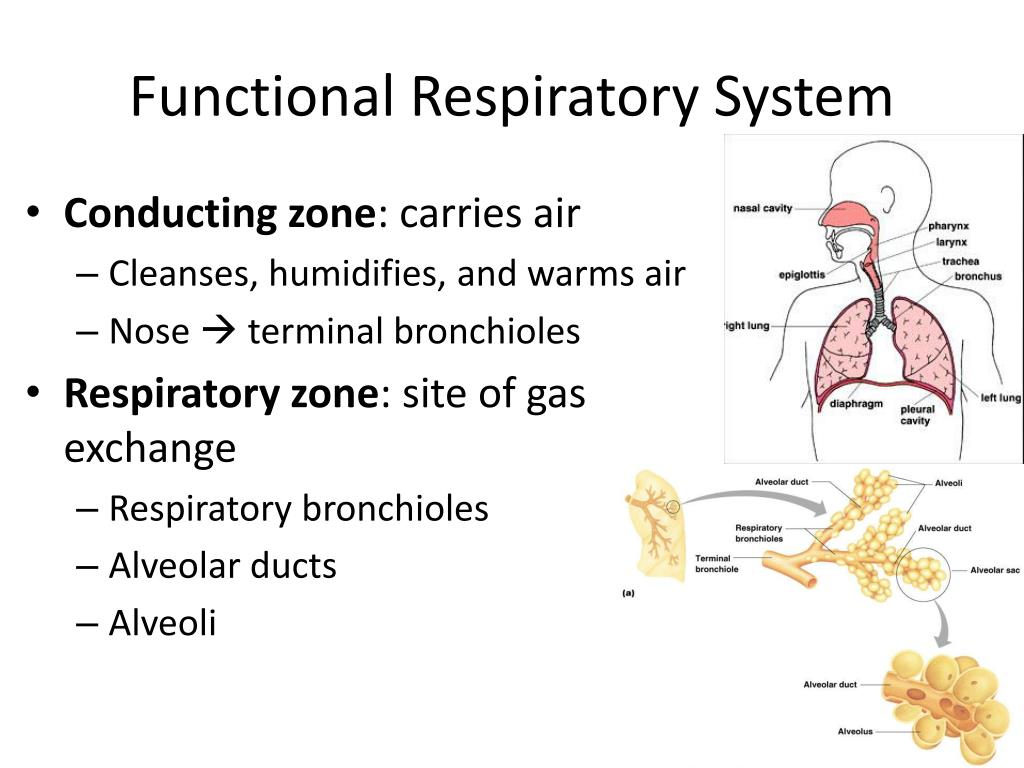
What is the difference between conducting and respiratory zone?
What are the Similarities Between Terminal and Respiratory Bronchioles?
- Terminal and respiratory bronchioles are two parts of the respiratory system.
- Terminal bronchioles divide to form respiratory bronchioles.
- Both terminal and respiratory bronchioles are airways.
- They are lined by an epithelium.
How does respiratory zone and the conducting zone differ?
The conducting zone of the respiratory system carries oxygen into the lungs and carbon dioxide out of the lungs. The respiratory zone is where oxygen and carbon dioxide move into and out of the blood.
What are the 10 parts of the respiratory system?
Respiratory system. The respiratory system is made up of the organs included in the exchange of oxygen and carbon dioxide. These are the parts: Nose. Mouth. Throat (pharynx) Voice box (larynx) Windpipe (trachea) Large airways (bronchi) Small airways (bronchioles) Lungs. The upper respiratory tract is made up of the: Nose. Nasal cavity. Sinuses ...
What is the conducting zone structure?
The conducting zone consists of the nose, pharynx, larynx, trachea, bronchi, and bronchioles. These structures form a continuous passageway for air to move in and out of the lungs. These structures form a continuous passageway for air to move in and out of the lungs.

What is the conducting and respiratory zones?
