cost will depend on which bone marrow transplant (B...
2. Does the Human Bone Marrow Have a Regenerative Property?
Ans. When the bone marrow is damaged then a bone marrow transplant treatment is recommended which is basically the installation of stem cells via t...
3. What Happens to a Body With No Bone Marrow?
Ans. The bone marrow is the blood cell 'factory' that produces red blood cells to carry oxygen through the bloodstream to the entire body, white bl...
What is the function of bone marrow?
It contains stem cells that develop into red blood cells, white blood cells, or platelets, which are involved in oxygen transportation, immune function, and blood clotting ( 1 ). The bone marrow of animals like cows, lambs, caribou, and moose is commonly consumed in many types of cuisine.
What is bone marrow used for?
Bone marrow can also be used to make bone broth or spread over bread, roasted vegetables, or meat dishes. Bone marrow is a type of tissue found in bones. The bone marrow of animals is often served alongside toast, used as a base for soup, or spread over a variety of foods.
How much bone marrow is good for you?
Bone marrow contains a good amount of calories and fat, as well as small amounts of nutrients like protein and vitamin B12. For example, one tablespoon (14 grams) of raw caribou bone marrow provides ( 2. Trusted Source.
What is the role of bone marrow in the immune system?
Bone marrow also contains adiponectin, a type of protein hormone that has been shown to play a central role in regulating inflammation and immune function ( 18, 19 ).
How long to cook bone marrow in oven?
To prepare bone marrow, place marrow bones in a 450℉ (232℃) oven and roast for about 15 minutes. Bone marrow can be scooped out after cooking. It’s often served with toast and marmalade. It can also be spread over your favorite dishes, including meats, bread, roasted veggies, and more.
Is bone marrow high in fat?
Bone marrow is high in calories and fat. It also contains protein, vitamin B12, riboflavin, collagen, and conjugated linoleic acid.
Can you use bone marrow in soup?
If you’re planning on using your bone marrow as a base for bone broth or soups, you can use the whole bone in your recipe rather than extracting the marrow separately.
What is bone marrow?
Regina Bailey. Updated October 05, 2019. Bone marrow is the soft, flexible connective tissue within bone cavities. A component of the lymphatic system, bone marrow functions primarily to produce blood cells and to store fat. Bone marrow is highly vascular, meaning that it is richly supplied with a large number of blood vessels.
What are the two types of bone marrow?
There are two major types of bone marrow tissue: red marrow and yellow marrow. Disease can impact the body's bone marrow. Low blood cell production is often a result of damage or disease. To correct, a bone marrow transplant may be performed so that the body can produce enough healthy blood cells.
Why do we need bone marrow transplants?
A bone marrow transplant may be performed in order to treat blood and marrow diseases. In the process, damaged blood stem cells are replaced by healthy cells obtained from a donor. The healthy stem cells can be obtained from the donor's blood or bone marrow.
Which section of the bone marrow contains blood vessels that supply the bone with nutrients and transport blood stem cells and mature?
The vascular section contains blood vessels that supply the bone with nutrients and transport blood stem cells and mature blood cells away from the bone and into circulation. The non-vascular sections of the bone marrow are where hematopoiesis or blood cell formation occurs.
What is the soft and flexible tissue in the cavities of bone?
Bone marrow, a component of the lymphatic system, is the soft and flexible tissue in the cavities of bone.
Where are white blood cells derived from?
While all blood cells are derived from bone marrow, some white blood cells mature in other organs such as the spleen , lymph nodes, and thymus gland.
Where is red marrow found?
In adults, red marrow is confined mostly to skeletal system bones of the skull, pelvis, spine, ribs, sternum, shoulder blades, and near the point of attachment of the long bones of the arms and legs. Not only does red marrow produce blood cells, but it also helps to remove old cells from circulation.
What is the composition of marrow?
The composition of marrow is dynamic, as the mixture of cellular and non-cellular components (connective tissue) shifts with age and in response to systemic factors. In humans, marrow is colloquially characterized as "red" or "yellow" marrow ( Latin: medulla ossium rubra, Latin: medulla ossium flava, respectively) depending on the prevalence ...
What is bone marrow?
Anatomical terminology. Bone marrow is a semi-solid tissue found within the spongy or cancellous portions of bones. In birds and mammals, bone marrow is the primary site of new blood cell production or haematopoiesis. It is composed of hematopoietic cells, marrow adipose tissue, and supportive stromal cells.
What are the precursor cells of bone marrow?
Hematopoietic precursor cells: promyelocyte in the center, two metamyelocytes next to it and band cells from a bone marrow aspirate. At the cellular level, the main functional component of bone marrow includes the progenitor cells which are destined to mature into blood and lymphoid cells.
How are stem cells used in bone marrow transplants?
In a bone marrow transplant, hematopo ietic stem cells are removed from a person and infused into another person ( allogenic) or into the same person at a later time ( autologous ). If the donor and recipient are compatible, these infused cells will then travel to the bone marrow and initiate blood cell production. Transplantation from one person to another is conducted for the treatment of severe bone marrow diseases, such as congenital defects, autoimmune diseases or malignancies. The patient's own marrow is first killed off with drugs or radiation, and then the new stem cells are introduced. Before radiation therapy or chemotherapy in cases of cancer, some of the patient's hematopoietic stem cells are sometimes harvested and later infused back when the therapy is finished to restore the immune system.
