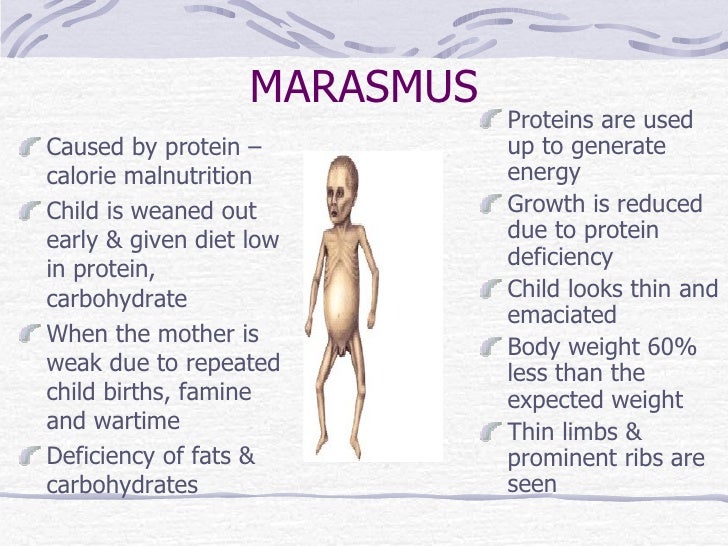
What is marasmus in children?
Marasmus. Marasmus is a form of severe malnutrition characterized by energy deficiency. It can occur in anyone with severe malnutrition but usually occurs in children. A child with marasmus looks emaciated. Body weight is reduced to less than 62% of the normal (expected) body weight for the age.
What is the prognosis of marasmus?
Marasmus is a manifestation of severe dietary malnutrition which occurs as a result of a calorie deficiency. Marasmus is associated with a better prognosis than kwashiorkor but it is still associated with relatively high mortality.
Can you get marasmus from not eating enough food?
Although marasmus in developed countries is quite rare, any person can get this condition if they are subject to a severe lack of nutrients. If someone isn't getting enough food due to an eating disorder, their body will be at risk of malnutrition. Like marasmus, kwashiorkor is a type of malnutrition caused by protein deficiency.
What are the risk factors of marasmus?
Marasmus is mainly caused by nutrient deficiency due to malnourishment. Here are some risk factors of marasmus: Poor diet. A nutrient-rich, balanced diet is important for growth, especially in children. If you have a poor diet that lacks essential nutrients, you may be at risk of developing marasmus. Food shortages.

Is marasmus a protein deficiency disease?
Marasmus is a severe manifestation of protein-energy malnutrition. It occurs as a result of total calorie insufficiency. This leads to overt loss of adipose tissue and muscle. The child may have a weight-for-height value that is more than 3 standard deviations below the average for age or sex.
What type of deficiency is kwashiorkor?
Kwashiorkor is a severe form of malnutrition. It's most common in some developing regions where babies and children do not get enough protein or other essential nutrients in their diet. The main sign of kwashiorkor is too much fluid in the body's tissues, which causes swelling under the skin (oedema).
What vitamin is deficient in kwashiorkor?
Vitamin A Deficiency in Kwashiorkor.
What causes marasmus in children?
Nutrient deficiency is the main cause of marasmus. It occurs in children that don't ingest enough protein, calories, carbohydrates, and other important nutrients. This is usually due to poverty and a scarcity of food. There are several types of malnutrition.
What is the difference between kwashiorkor and marasmus?
Kwashiorkor, a severe protein deficiency, causes fluid retention and a protruding abdomen. On the other hand, the condition marasmus, which results from severe calorie deficiency, leads to wasting and significant fat and muscle loss (5). Undernutrition can also result in micronutrient deficiencies.
Why is it called kwashiorkor?
The name is derived from the Ga language of coastal Ghana, translated as "the sickness the baby gets when the new baby comes" or "the disease of the deposed child", and reflecting the development of the condition in an older child who has been weaned from the breast when a younger sibling comes.
What is protein deficiency called?
kwashiorkor, also called protein malnutrition, condition caused by severe protein deficiency. Kwashiorkor is most often encountered in developing countries in which the diet is high in starch and low in proteins.
What are symptoms of marasmus?
Symptoms of MarasmusWeight loss.Stunted growth.Dry skin and eyes.Brittle hair.Diarrhea.Lower immunity.Stomach infection and lactose intolerance.Respiratory infections.More items...•
What are protein deficiency diseases?
