Cyclic electron flow around photosystem I is essential for photosynthesis
- Abstract. Photosynthesis provides at least two routes through which light energy can be used to generate a proton gradient across the thylakoid membrane of chloroplasts, which is subsequently used to ...
- Main. ...
- Methods. ...
- Acknowledgements. ...
- Author information. ...
- Ethics declarations. ...
- Supplementary information. ...
- Rights and permissions
- About this article. ...
- Comments. ...
What is the purpose of the cyclic electron flow?
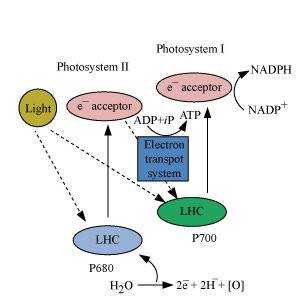
What is the purpose of cyclic electron flow? In higher plants, the generation of proton gradient across the thylakoid membrane (ΔpH) through cyclic electron flow (CEF) has mainly two functions: (1) to generate ATP and balance the ATP/NADPH energy budget, and (2) to protect photosystems I and II against photoinhibition.
Does cyclic electron flow use light?
In cyclic electron flow, light energy harvested at photosystem I is used for ATP synthesis rather than NADPH synthesis (Figure 10.23). Instead of being transferred to NADP+, high-energy electrons from photosystem I are transferred to the cytochrome bfcomplex.
What is linear and cyclic electron flow?
Linear electron flow is the electrons that pass through the two photosystems from water to NADP+. Cyclic electron flow are the electrons excited from P700 in PSI are passed from Fd to the cytochrome complex and back to P700. What does non cyclic electron flow produce?
What does the cyclic electron flow generate?
Cyclic Electron Flow It results in the production of ATP but not O2 or NADPH. Only photosystem I is present in this reaction. These reactions are meant to produce ATP from ADP and inorganic phosphate in a process called cyclic photophosphorylation by pumping protons across the thylakoid membrane.

Why is cyclic electron flow important for photosynthesis?
The role of cyclic electron transport around PS I is proposed to be essential for balancing the ATP/NADPH production ratio and/or for protecting both photosystems from the damage via stromal over-reduction1.
What makes cyclic electron flow?
0:232:51Cyclic Electron Flow - YouTubeYouTubeStart of suggested clipEnd of suggested clipThe electron gets excited to pick that by the primary electron acceptor. And so now it'll be passed.MoreThe electron gets excited to pick that by the primary electron acceptor. And so now it'll be passed. Still to ferredoxin. But from ferredoxin instead of going to et+ reductase.
Can cyclic electron flow support photosynthesis?
► Cyclic electron flow around Photosystem I has been shown to play an essential role in photosynthesis. ► Cyclic flow makes ATP and protects plants from stress by triggering non photochemical quenching.
What does cyclic electron flow in the chloroplast produce?
Linear electron transport in the thylakoid membrane drives photosynthetic NADPH and ATP production, while cyclic electron flow (CEF) around photosystem I only promotes the translocation of protons from stroma to thylakoid lumen.
What's the difference between cyclic and noncyclic electron flow?
The non-cyclic photophosphorylation involves both the photosystems and ATP and NADPH are produced, whereas cyclic photophosphorylation involves only PSI and only ATP is produced.
Does cyclic electron flow produce ATP?
Cyclically flowing electrons result in the production of ATP (because protons are pumped into the thylakoid lumen), but do not result in the production of NADPH (because electrons are not passed to NADP + ^+ +start superscript, plus, end superscript reductase).
What are the products of cyclic electron flow during the light reactions of photosynthesis?
~ATP, oxygen, and NADPH are the products of the light-dependent reactions. ATP is made from the ATP synthase complex as protons flow down a concentration gradient.