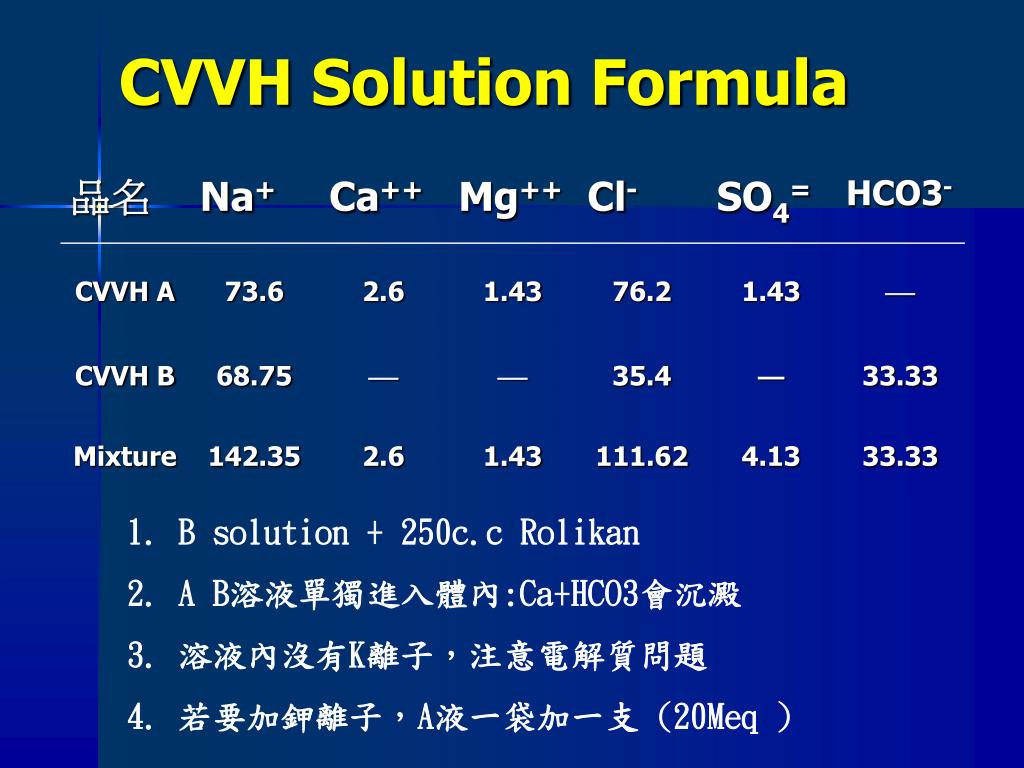
How to do cost-volume-profit (CVP) analysis?
How to perform a cost volume profit analysis (CVP) analysis Sum fixed costs. Not every account in your books is strictly fixed or variable. ... Determine the product's selling price. CVP analysis can assess whether your target selling price gives you the profits you desire. ... Calculate the variable cost per unit. ... Calculate the unit CM and CM ratio. ... Complete the CVP analysis. ...
How to figure profit vs. cost?
How to Figure Profit Vs. Cost. A business’s profit is the amount of money remaining after the company pays its costs and expenses. Costs are the expenses involved in developing, creating and ...
How to perform a cost volume profit (CVP) analysis?
Overview: What is cost volume profit analysis? What is the cost volume profit formula? How to perform a cost volume profit analysis (CVP) analysis. 1. Sum fixed costs; 2. Determine the product’s selling price; 3. Calculate the variable cost per unit; 4. Calculate the unit CM and CM ratio; 5. Complete the CVP analysis; A cost volume profit analysis example. 1.
How to analyze profitability?
- Determine the type of profit margin needed. Profit margins can be calculated to get the gross, operating or net profit margin of a business. ...
- Gather financial data. Regardless of which type of profit margin you choose, you will need to gather certain data to make the calculations. ...
- Input your data. ...
- Complete calculations. ...
What is CVP ratio?
If a company sells more than one product, they are sold in the same mix. CVP analysis requires that all the company's costs, including manufacturing, selling, and administrative costs, be identified as variable or fixed. Contribution margin and contribution margin ratio.
Is CVP easy to calculate?
