How many leatherback sea turtles exist?
The Pacific leatherback turtle populations are most at-risk of extinction. Pacific leatherbacks are one of nine ESA-listed species identified in NOAA's Species in the Spotlight initiative....Scientific Classification.KingdomAnimaliaFamilyDermochelyidaeGenusDermochelysSpeciescoriacea3 more rows
Are leatherback turtles endangered 2022?
Six sea turtle species are found in U.S. waters and all are threatened or endangered. The largest among them—the Pacific leatherback—is one of NOAA Fisheries' Species in the Spotlight.
What is the current population of sea turtles?
Recent estimates show us that there are nearly 6.5 million sea turtles left in the wild with very different numbers for each species, e.g. population estimates for the critically endangered hawksbill turtle range from 83,000 to possibly only 57,000 individuals left worldwide.
What sea turtle has the largest population on earth?
The olive ridley is the most abundant sea turtle in the world. Each year, there are probably about 500,000 to 600,000 females nesting in arribadas (mass nesting sites) in Costa Rica, 450,000 in Mexico and about 135,000 in India; with a total female population of about 2 million turtles.
How many leatherbacks are left in the world?
Leatherback numbers have declined in Mexico, Costa Rica, Malaysia, India, Sri Lanka, Thailand, Trinidad, Tobago and Papua New Guinea [7]. In 1980 there were over 115,000 adult female leatherbacks worldwide. Now there are less than 25,000 [6].
How many sea turtles are left in the world 2022?
6.5 million sea turtlesThere are over 2,500 species of sea turtles. Recent estimates of sea turtle populations state that nearly 6.5 million sea turtles are left in the wild today. The numbers vary for each species. The population of the Hawksbill turtle, a critically endangered species, ranges from 57,000 to 83,000.
How many turtles are killed each year?
4,600 Sea Turtles Killed Yearly in U.S. Fisheries, Study Finds - Oceana.
How many sea turtles are left in the world today?
There are an estimated 1,030,000 nesting female sea turtles living in our oceans. If 90% of all sea turtles are female, the additional 10% of male sea turtles puts the total figure for sea turtles left in the world at around 1,133,000 - one-million, one-hundred and thirty-three thousand.
How much has the sea turtle population dropped?
Illegal Sea Turtle Shell Trade Scientists estimate that hawksbill populations have declined by 90 percent during the past 100 years. While illegal trade is the primary cause of this decline, the demand for shells continues today on the black market.
What is the heaviest turtle in the world?
Leatherback sea turtlesThe leatherback is the largest living sea turtle. Weighing in at between 550 and 2,000 pounds with lengths of up to six feet, the leatherback is a big turtle! Leatherback sea turtles can be distinguished from other species of sea turtle by its lack of a hard shell or scales.
Is hope the turtle Still Alive 2021?
The Turtle Hospital is sad to report the passing away of our sea turtle patient, “Good Hope,” a pregnant hawksbill airlifted for treatment from St. Croix exactly one month ago. Good Hope's passing came as a surprise to hospital staff.
What would happen if leatherback turtles went extinct?
If sea turtles went extinct, dune vegetation would lose a major source of nutrients and would not be as healthy and would not be strong enough to maintain the dunes, resulting in increased erosion. Once again, all parts of an ecosystem are important, if you lose one, the rest will eventually follow.
Is the leatherback sea turtle endangered?
Vulnerable (Population decreasing)Leatherback sea turtle / Conservation status
What is killing the leatherback turtle?
Incidental capture by fishing gear is the greatest threat to most sea turtles, especially endangered loggerheads, greens, and leatherbacks. This threat is increasing as fishing activity expands.
What would happen if leatherback turtles went extinct?
If sea turtles went extinct, dune vegetation would lose a major source of nutrients and would not be as healthy and would not be strong enough to maintain the dunes, resulting in increased erosion. Once again, all parts of an ecosystem are important, if you lose one, the rest will eventually follow.
When was the leatherback sea turtle listed as endangered?
In 1970, leatherback sea turtles were listed as endangered under the Endangered Species Conservation Act, the predecessor to the Endangered Species Act (ESA). When the ESA was passed in 1973, leatherbacks were listed as endangered.
How many leatherback turtles are there in the world?
The Pacific population of leatherback sea turtles has suffered most over the last twenty years: as few as 2,300 adult females now remain, making the Pacific leatherback the world's most endangered marine turtle population.#N#Although Atlantic populations are rather more stable, scientists believe that they, too, will decline due to the large numbers of adults being killed accidentally by fishing fleets. In the Atlantic, the fact that they are widely distributed during the migration process increases the risk of interaction of leatherback turtles with longline fisheries.
How big is the leatherback turtle?
The biggest ever recorded leatherback turtle was a male stranded on a Welsh beach that measured 256cm and weighed 916 kg. A leatherback was recorded to have descended to a maximum depth of 1,230 metres, which represents the deepest dive ever recorded for a reptile. © Coral triangle blog © WWF. © Leatherback turtle.
