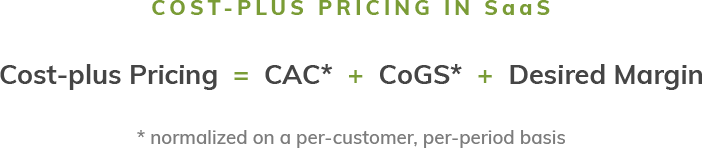What are the cost-based pricing formulas?
- Cost-plus pricing formula. The cost-plus formula takes the cost per unit a company pays and adds the fixed percentage of expected return to get the selling price.
- Markup pricing formula. Markup pricing uses this formula where the markup rate is (cost per unit) ÷ (1 - desired sales return).
- Target profit pricing formula. ...
- Break-even pricing formula. ...
How do you calculate cost plus pricing?
Cost plus pricing involves adding a markup to the cost of goods and services to arrive at a selling price. Under this approach, you add together the direct material cost, direct labor cost, and overhead costs for a product, and add to it a markup percentage in order to derive the price of the product.
What is full cost plus pricing?
Full cost plus pricing is a price-setting method under which you add together the direct material cost, direct labor cost, selling and administrative costs, and overhead costs for a product, and add to it a markup percentage (to create a profit margin) in order to derive the price of the product. The pricing formula is:
What is the difference between cost-plus pricing and pricing strategy?
An effective pricing strategy sets a sales price that is reasonable considering the product being sold, ensures the required profit margin for the company, and recoups all the expenses of producing the item. Cost-plus pricing simply multiplies the break-even price by the profit margin to arrive at the final price.
What is cost-plus pricing for printers?
Cost-plus pricing = $97.50 Using cost-plus pricing, you determine the price of the printer to be $97.50. This allows the company to recoup the cost of producing the printer, while earning a 25% profit margin on each unit sold. Cost-plus pricing is not only for products, but for services as well.

What is cost-plus pricing method example?
What is Cost Plus Pricing? Cost Plus Pricing is a very simple pricing strategy where you decide how much extra you will charge for an item over the cost. For example, you may decide you want to sell pies for 10% more than the ingredients cost to make them. Your price would then be 110% of your cost.
What does cost plus mean in pricing?
The idea behind cost-plus pricing is straightforward. The seller calculates all costs, fixed and variable, that have been or will be incurred in manufacturing the product, and then applies a markup percentage to these costs to estimate the asking price.
How is cost plus markup calculated?
All you need to do is subtract the cost of the product from the end price. Divide that number by the cost of the product, and multiply the result by 100 to find the markup percentage.
What does cost plus 20% mean?
Cost Plus Percentage Of Cost: Everything You Need to Know. Cost plus percentage of cost is a method contractors often use to price services. This type of contract specifies that the buyer must pay all the project costs incurred by the seller, plus an additional amount for profit.
What does cost-plus 10% mean?
Cost plus is about as simple as it sounds. Retailers set shelf pricing for every item in the store at their cost — the item, transportation and warehousing costs and labor to get it on the shelf — and simply charge consumers 10% of their total basket at checkout.
How do you calculate price markup and selling price?
Simply take the sales price minus the unit cost, and divide that number by the unit cost. Then, multiply by 100 to determine the markup percentage. For example, if your product costs $50 to make and the selling price is $75, then the markup percentage would be 50%: ( $75 – $50) / $50 = . 50 x 100 = 50%.
What is cost price formula?
Cost price = Selling price − profit ( when selling price and profit is given ) Cost price = Selling price + loss ( when selling price and loss is given )
How do you calculate cost price?
CP = ( SP * 100 ) / ( 100 + percentage profit).
How do you calculate cost-plus margin in Excel?
Click on the first cell beneath “Price.” Click the “Autosum” button and press “Enter” on the keyboard. This will automatically add the cost and markup values using the formula “=SUM(B2:C2).”
What is a good cost-plus percentage?
10 to 20 percentAlthough there is no industry standard, the "plus" part of cost-plus contracts is usually in the range of 10 to 20 percent of the project's total cost.
What is the right match for cost-plus contract?
This contract works best if the actual cost of the project is assumed to be below the projected cost. This type of contract focuses more on the quality of the project than on the overall cost of the project. If the budget for construction is low, this contract will fit. Simply put, it is a budget-friendly contract.
What is a cost-plus GMP?
Cost-Plus GMP Contract Agreements are “cost reimbursement” contracts. In a Cost-Plus price arrangement, there is no set or Fixed Fee. In other words, the contractor is paid for the Cost of the Work it incurs to complete the project, plus a Fee, not-to-exceed the GMP (absent scope changes or extenuating circumstances).
What is the difference between rate minus and cost-plus?
The “minus” is the negotiated rebate that your fuel card provider pays you later on gallons you purchase. With the cost-plus model, you do not pay the retail price.