The most common diseases as a result of protein deficiency are Kwashiorkor and Marasmus. Kwashiorkor is a protein deficiency disease that is manifested as edema and liver enlargement. Fatty infiltrations are also present. The disease is caused by deficiency caused due to less protein intake.
What is the causes of marasmus?
It results from an overall lack of calories. Marasmus is a deficiency of all macronutrients: carbohydrates, fats, and protein. If you have marasmus, you lack the fuel necessary to maintain normal body functions. People with marasmus are visibly depleted, severely underweight and emaciated.
When does marasmus occur?
Marasmus is a form of malnutrition. It happens when the intake of nutrients and energy is too low for a person's needs. It leads to wasting, or the loss of body fat and muscle. A child with marasmus may not grow as children usually do.
What causes kwashiorkor and marasmus?
Causes of marasmus and kwashiorkor The main cause of both of these conditions is a lack of access to food. Some things that may affect a person's access to food include: famine. a caregiver's inability to get food due to lack of transportation or a physical inability.
What is protein deficiency called?
kwashiorkor, also called protein malnutrition, condition caused by severe protein deficiency. Kwashiorkor is most often encountered in developing countries in which the diet is high in starch and low in proteins.
What is the protein deficiency disease?
Kwashiorkor, also known as “edematous malnutrition” because of its association with edema (fluid retention), is a nutritional disorder most often seen in regions experiencing famine. It is a form of malnutrition caused by a lack of protein in the diet.
What is a protein deficiency?
Summary: Protein deficiency is when people do not get adequate amounts of protein from their diet. Kwashiorkor, its most severe form, is most commonly seen in children in developing countries.
What is carbohydrate deficiency called?
When you don't get enough carbohydrates, the level of sugar in your blood may drop to below the normal range (70-99 mg/dL), causing hypoglycemia. Your body then starts to burn fat for energy, leading to ketosis. Symptoms of hypoglycemia include: Hunger.
What are the different types of malnutrition?
The different types of malnutrition include: Protein-Energy Malnutrition Micronutrient-deficiency Malnutrition
How is Marasmus caused?
Marasmus is caused due to the deficiency of nutrients such as protein, carbohydrates and calories. It mainly occurs due to poverty and food scarcity.
What are the symptoms of Marasmus?
Loss of body weight and muscles are the main symptoms of Marasmus. This leads to an extremely low body mass index (BMI). Other symptoms include diz...
How is Marasmus different from Kwashiorkor?
Marasmus is severe malnutrition characterized by energy deficiency. Kwashiorkor is a protein deficiency with adequate energy intake, whereas Marasm...
Which is the most common form of malnutrition?
Protein-Energy Malnutrition is the most common form of malnutrition. Marasmus and Kwashiorkor are two forms of protein-energy malnutrition.
Why is marasmus difficult to diagnose?
Marasmus is difficult to diagnose using blood tests. This is because many children with marasmus also have infections that can affect blood test results.
How to diagnose marasmus?
A doctor can often make a preliminary diagnosis of marasmus through a physical exam. Measurements, such as height and weight, can help determine whether a child has marasmus. When those measurements are well below the measurements that a healthy child of a particular age should have, marasmus may be the cause.
What are the symptoms of kwashiorkor?
intellectual disability. stunted growth. Seriously malnourished children may look older and have little to no energy or enthusiasm for anything. Marasmus can also make children short-tempered and irritable, but this is usually a more common symptom of kwashiorkor.
What is the treatment for marasmus?
Initial treatment of marasmus often includes dried skim milk powder mixed with boiled water. Later, the mixture can also include a vegetable oil such as sesame, casein, and sugar. Casein is milk protein. The oil increases the energy content and density of the mixture.
What are the different types of malnutrition?
There are several types of malnutrition. A malnourished child may have something other than marasmus. Among the more common types of malnutrition are serious deficiencies in: 1 iron 2 iodine 3 zinc 4 vitamin A
What are the symptoms of marasmus?
Symptoms of marasmus. The main symptom of marasmus is being underweight. Children with this condition have lost a lot of muscle mass and subcutaneous fat. Subcutaneous fat is the layer of fat just under the skin. Dry skin and brittle hair are also symptoms of marasmus.
What can relief workers do to help children with marasmus?
With proper nutrition and medical care, the outlook can be a positive one. Relief workers can provide food and healthcare to regions where marasmus and other malnutrition problems are common. The best outcomes occur when a child’s parents or guardians know about the importance of nutrition and how to prepare foods properly.
What is marasmus associated with?
The child will be less than 60% of the weight for age. Long-standing marasmus is associated with growth stunting; this may lead to the weight for height being within the normal range. Marasmus is frequently associated with symptoms of anemia and rickets. As marasmus progresses, several body systems may be affected.