What is the role of leatherback turtles in jellyfish?
As a major jellyfish predator, the leatherback turtle provides natural ecological control of jellyfish populations. Overabundance of jellyfish may reduce fish populations as jellyfish can feed on fish larvae and reduce population growth of commercially important fish.
What is the largest turtle in the world?
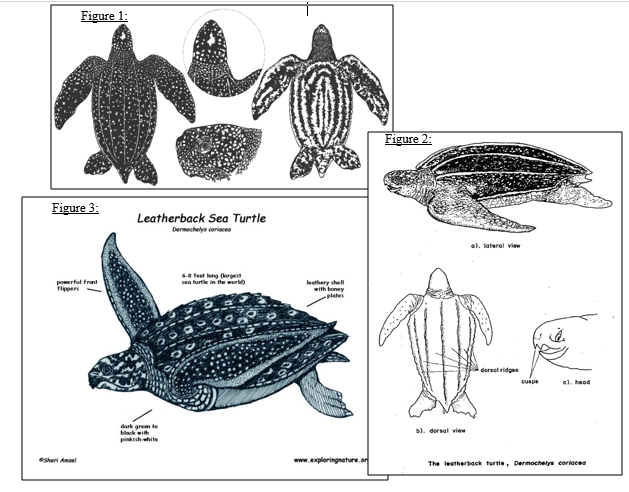
The leatherback turtle is the largest marine turtle and one of the largest living reptiles. Leatherbacks are one of the most migratory of all marine turtle species, making both trans-Atlantic and trans-Pacific crossings. They are easily distinguished by their carapace, which is leathery, not hard as in other turtles, and by their long front flippers.
How to help a turtle?
How you can help 1 Send a turtle to rehab! Help the recuperation process for thousands of sick and injured turtles. 2 Don't buy products which have been made from sea turtle parts. Guitars, ashtrays, jewellry and other products made from sea turtles are sold to tourists around the world.
What is the diet of a leatherback?
Diet. The large size of leatherbacks is all the more remarkable given their low energy, low protein diet of soft-bodied creatures such as jellyfish , squid and tunicates ("jelly fish-like" marine invertebrates). Previous Population and Distribution.
How many times do leatherbacks lay eggs?
Breeding. Female leatherbacks may lay 4 to 5 times per season, each time depositing 60 to 120 eggs. Leatherbacks appear to nest once every two or three years with an incubation period of approximately 60 days. Diet.
Where are leatherback sea turtles found?
An international team of scientists led by the Wildlife Conservation Society and the University of Exeter have discovered the world’s largest nesting population of leatherback turtles in Gabon, West Africa. The leatherback is critically endangered, so this find makes Gabon a key location in ...
How big is a leatherback turtle?
About leatherback turtles. The leatherback is the largest sea turtle, reaching up to nearly 6.5 feet (2 meters) in length and weighing 1,190 pounds (540kg). Unlike other sea turtles, the leatherback does not have a hard shell. Its shell is made-up of a mosaic of small bones covered by firm, rubbery skin with seven longitudinal ridges.
What is the Gabon Sea Turtle Partnership?
The research was led by the University of Exeter working in collaboration with the Wildlife Conservation Society (WCS) which spearheads the Gabon Sea Turtle Partnership, a network of organizations concerned with the protection of marine turtles in Gabon.
How deep do leatherbacks dive?
Leatherbacks are the deepest diving of all sea turtles. The deepest recorded dive is ¾ mile (1.2 kilometers), which is slightly more than the deepest known dive of a sperm whale. As with other reptiles, the sex of leatherbacks-to-be is determined by the temperature of eggs during incubation.
When did leatherbacks first nest?
Leatherbacks were first described nesting in Gabon in 1984.
What percentage of sea turtles nest in protected areas?
Protected areas are key. The study also revealed that around 79 percent of the turtles' nesting occurs within National Parks and other protected areas. "These findings show the critical importance of protected areas to maintain populations of sea turtles," said Angela Formia of the Wildlife Conservation Society, a co-author of the paper.
What temperature do leatherbacks hatch?
With leatherbacks, temperatures above 84 degrees F, (29 degrees C) will result in female hatchlings. Leatherbacks are strong swimmers and tagged individuals have been known to cross ocean basins and are known to travel many thousands of miles in search of their jellyfish prey.
How big are leatherback turtles?
Weight. 600-1500 pounds. Length. 55-63 inches. Habitats. Oceans. Leatherback turtles are named for their shell, which is leather-like rather than hard, like other turtles. They are the largest sea turtle species and also one of the most migratory, crossing both the Atlantic and Pacific Oceans. Pacific leatherbacks migrate from nesting beaches in ...
Why are leatherback turtles declining?
Although their distribution is wide, numbers of leatherback turtles have seriously declined during the last century as a result of intense egg collection and fisheries bycatch. Globally, leatherback status according to IUCN is listed as Vulnerable, but many subpopulations (such as in the Pacific and Southwest Atlantic) are Critically Endangered.
How does WWF help turtles?