How much bone marrow does a human have?
Bone marrow comprises approximately 5% of total body mass in healthy adult humans, such that a man weighing 73 kg (161 lbs) will have around 3.65 kg (8 lbs) of bone marrow.
Which organs produce lymphocytes?
The bone marrow and thymus constitute the primary lymphoid tissues involved in the production and early selection of lymphocytes.
Where are hematopoietic cells found?
All types of hematopoietic cells, including both myeloid and lymphoid lineages, are created in bone marrow; however, lymphoid cells must migrate to other lymphoid organs (e.g. thymus) in order to complete maturation.
What is bone marrow?
Bone marrow definition can be stated that it is the soft blood-forming tissue that fills the bone cavities. This tissue contains fat and immature blood cells and is responsible for producing mature blood cells, white blood cells, that helps fight diseases and build immunity, helps to form red blood cells and platelets. And any diseases or drugs that affect the human body and the human bone marrow also affects the total counts of these cells and in turn, may lead to fatal consequences and life-threatening diseases.
Which bone marrow is prominent in many bones?
2. Dominates during the adolescence stage and in the adulthood stage, the yellow bone marrow is prominent in many bones.
Where is Bone Marrow Located?
The location of the bone marrow in the human body is of vital importance as it plays a major role in blood cells production. The bone marrow approximately comprises 5 percent of the total body mass in a healthy adult human. For instance, if a man weighs 73 kg then the body contains around 3.65kg of the marrow in the bone. In adult humans, the bone marrow is primarily located in
How much does bone marrow transplant cost in India?
Ans. In India, the bone marrow transplant cost ranges from 15, 00,000 to 40, 00,000. The actual cost will depend on which bone marrow transplant (BMT) procedure has been recommended for you. If the BMT is recommended along with chemotherapy and radiation treatment, it will cost you more.
What are the cells that make up the hemopoietic system?
The hemopoietic cells are packed between fat cells, collagen fibres, dendritic cells and fibroblasts of the bone.
Why is bone marrow important?
Bones are the entire skeletal system of the body that is constantly providing us support and the marrow has an important role in the circulation of blood and the blood health along with our immune system. Especially after the age of 30, the strength of the bone starts to weaken and if proper care is not taken then with weakening bones the bone marrow also fails to function properly and support the body. One must take care and stay healthy and bone health is as important as any other part of the body.
When is bone marrow transplant done?
The bone marrow transplant is only done when an expert or a professional recommends it since it is a medical procedure that involves risk both to the donor and the recipient.
What is bone marrow smear?
A bone marrow smear typically shows areas where connective tissue adipocytes with large vacuoles predominate. Only if these adipocytes areas are present is it safe to assume that the smear contains bone marrow material and that an apparent deficit of bone marrow cells is real.
What is the cytochemistry of acute leukemia?
Cytochemistry. To distinguish between reactive processes and chronic myeloid leukemia, leukocyte alkaline phosphatase is determined in fresh smears of blood. To distinguish between different types of acute leukemia, the peroxidase and esterase reactions are carried out (pp. 97 and 99), and iron staining is performed (p. 109) if myelodysplasia is suspected.
Is lymphocyte count a quantitative or qualitative assessment?
Qualitative and Quantitative Assessment of the Remaining Cells. Lymphocyte counts may be slightly raised in reactive processes, but a significant increase suggests a disease of the lymphatic system. The exact classification of these disease follows the criteria of lymphocyte morphology (Fig. 16). If elevated lymphocyte counts are found only in one preparation or within a circumscribed area, physiological lymph follicles in the bone marrow are likely to be the source. In a borderline case, the histology and analysis of lymphocyte surface markers yield more definitive data.
Where is the bone marrow found?
Bone marrow is found in the bones throughout your body. There are two types of bone marrow. Red bone marrow is involved in production of blood cells, while yellow marrow is important for fat storage. As you age, yellow bone marrow replaces red bone marrow.
Why is bone marrow important?
Bone marrow is crucial for producing blood cells . Therefore, a range of blood-related conditions involve issues with bone marrow. Many of these conditions affect the numbers of blood cells produced in bone marrow. This causes them to share many common symptoms, including:
What is the condition where bone marrow doesn't produce enough blood cells?
Aplastic anemia. Aplastic anemia occurs when bone marrow doesn’t produce enough new blood cells. It occurs from damage to the stem cells of bone marrow. This makes it harder from them to grow and develop into new blood cells.
How do white blood cells work?
There are several types of white blood cells. They all work to help your body fight off infections. Newly produced blood cells enter your bloodstream through vessels called sinusoids. As you age, your red bone marrow is gradually replaced with yellow bone marrow.
What is the spongy tissue that fills the inside of your bones?