What causes marasmus in children?
The underlying social cause of marasmus in children is poverty. [4][3] Poverty may occur as a result of low status and insufficient education of mothers along with war, natural disasters, and civil instability. Poverty directly influences the ability of a household to secure a reliable source of food for children leading to an insufficient calorie supply. Unstable and unreliable childcare may occur in mothers that are unable to care for their children as a result of displacement, along with an unhygienic environment; this contributes to a higher frequency of infections such as diarrhea. In particular, the HIV/AIDS epidemic has been shown to create a significant burden of disease in South African households leading to reduced viability of agrarian livelihoods. [5]
What is marasmus 2021?
Last Update: February 6, 2021. Continuing Education Activity. Marasmus is a manifestation of severe dietary malnutrition which occurs as a result of a calorie deficiency. Marasmus is associated with a better prognosis than kwashiorkor but it is still associated with relatively high mortality. As such, it is important to know how to prevent ...
Why does marasmus cause pitting?
A child with marasmus may develop pitting edema due to protein insufficiency , this is known as marasmic-kwashiorkor. This article will review the etiology, epidemiology, history, evaluation, and management of marasmus. Etiology. The underlying cause of marasmus is insufficient total calorie intake.[2] .
What is the term for an inadequate weight relative to vertical height?
Acute malnutrition is an inadequate weight relative to vertical height. Severe acute malnutrition is further divided into two main categories: marasmus and kwashiorkor. Chronic malnutrition, otherwise known as growth stunting, is characterized by linear growth (length/height) below the average for age.
Why do infants have sunken fontanelles?
In infants, it may be associated with irritability and apathy. Furthermore, infants may have sunken fontanelles as a result of dehydration. The general appearance is shrunken and wasted due to reduced levels of subcutaneous fat.[24] .
Is marasmus a Gram negative infection?
In particular, infection with Gram-negative organisms is associated with marasmus. Infections of the urinary, gastrointestinal, and respiratory tracts are associated with marasmus; however, patients suffering from marasmus may not present with the typical features of an infection such as fever.
What causes marasmus in children?
This can lead to a low intake of essential nutrients in infected children and adults. Diseases such as HIV/AIDS and malaria in rural areas can cause marasmus.
What are the symptoms of marasmus?
The most common symptom of marasmus is being underweight due to malnourishment. The following symptoms can occur due to deficiency, dehydration, electrolyte imbalance, or infection if marasmus remains untreated for a long time:. Weight loss. Stunted growth.
How to tell if a child has marasmus or kwashiorkor?
Doctors can differentiate kwashiorkor from marasmus by the presence of edema or swelling. But some children may show symptoms of both. This is known as marasmic kwashiorkor.
How to tell if you have marasmus?
Severe protein and calorie deficiency in children can result in loss of fat and muscle mass. The most common symptom of marasmus is being underweight due to malnourishment. The following symptoms can occur due to deficiency, dehydration, electrolyte imbalance, or infection if marasmus remains untreated for a long time: 1 Weight loss 2 Stunted growth 3 Dry skin and eyes 4 Brittle hair 5 Diarrhea 6 Lower immunity 7 Stomach infection and lactose intolerance 8 Respiratory infections 9 Rickets due to calcium and vitamin D deficiency 10 Anemia due to iron deficiency 11 Impaired brain function and intellectual disability 12 Low blood pressure or hypotension 13 Low body temperature or hypothermia 14 Slow heart rate or bradycardia
Why do people get marasmus?
You can get marasmus if you have a severe deficiency of nutrients like calories, proteins, carbohydrates, vitamins, and minerals. . It is more common in developing countries, like in some areas of Asia and Africa. People in these nations are prone to having poor access to food, making it difficult to get enough nutrients.
Why do children have marasmus?
A lack of food and nutrients can cause both the body and mind to suffer. Children with severe marasmus tend to appear tired and bored. They are always low in energy and enthusiasm. Such children are often irritable, short-tempered, and uninterested in things. This symptom can be confused as a sign of kwashiorkor, which is another type of malnutrition.
What are the risks of marasmus?
If you have a poor diet that lacks essential nutrients, you may be at risk of developing marasmus. . Food shortages. Marasmus is more common in developing countries that have high poverty and lack of food. These regions also have frequent famines and natural disasters, resulting in food shortages.
What is the disease of Marasmus?
Marasmus. There are different types of nutrition deficiency diseases which occur both in children and in adults. This nutrition deficiency disorder is also called as the Malnutrition. The deficiency diseases are mainly seen in developing countries, areas with high rates of poverty or individuals who have very poor knowledge about ...