WWF aims to reduce turtle bycatch by working with fisheries to switch to more turtle-friendly fishing hooks ("circle" hooks) and advocates for the use of devices that exclude turtles from nets.
What is WWF in turtle conservation?
WWF works around the world to establish marine protected areas (MPA) to ensure marine turtles have a safe place to nest, feed and migrate freely. In the Bird's Head Seascape of the Coral Triangle, we work to protect the nesting area of the largest remaining population of leatherback turtles in the Pacific Ocean. WWF also supports the patrolling of leatherback turtle nest beaches and helps equip local turtle conservationists. These conservation efforts often lead to ecotourism opportunities and offer alternative livelihoods for local communities.
How does satellite telemetry help turtles?
Satellite telemetry allows researchers to track marine turtles as they swim from place to place. These satellite tags do not harm the turtles in any way and are designed to eventually fall off. The data will tell us where important feeding areas are, help us understand migration patterns, and anticipate where turtles may come in contact with fisheries and their gear. More than 20 leatherbacks have been fitted with transmitters to analyze their migratory routes in the Atlantic Ocean and hopefully reduce bycatch mortalities.
Why are sea turtles dependent on beaches?
Sea turtles are dependent on beaches for nesting. Sea level rise, uncontrolled coastal development, vehicle traffic on beaches, and other human activities have directly destroyed or disturbed sea turtle nesting beaches around the world.
What do leatherbacks eat?
Leatherbacks feed almost exclusively on jellyfish, making them susceptible to mistakenly swallowing plastic bags floating in the ocean, which can kill them.
How long do leatherback turtles live?
Unfortunately, we know very little about leatherback turtles’ lifespan, although most estimates assume they live somewhere up to around 50 years.
Why are leatherback sea turtles so big?
Because of their size, leatherback sea turtles are too large to benefit from the turtle excluder devices used by fishermen to avoid turtles being caught within their nets. The result is that hundreds of leatherback turtles are caught by fishermen every year.
What is the largest turtle in the world?
The leatherback turtle is the largest turtle in the world.
What is a leatherback turtle?
The leatherback sea turtle, often referred to as the lute turtle or leathery turtle – and known scientifically as Dermochelys coriacea – is a large sea turtle, named for its unique shell.
Which turtle has skin over its shell?
The leatherback turtle is the only turtles who have skin over the shells rather than bone.
Do leatherback sea turtles hunt in shallow water?
They typically avoid coral reefs, although where they go depends heavily on where their prey is. Therefore, in the daytime, they can be found hunting in deeper waters, and at night they are often found in shallower waters. Although they prefer open waters, because nesting takes place on beaches, leatherback sea turtles can also be found near the shoreline.
Do leatherback sea turtles have predators?
Leatherback sea turtles have very few natural predators, likely due to their size. However, when they are young and small, they are more vulnerable . Shorebirds, such as storks or herons, often prey on the hatchlings as they struggle to get across the beach upon which they are born. As well, before they hatch, mammals and birds will often eat the turtles’ eggs.
Where do leatherback turtles migrate?
Pacific leatherback turtles migrate from their nesting site in Indonesia to feeding grounds near the Americas. Environmental changes caused by the El Niño/La Niña climate oscillation may also have affected turtles by reducing their food sources, particularly jellyfish.
How much does a leatherback turtle weigh?
Their unique "leathery" shells can reach 6.5 feet (2 meters) in length and they weigh up to 1,190 pounds (540 kilograms).
How long does it take for a leatherback turtle to disappear?
The Pacific leatherback turtle's last population stronghold could disappear within 20 years if conservation efforts aren't expanded, a new study finds.
Why are there conservation efforts at Indonesia beaches?
Conservation efforts at Indonesia's beaches include patrols by local residents to protect nests from predators and relocating eggs to areas with cooler sand. (The sand temperature influences the sex of hatchlings — cool sand means more male turtles .)
Where do pigs dig up turtle eggs?
Before the practice was outlawed in 1993, villagers and fisherman collected turtle eggs by the thousands in Indonesia. Dogs and pigs still dig up turtle eggs along Bird's Head's beaches, Ricardo Tapilatu, lead study author and a doctoral student at UAB, said in a statement.
Where is Tapilatu from?
But Tapilatu, a native of western Papua, Indonesia, who has worked on turtle conservation since 2004, said beach conservation alone is unlikely to tip the scales in favor of the recovery.
Is the leatherback turtle endangered?
Although Atlantic populations have increased in recent years, the Pacific leatherback population has dropped more than 95 percent since the 1980s. The leatherback turtle was listed as endangered in the United States in 1970. Much of the decline is due to humans.
Why are leatherbacks so big?
Leatherbacks' large size even as hatchlings, helps them stay warmer in cold pelagic waters.
Where is TLT located?
TLT works with resource managers and local communities to enhance habitat protection at Las Baulas National Park and secondary nesting beaches in Costa Rica (Cabuyal, Naranjo, Junquillal, Nombre de Jesús, Ostional and Camaronal).