The conducting zone, which includes everything from the nose to the smallest bronchioles, moves air into and out of the lungs. The respiratory zone includes the respiratory bronchioles and alveoli and moves the respiratory gases, that is oxygen and carbon dioxide, in and out of the blood.
What is the function of the conducting zone of the respiratory system?
The major functions of the conducting zone are to provide a route for incoming and outgoing air, remove debris and pathogens from the incoming air, and warm and humidify the incoming air. Several structures within the conducting zone perform other functions as well.
What is conduction in respiratory system?
The. conducting zone consists of the nose, pharynx, larynx, trachea, bronchi, and bronchioles. These structures form a continuous passageway for air to move in and out of the lungs.
What are the two zones of the respiratory system?
The respiratory system, functionally, can be separated in two zones; conducting zones (nose to bronchioles) form a path for conduction of the inhaled gases and respiratory zone (alveolar duct to alveoli) where the gas exchange takes place.
What is the conducting zone quizlet?
The conducting zone of the respiratory system includes the nose, pharynx, larynx, trachea, bronchi, and bronchioles (except the respiratory bronchioles).
How do the respiratory zone and the conducting zone differ?
How do the respiratory zone and conducting zone differ? The conducting zone consists of a series of interconnecting cavities and tubes both outside and within the lungs. The respiratory zone consists of tubes and tissues within the lungs where gas exchange occurs.
Are alveoli part of the conducting zone?
The lungs contain some 300×106 alveoli. Thus the airways from nose to alveoli consist of a conducting zone of generations 0–16 and a respiratory zone in series with the conducting zone, with the respiratory zone consisting of generations 17–23. Figure 6.1.
Which is not part of the conducting portion of the respiratory system?
Which is not part of the conducting portion of the respiratory system? The epithelial lining of the oropharynx and the superior larynx (vocal cords) is nonkeratinized stratified squamous. In general, respiratory zone structures are lined with a thicker mucosa than conducting zone structures.
What is the function of the respiratory zone?
Note that the function of both zones is to move oxygen and carbon dioxide.
What is the conducting zone?
Conducting Zone: Air Movement. Let's explore the conducting zone in more detail. The conducting zone begins with the nose and nasal cavity. The trachea is part of the conducting zone, and it branches into right and left primary bronchi, carrying air to and from the right and left lung, respectively.
What are the respiratory systems?
Respiratory Systems. Respiratory systems include lungs and other organs that help get oxygen into and carbon dioxide out of the body. Lungs are contained within the thoracic cavity, the section of the human body encased by the rib cage and separated from the abdominal cavity by the diaphragm. The thoracic cavity includes other organs such as ...
How many alveoli are in the lungs?
Now, multiply what you see by hundreds of millions, as each of our lungs contain over 100 million alveoli.
Which zone of the respiratory system carries oxygen into the lungs?
The conducting zone of the respiratory system carries oxygen into the lungs and carbon dioxide out of the lungs. The respiratory zone is where oxygen and carbon dioxide move into and out of the blood. Create an account.
Which part of the respiratory system moves air into and out of the lungs?
Functionally, the respiratory system is divided into the conducting zone, which moves air into and out of the lungs, and the respiratory zone, which moves oxygen and carbon dioxide into and out of the blood. The process of gas exchange that occurs in ...
Which zone adds water vapor to the inspired air?
Its temperature equilibrates with body temperature, regardless of the temperature on the outside. Finally, the conducting zone adds water vapor to the inspired air. Respiratory Zone: Gas Exchange. Now that we've studied the conducting zone, let's take a look at the respiratory zone.
What is the respiratory zone?
The respiratory zone begins where the terminal bronchioles join a respiratory bronchiole, the smallest type of bronchiole (Figure 2.16 “Respiratory Zone”), which then leads to an alveolar duct, opening into a cluster of alveoli. Figure 2.16 Respiratory Zone.
Which zone of the respiratory system is not directly involved in gas exchange?
The conducting zone of the respiratory system includes the organs and structures not directly involved in gas exchange (trachea and bronchi). The gas exchange occurs in the respiratory zone.