What does it mean by cost-plus pricing and what are the problems of using this approach?
Cost plus pricing involves adding a markup to the cost of goods and services to arrive at a selling price. Under this approach, you add together the direct material cost, direct labor cost, and overhead costs for a product, and add to it a markup percentage in order to derive the price of the product.
Why do firms use cost-plus pricing?
Locking revenues in with a contract: Any supplier would like to have a contract with cost-plus pricing because it essentially guarantees sales with a certain profit percentage and coverage of all production costs with no risk of having a loss.
Why is cost-plus pricing good?
As long as whoever is calculating the costs per user or item is adding everything up correctly, cost plus pricing ensures that the full cost of creating the product or fulfilling the service is covered, allowing the mark-up to ensure a positive rate of return.
How to determine if cost plus pricing is a good pricing strategy for my business?
Cost plus pricing is a relevant product pricing strategy for physical products as it involves adding a markup to the original cost of the product....
What are the advantages of cost plus pricing?
The advantages of cost-plus pricing is a simple strategy to understand, the cost can be proven (eg, cost of labor, material cost, cost of productio...
What are the disadvantages of cost plus pricing?
The disadvantages of cost-plus pricing is the risk that consumers do not value your product at the set price, cost-plus pricing is inflexible and c...
Is cost plus pricing a good pricing strategy?
It depends on your business model. If your product’s value is derived from it’s cost of production, this is a legitimate way to increase profit mar...
What is a cost-based pricing example?
For instance, if the cost of manufacturing a certain product is $1,000 and a business wants to achieve a 20% markup, the selling price of a product...
What is usually the first step in cost-based pricing?
In the majority of cases, the first step involves calculating the costs of production. Alternatively, businesses can choose to first evaluate custo...
What is cost plus pricing?
What’s it: Cost-plus pricing is a pricing strategy in which the company adds up the profit margin (markup) to the cost of making the product. This is the most basic and simplest method because it uses cost as the basis of calculation. Another term for cost-plus pricing is markup pricing.
Why do retailers use cost plus pricing?
Retailers usually want to calculate for sure the gross profit margin of each unit sold. Apart from being easy to calculate, the cost-plus pricing approach allows companies to ensure that their costs are covered. This strategy also provides certainty for their suppliers.
What happens if a company adopts cost plus pricing?
Assume that market prices fall to a level below the firm’s unit cost. If it adopts cost-plus pricing, the company cannot reduce the price below the cost per unit. That is the minimum limit for determining the selling price. And, at that level (cost per unit), the company doesn’t make a profit.
Why can't contractors spread costs across multiple outputs?
Also, contractors cannot spread costs across multiple outputs (like manufacturing) because they will only work on a few projects. Advantages of cost-plus pricing. The first advantage of cost-plus pricing is that it is simple and straightforward. The company does not require customer surveys when setting sale prices.
Is the final price too expensive?
The company will probably take the low percentage of markup. So, the final price is not too expensive.
Does cost plus pricing guarantee demand?
Although easy, cost-plus pricing does not guarantee demand. This approach is only oriented internally (cost) rather than external (customers and competitors). Take the example of a new company. They will usually have a higher fee structure than the existing companies.
How to calculate cost plus pricing?
The cost-plus pricing formula is calculated by adding material, labor, and overhead costs and multiplying it by (1 + the markup amount). Overhead costs are costs that can't directly be traced back to material or labor costs, and they're often operational costs involved with creating a product.
What is cost plus pricing?
A cost-plus pricing strategy, or markup pricing strategy, is a simple pricing method where a fixed percentage is added on top of the production cost for one unit of product (unit cost). This pricing strategy ignores consumer demand and competitor prices. And it's often used by retail stores to price their products.
What are the advantages of cost plus pricing?
It's simple to use. Using a cost-plus pricing strategy doesn't require extensive research. You just need to analyze your production costs (e.g., labor, materials, and overhead) and determine a markup price. 2. The price can be justified.
How to find markup percentage?
Markup can be calculated by subtracting the unit cost from the sales price and dividing the resulting number by unit cost. Then multiply the final result by 100 to get the markup percentage.
Why is cost plus pricing important?
The cost-plus pricing strategy makes it easy to communicate to consumers why price changes are made. If a company needs to raise the selling price of its product due to rising production costs, the increase can be justified. 3. It provides a consistent rate of return.
How much does it cost to make an iPhone X?
It costs Apple $370.25 to produce one iPhone X -- but its final selling price is $999. The price of the device is marked up by 170%, and this is how Apple makes its profit.
Is there a guarantee that all costs will be covered?
There's no guarantee all costs will be covered . Sales volume is projected before pricing the product, and sometimes this estimate is inaccurate. If sales are overestimated and a low markup is used to price the product, fewer items are sold and the costs to produce the product might not be covered.