The limitations of CVP analysis A CVP analysis keeps calculations simple – but that means it has to make some assumptions upfront. For example, a CVP analysis assumes that all the units you produce will be sold and also assumes that your fixed and variable costs are constant.
What are the 3 elements of CVP analysis?
The point of a CVP analysis is to determine how changes in variable and fixed costs will affect profits. What are the three elements of cost-volume-profit analysis? The three main elements are cost, sales volume and price. A CVP analysis looks at how these elements influence profit.
What is CVP analysis example?
Profit may be added to the fixed costs to perform CVP analysis on the desired outcome. For example, if the previous company desired a profit of $50,000, the necessary total sales revenue is found by dividing $150,000 (the sum of fixed costs and desired profit) by the contribution margin of 40%.
Why do we use CVP?
Central venous pressure (CVP) is the pressure in the thoracic vena cava near the right atrium. CVP is an important factor in critical care medicine because it can be used to estimate a patient's fluid volume status, assess cardiac function, and gauge how well the right ventricle of the heart is functioning (1).
How do you do a CVP analysis?
How to perform a cost volume profit analysis (CVP) analysisSum fixed costs. Tally your company's fixed costs: ... Determine the product's selling price. ... Calculate the variable cost per unit. ... Calculate the unit CM and CM ratio. ... Complete the CVP analysis.
How do you calculate profit in CVP analysis?
CVP Analysis helps them to BEP Formula. It is determined by dividing the total fixed costs of production by the contribution margin per unit of product manufactured. Break-Even Point in Units = Fixed Costs/Contribution Margin read more for different sales volume and cost structures.
What are the 4 assumptions of CVP analysis?
(i) All costs can be resolved into fixed and variable elements. (ii) Over the activity range being considered costs and revenues behave in a linear fashion. (iii) The only factor affecting costs and revenues is volume. (iv) The technology, production methods and efficiency remain unchanged.
What are the limitations of CVP analysis?
Limitations of CVP Fixed costs not always fixed. Proportionate relation between variable cost and volume of output not always effective. Unit selling price not always constant. Not suitable for a multiproduct firm.
How do you perform a CVP analysis?
How to perform a cost volume profit analysis (CVP) analysisSum fixed costs. Tally your company's fixed costs: ... Determine the product's selling price. ... Calculate the variable cost per unit. ... Calculate the unit CM and CM ratio. ... Complete the CVP analysis.
What is the costing method that can be used most easily with break-even analysis and other cost volume profit techniques?
The costing method that can be used most easily with break-even analysis and other cost volume-profit techniques is: variable costing.
What are five assumptions that underlie the cost-volume-profit analysis?
(i) All costs can be resolved into fixed and variable elements. (ii) Over the activity range being considered costs and revenues behave in a linear fashion. (iii) The only factor affecting costs and revenues is volume. (iv) The technology, production methods and efficiency remain unchanged.
What is CVP analysis?
Cost-Volume-Profit Analysis (CVP analysis), also commonly referred to as Break-Even Analysis, is a way for companies to determine how changes in costs (both variable and fixed Fixed and Variable CostsCost is something that can be classified in several ways depending on its nature. One of the most popular methods is classification according) and sales volume affect a company’s profit. With this information, companies can better understand overall performance by looking at how many units must be sold to break even or to reach a certain profit threshold or the margin of safety.
What is the break even point in units?
The break-even point (BEP), in units, is the number of products the company must sell to cover all production costs. Similarly, the break-even point in dollars is the amount of sales the company must generate to cover all production costs (variable and fixed costs).
What does a high CM ratio and a low variable expense ratio indicate?
A high CM ratio and a low variable expense ratio indicate low levels of variable costs incurred.
What is the BEP of a company?
The BEP, in units, would be equal to 240,000/15 = 16,000 units. Therefore, if the company sells 16,000 units, the profit will be zero and the company will “break even” and only cover its production costs.
What is CM ratio?
CM ratios and variable expense ratios are numbers that companies generally want to see to get an idea of how significant variable costs are.
How to calculate volume profit?
The cost volume profit analysis can help you estimate if your selling price can help you earn your desired profits. Determine the selling product of your price by evaluating your variable costs and net sales. Start by calculating the variable cost per unit by dividing your total variable costs for a period by the number of units produced during that period. For example, if you produced 100 tables in a month and your total variable costs were $10,000, your variable cost per unit would be $100.