Bone marrow is the spongy or viscous tissue that fills the inside of your bones. There are actually two types of bone marrow: Yellow bone marrow helps store fat. Read on to learn more about different functions of red and yellow bone marrow as well as the conditions that affect bone marrow.
What is the function of yellow bone marrow?
Yellow bone marrow is involved in the storage of fats. The fats in yellow bone marrow are stored in cells called adipocytes. This fat can be used as an energy source as needed. Yellow bone marrow also contains mesenchymal stem cells. These are cells that can develop into bone, fat, cartilage, or muscle cells.
Where are stem cells found?
Hematopoietic stem cells that are found in red bone marrow can develop into a variety of different blood cells, including: Red blood cells. These are the cells that work to carry oxygen-rich blood to the cells of the body. Old red blood cells can also be broken down in red bone marrow, but this task is mostly performed in the liver and spleen.
What is the structure of bone marrow?
The structure of bone marrow constitutes of hematopoietic tissue islands and adipose cells surrounded by vascular sinuses interspersed within a meshwork of trabecular bone. The bone marrow is composed of both cellular and non-cellular components and structurally be divided into vascular and non-vascular regions.
What is bone marrow?
Bone Marrow- Types, Structure and Functions. Bone Marrow is the soft, highly vascular and flexible connective tissue within bone cavities which serve as the primary site of new blood cell production or hematopoiesis.
What is the non-vascular section of bone marrow?
The non-vascular section of bone marrow is composed of hemopoietic cells of various lineages and maturity, packed between fat cells, thin bands of bony tissue (trabeculae), collagen fibers, fibroblasts and dendritic cells. This is where hematopoiesis takes place.
What is the function of red marrow?
In adults, red marrow is confined mostly to skeletal system bones that serve to produce blood cells and help remove old cells from circulation. They contain hematopoietic stem cells that produce two other types of stem cells: myeloid stem cells and lymphoid stem cells. These cells develop into red blood cells, white blood cells, or platelets.
What is the yellow marrow in bones?
Yellow marrow found in spongy bones and in the shaft of long bones, is non-vascular and consists primarily of fat cells. It is composed of hematopoietic tissue that has become inactive.
Which tissue contains all the lymphoid cells?
Since the bone marrow constitutes of the hemopoietic cells derived from multipotential stem cells, they not only give rise to all of the lymphoid cells found in the lymphoid tissue, but also to all of the cells found in the blood.
What type of cell is the immune system made of?
The majority of the cell types involved in the immune system is produced from a common hemopoietic stem cell (HSC).
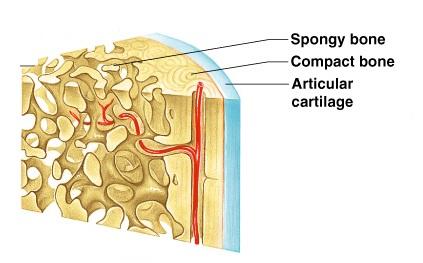
Overview
Structure
The composition of marrow is dynamic, as the mixture of cellular and non-cellular components (connective tissue) shifts with age and in response to systemic factors. In humans, marrow is colloquially characterized as "red" or "yellow" marrow (Latin: medulla ossium rubra, Latin: medulla ossium flava, respectively) depending on the prevalence of hematopoietic cells vs fat cells. While the precise mechanisms underlying marrow regulation are not understood, compositional chang…
Function
The bone marrow stroma contains mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs), which are also known as marrow stromal cells. These are multipotent stem cells that can differentiate into a variety of cell types. MSCs have been shown to differentiate, in vitro or in vivo, into osteoblasts, chondrocytes, myocytes, marrow adipocytes and beta-pancreatic islets cells.
The blood vessels of the bone marrow constitute a barrier, inhibiting immature blood cells from l…
As food
Animal bone marrow has been used in cuisine worldwide for millennia, such as the famed Milanese Ossobuco.
Clinical significance
The normal bone marrow architecture can be damaged or displaced by aplastic anemia, malignancies such as multiple myeloma, or infections such as tuberculosis, leading to a decrease in the production of blood cells and blood platelets. The bone marrow can also be affected by various forms of leukemia, which attacks its hematologic progenitor cells. Furthermore, exposure to radiat…
Fossil record
The earliest fossilised evidence of bone marrow was discovered in 2014 in Eusthenopteron, a lobe-finned fish which lived during the Devonian period approximately 370 million years ago. Scientists from Uppsala University and the European Synchrotron Radiation Facility used X-ray synchrotron microtomography to study the fossilised interior of the skeleton's humerus, finding organised tubular structures akin to modern vertebrate bone marrow. Eusthenopteron is closely related to t…
See also
• Myelonecrosis
• National Marrow Donor Program
• Gift of Life Marrow Registry
Further reading
• Nature Bone Marrow Transplantation (Nature Publishing Group) – specialist scientific journal with articles on bone marrow biology and clinical uses.
• Cooper, B (2011). "The origins of bone marrow as the seedbed of our blood: from antiquity to the time of Osler". Baylor University Medical Center Proceedings. 24 (2): 115–8. doi:10.1080/08998280.2011.11928697. PMC 3069519. PMID 21566758.