What is cost plus pricing?
Cost-plus pricing is not only for products, but for services as well. Many companies that provide consulting services rely on cost-plus pricing. For instance, let's say your company offers a repair service for small businesses who own your printers.
What are the disadvantages of Cost Plus?
There are several issues, but there are two significant disadvantages to consider. Cost-plus pricing does not take into account what competitors are charging for similar products. For example, if your competitors are selling a similar printer for $92, you may lose sales because their printers are cheaper than yours.
What happens if you sell a printer at $78?
If you sold the printer at $78 your company would break even , meaning there would be no profit or loss. However, your company definitely plans to earn money from the sale of the printers. In fact, the goal is to earn 25% on each printer. So, you implement the following formula for cost-plus pricing to arrive at the sales price: ...
A cost-plus pricing example
To provide an example of cost-plus pricing, let’s pretend that we are operating in the sporting goods retail market. We’ll also presume we know from our direct involvement in this industry, that our suppliers, including Adidas and Nike, suggest a mark-up of 80 per cent.
Is mark-up and gross margin the same?
No, definitely not. Many small business managers confuse mark-up with gross profit margin (GPM). In fact, they’re completely different terms. Under the next heading, I’ll do my best to clear up the confusion.
Gross profit margin (GPM) demystified
If we look at our Adidas footwear example, above, we can see how we arrive at our recommended retail price. And we have done so simply by using a cost-plus price setting method. But our gross profit isn’t, unfortunately, 80 per cent. Actually, it’s only 44.44 per cent. Or expressed in monetary terms, $44 per pair.
Calculating gross profit margin in percentage terms
As I have just explained, there is a distinct difference between mark-up and gross margin. It is important for all managers — regardless of business size — to understand this. Lack of understanding here, can mean the difference between showing a profit (or) recording a loss.
What is cost plus pricing?
However, it means adding the original cost of the product plus overhead expenses like labor cost, transportation cost, rent, and a profit margin or the markup. When you add all of these costs together, then it’ll be a cost-plus pricing strategy.
What happens if a company starts pricing based on cost plus formula?
When a business starts pricing based on cost-plus formula by utterly avoiding the competitors’ prices in the market, then it would end up charging either too high or too low. People won’t buy a company’s product if the price is too high, or it would cost the company if it’s too low. Either way, it would very badly impact the market share of the company. In other words, it’ll be a lose-lose situation for the company.
What happens if a company doesn't do market research on competitors pricing scheme?
When a company doesn’t do market research on competitors’ pricing scheme, then losing market share is one thing. It would also lose the customer’s perceived because some customers value the product based on its price.
Why can companies defend and justify their products' prices?
Companies can defend and justify their products’ prices because they print a complete pricing mechanism on the packing. As a result, customers are satisfied with the pricing that what they are paying is right.
Is cost plus good for business?
Cost-plus strategy could be ideal for some businesses, but it’s not for most businesses . The mistake most companies make while pricing is that they don’t give importance to market demand, and competitor’s prices. Therefore, whether customers would perceive its value too high or too low, it’s not good for the company either way.
How to use cost plus pricing?
To use the cost-plus pricing strategy, you need to know: 1 How much it costs you to make the product#N#Direct labor#N#Direct materials#N#Overhead associated with producing product 2 Your markup percentage
Why do businesses justify their prices?
You can justify your prices: Another reason businesses opt for this pricing strategy is that prices are justifiable. If your production costs increase, you can clearly explain why your selling prices increase, too. This could potentially boost business transparency … and help you raise prices without losing customers .
Do you cover all your costs?
You might not cover all your costs: Depending on how good you are at estimating and allocating costs, you might end up setting a selling price that’s lower than all of your business’s costs. Remember: product costs aren’t the only expenses you have.
Does cost plus pricing require market analysis?
Cost-plus pricing doesn’t require a thorough market analysis on your competitors’ pricing or what customers are willing to spend (which is also a con that we’ll get to later). Instead, you simply need to identify how much it costs to make a product and use the cost-plus pricing formula to get your selling price.
What is Full Cost Pricing?
Full cost plus pricing is a price-setting method under which you add together the direct material cost, direct labor cost, selling and administrative costs, and overhead costs for a product, and add to it a markup percentage (to create a profit margin) in order to derive the price of the product. The pricing formula is:
Example of Full Cost Pricing
ABC International expects to incur the following costs in its business in the upcoming year:
Advantages of Full Cost Plus Pricing
The following are advantages to using the full cost plus pricing method:
Disadvantages of Full Cost Plus Pricing
The following are disadvantages of using the full cost plus pricing method:
Evaluation of Full Cost Plus Pricing
This method is not acceptable for deriving the price of a product that is to be sold in a competitive market, for several reasons. First, it does not factor in the prices charged by competitors. Second, it does not factor in the value of the product to the customer.