What is cost volume profit analysis?
Cost volume profit analysis is a mathematical equation businesses apply to see how many units of a product they need to sell to gain a profit or cover costs. Some also refer to this as break-even analysis. Businesses use this formula to determine how the changes in fixed costs, variable costs and sales volume can contribute to the profits of a business.
How to calculate variable cost per unit?
Add these costs together to calculate the variable cost per unit. For example, the sock manufacturer may say they are taking $10 in direct material, $10 in direct labor and $20 in overhead to manufacture one set of socks. The variable cost per unit is $40, which is the sum of direct material, direct labor and variable manufacturing overhead.;
How to calculate contribution margin?
Determine your company's net sales, which is the money you earn for selling the product after subtracting discounts, returns and allowances. Use net sales and the total variable costs to determine the contribution margin per unit . Subtract the total variable costs from the total net sales, and divide this number by the number of units produced. For example, if you produced 200 lamps for a variable cost of $8,000 and net sales of $13,000, the contribution margin would be $5,000 with a contribution margin per unit of $25.
Why do businesses use cost volume profit analysis?
Many businesses use certain calculations to help managers carry out their responsibilities effectively . Cost volume profit analysis is a common method used to calculate future business revenues. The technique is effective in helping businesses plan well. In this article, we define what cost volume profit analysis is and how to it and provide an example of cost volume profit analysis.
How to find contribution margin ratio?
To find the contribution margin ratio, divide the contribution margin by the unit selling price. Here is the formula:
What is sales volume?
Sales volume: This is the quantity of products businesses sell during a specific period.
What is CVP analysis?
Cost-volume-profit (CVP) analysis is used to determine how changes in costs and volume affect a company’s operating income and net income.
How to calculate breakeven volume?
To calculate the breakeven sales volume, you need to first find the contribution margin and then divide fixed costs by contribution margin.
What is the breakeven point in cost accounting?
This method of cost accounting is used to look at the breakeven point or in other words, the number of units that need to be sold in order to break even and cover fixed costs.
How many units do you need to breakeven?
This tells us that in order to breakeven and cover our fixed costs, we need to produce at least 50 Units for the first product, 25 units for the second product, and 20 units for the third product:
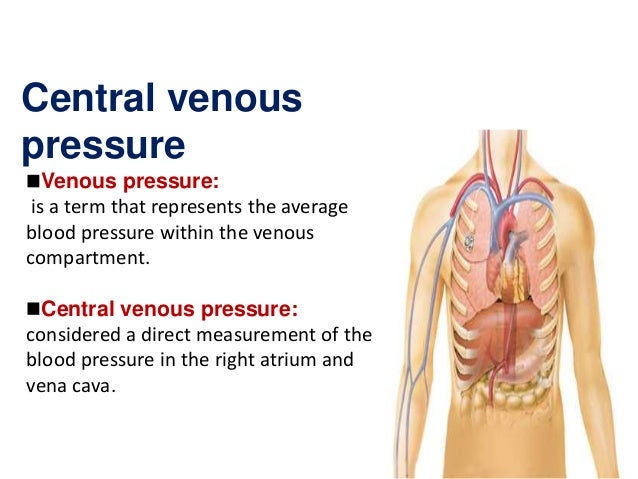
What is the CVP of the heart?
Central venous pressure (CVP) describes the pressure of blood in the thoracic vena cava, near the right atrium of the heart. CVP reflects the amount of blood returning to the heart and the ability of the heart to pump the blood into the arterial system.
How does the CVP read?
The reading is reflected by the height of a column of fluid in the manometer when there’s open communication between the catheter and the manometer. The fluid in the manometer will fluctuates slightly with the patient’s respirations. This confirms that the CVP is not obstructed by clotted blood.
What is a CVP site?
The CVP site is surgically cleansed. The physician, introduces the CVP catheter percutaneously or by direct venous cutdown and threaded through an antecubital, subclavian, or internal or external jugular vein into the superior vena cava just before it enters the right atrium.
How can CVP be inaccurate?
Serial CVP readings should be made with the patient in the same position. Inaccuracies in CVP readings can be produced by changes in positions, coughing, or straining during the reading.
What is change in CVP?