Where do bronchioles lead to?
Bronchioles lead to alveolar sacs in the respiratory zone, where gas exchange occurs.
How is carbon dioxide exhaled?
Carbon dioxide is exhaled and oxygen is inhaled through the respiratory system , which includes muscles to move air into and out of the lungs, passageways through which air moves, and microscopic gas exchange surfaces covered by capillaries.
What are the functions of the conducting zone?
The major functions of the conducting zone are to provide a route for incoming and outgoing air, remove debris and pathogens from the incoming air, and warm and humidify the incoming air. Several structures within the conducting zone perform other functions as well. The epithelium of the nasal passages, for example, is essential to sensing odors, and the bronchial epithelium that lines the lungs can metabolize some airborne carcinogens. The conducting zone includes the nose and its adjacent structures, the pharynx, the larynx, the trachea, and the bronchi.
What are the respiratory systems used for?
Portions of the respiratory system are also used for non-vital functions, such as sensing odors, producing speech, and for straining, such as during childbirth or coughing. Figure 2.15 Major Respiratory Structures. The major respiratory structures span the nasal cavity to the diaphragm. Functionally, the respiratory system can be divided ...
What are the functions of the respiratory system?
The major organs of the respiratory system function primarily to provide oxygen to body tissues for cellular respiration, remove the waste product carbon dioxide, and help to maintain acid-base balance. Portions of the respiratory system are also used for non-vital functions, such as sensing odors, producing speech, and for straining, ...
Which respiratory system is the conducting system?
The conducting one of the respiratory systems consists of the mouth, nose, pharynx, trachea, primary bronchi, and all successive branching of the bronchioles up to and including the terminal bronchioles.
What is the function of mucus in the conducting zone?
Mucus secreted by cells of the conducting zone serves to trap small particles in the inspired air and thereby perform a filtration function. This mucus is moved along at a rate of 1-2 cms per minute by cilia projecting from the tops of epithelial cells that line the conducting zone.
What is the last 7 generations of the respiratory system?
The first 16 generations (Z) make up the conducting airways, and the last 7 the respiratory zone, BR, Bronchus; BL; Bronchiole; TBL, Terminal bronchiole RBL respiratory bronchiole, AD, alveolar duct; AS, alveolar sac.
What is the respiratory system?
The respiratory system allows oxygen in the air to be taken into the body, and it enables the body to get rid of carbon dioxide in the air breathed out, It consists of all the organs involved in breath ing, These include the nose, pharynx, larynx, trachea, bronchi, and lungs, Human respiratory system suffers from common respiratory symptoms include breathlessness, cough, and chest pain.
Which generation of the airway tree is the largest?
Airways: The tracheobronchial tree, an arrangement of branching tubes begins at the larynx, The largest airway is the trachea designated as (generation 0), The airway tree progressively bifurcates down to the alveolar sacs (generation 23), Each generation is progressively smaller in both diameter and length, The larger conducting airways (generations 0 through 16) transport air between the outside and the gas-exchanging regions of the lungs, The smaller respiratory airways (generations 17 through 23) not only conduct air but also permit gas diffusion which increases in significance closer to the alveoli.
What is the exchange of gases between the air in the alveoli and the blood in pulmonary capillaries?
Diffusion: exchange of gases ( O 2 and CO 2) between the air in the alveoli and the blood in pulmonary capillaries.
What temperature does inspired air reach?
When the inspired air reaches the respiratory zone, its temperature is 37° C (body temperature) regardless of the temperature. This function is needed to maintain a constant internal body temperature. The mucosa of the nose, mouth, and pharynx has a large surface area and a rich blood supply, This adds heat to cold air or removes heat from hot air.
Which tissue helps to move particles up and out of the trachea?
Ciliated tissue which helps to move particles up and out of the trachea, bronchioles.
Where is the nasopharynx located?
Part of the nasopharynx, located at back of mouth, keeps food out of nasal cavity
Where does external gas exchange take place?
External- Gas exchange between blood and air, takes place at the alveoli