The change in CVP is a more useful indication of adequacy of venous blood volume and alterations of cardiovascular function. CVP is a dynamic measurement. The normal values may change from patient to patient. The management of the patient’s not based on one reading but on repeated serial readings in correlation with patient’s clinical status.
Where is intravascular pressure measured?
Intravascular pressures are measured to the atmospheric pressure at the middle of the right atrium; this is the zero point or external reference point. The zero point or baseline for the manometer should be on level with the patient’s right atrium.
Can you rely on CVP alone?
Nursing Alert: Don’t rely on CVP alone, use them in conjunction with other assessment data. Report abnormal findings to the doctor.
What is CVP in vivo?
In vivo, the CVP is a functional measure of right atrial and juxta-cardiac pressures (derived from pericardial and thoracic compartments) [7]
What is the normal pressure of the vena cava?
The central venous pressure can be measured using a central venous catheter advanced via the internal jugular vein and placed in the superior vena cava near the right atrium. A normal central venous pressure reading is between 8 to 12 mmHg. This value is altered by volume status and/or venous compliance. [1][2][3]
What causes the vena cavae to collapse?
A decrease in intrathoracic pressure caused by forced inspiration causes the vena cavae to collapse which decreases the venous return and, in turn, decreases the central venous pressure. Elevated Central Venous Pressure.
How is central venous pressure measured?
The central venous pressure is measured by a central venous catheter placed through either the subclavian or internal jugular veins. The central venous pressure can be monitored using a pressure transducer or amplifier. First, the transducer or amplifier must be zeroed to atmospheric pressure.
What is the purpose of central venous pressure?
Central venous pressure, which is a measure of pressure in the vena cava, can be used as an estimation of preload and right atrial pressure. Central venous pressure is often used as an assessment of hemodynamic status, particularly in the intensive care unit.
What is the role of central venous pressure in cardiac output?
The central venous pressure influences cardiac (left ventricle) output - this is driven by changes in central venous pressure which lead to changes in the filling pressures of the left heart.
What causes elevated venous pressure?
Elevated Central Venous Pressure can occur in heart failure due to decreased contractility, valve abnormalities, and dysrhythmias. Any patients on ventilator assistance that have excessive positive end-expiratory pressure would have an increase in pulmonary arterial resistance which causes an increase in central venous pressure. However, an increased central venous pressure caused by increased pulmonary arterial resistance can also be affected by a decrease in the fraction of inspired oxygen, an increase in ventilation/perfusion abnormalities in the lung, an increase in pericardial pressure, or an increase in intra-abdominal pressure which would increase thoracic pressure. Increased juxta-cardiac pressure - tension pneumothorax, pericardial tamponade, right ventricular infarct, right ventricular outflow obstruction - can also decrease venous return. [7]

What Is Cost-Volume-Profit (CVP) Analysis?
Understanding Cost-Volume-Profit (CVP) Analysis
- The cost-volume-profit analysis, also commonly known as breakeven analysis, looks to determine the breakeven point for different sales volumes and cost structures, which can be useful for managers making short-term business decisions. CVP analysis makes several assumptions, including that the sales price, fixed and variable costsper unit are consta...
Special Considerations
- CVP analysis is only reliable if costs are fixed within a specified production level. All units produced are assumed to be sold, and all fixed costs must be stable in CVP analysis. Another assumption is all changes in expenses occur because of changes in activity level. Semi-variable expenses must be split between expense classifications using the high-low method, scatter plot…
What Is Cost-Volume-Profit Analysis?
Example Cost-Volume-Profit Analysis
- Here is an example of how to calculate a cost-volume-profit analysis: Greg's Socks LLC calculated their fixed costs are $7,000 every month. The fixed costs include marketing, rent, insurance, salaries and raw materials. It costs $2.65 to produce a pair of socks and each pair sells for $8, earning a profit of $5.35 for each pair. Using the common formula, here's the cost-volume-profit …
Advantages of Using CVP Analysis
- The cost-volume-profit analysis offers advantages to help you make good business decisions. It is an effective method that helps accountants make decisions that help with future operations. Some advantages of using CVP analysis include: 1. Saves time:Helps accountants save time compared with other accounting analysis tools 2. Improves decision making:Helps managers m…