How to treat marasmus?
Treatment for Marasmus. The first and primary treatment prescribed for the patient suffering from marasmus includes: Multivitamin supplements to improve appetite and nutrition deficiency. Dehydration symptoms can be prevented by the intake of water and other fluids that contain electrolytes.
How long does it take to recover from Marasmus?
Complete recovery can take a month together even with proper diet and medication.
Why do people get marasmus?
Other causes of marasmus include: Poverty. Starvation. Famine or unavailability of food. Lack of education about nutritional requirements.
What are the symptoms of marasmus?
The symptoms of marasmus are more common to the symptoms of kwashiorkor, which includes: Weight loss. Dehydration. Stunted growth. Chronic Diarrhoea. Shrinkage of Stomach. Respiratory infections. Dry skin and brittle hair.
Why are people living in developing countries at risk of contracting marasmus?
The people living in developing countries are more at risk of contracting marasmus. The famine and poverty struck areas have a larger percentage of children suffering from marasmus. If the infants are not breastfed by nursing mothers due to malnutrition, the risk of marasmus increases in children.
What is the most common form of malnutrition?
Protein-Energy Malnutrition is the most common form of malnutrition. Marasmus and Kwashiorkor are two forms of protein-energy malnutrition.
Why does marasmus not grow?
It leads to wasting, or the loss of body fat and muscle. A child with marasmus may not grow as children usually do. Malnutrition happens when a lack of nutrients causes health problems, usually because a person’s diet does not contain all ...
What is the primary symptom of marasmus?
The primary symptom of marasmus is an acute loss of body fat and muscle tissues, leading to an unusually low body mass index ( BMI ). Marasmus is a type of wasting. In a child, the main symptom of marasmus is a failure to grow, known as stunted growth.
How much weight can a child with marasmus kwashiorkor lose?
In children with marasmus kwashiorkor, the weight will be less than 60 percent of the standard weight for their age. Immediate medical treatment is essential. As the condition progresses, recovery becomes more difficult, and the chances of survival reduce.
Why is marasmus so hard to recover?
Poor sanitation and hygiene can lead to infections that can worsen the symptoms of marasmus and other types of malnutrition and make it harder to recover.
What is the name of the condition where the body retains fluid in the lower legs, feet, arms, and hands?
Kwashiorkor. Kwashiorkor is another severe form of protein-energy malnutrition where the main deficiency is protein. Severe cases of malnutrition can lead to kwashiorkor. Unlike marasmus, kwashiorkor causes the body to retain fluid in the lower legs, feet, arms, hands, and face, leading to a swollen appearance.
What are the long term effects of marasmus?
dry skin. brittle hair. Apart from weight loss, long-term effects of marasmus in children include slow growth and repeated infections. Diarrhea, measles, or a respiratory infection are serious complications that can be fatal in a child with marasmus. Diarrhea can also be a contributing cause of marasmus.
Why do some people develop marasmus?
According to the FAO, it remains unclear why some people develop marasmus, and others develop kwashiorkor.
What is marasmus in medical terms?
Critical care medicine. Marasmus is a form of severe malnutrition characterized by energy deficiency. It can occur in anyone with severe malnutrition but usually occurs in children. Body weight is reduced to less than 62% of the normal (expected) body weight for the age. Marasmus occurrence increases prior to age 1, ...
What are the symptoms of marasmus?
Edema is not a sign of marasmus and is present in only kwashiorkor and marasmic kwashiorkor. Other symptoms of marasmus include unusual body temperature (hypothermia, pyrexia); anemia; dehydration (as characterized with consistent thirst and shrunken eyes); hypovolemic shock (weak radial pulse; cold extremities; decreased consciousness); tachypnea ( pneumonia, heart failure); abdominal manifestations (distension, decreased or metallic bowel sounds; large or small liver; blood or mucus in the stools), ocular manifestations (corneal lesions associated with vitamin A deficiency); dermal manifestations (evidence of infection, purpura, and ear, nose, and throat symptoms (otitis, rhinitis). Dry skin and brittle hair are also symptoms of marasmus. Marasmus can also make children short-tempered and irritable.
How to treat marasmus in children?
Once the child tolerates the milk, a vegetable mix can be added including sesame, casein, and sugar. Refeeding must be done slowly to avoid refeeding syndrome. Once children start to recover, they should have more balanced diets which meet their nutritional needs. Children with marasmus commonly develop infections and are consequently treated with antibiotics or other medications. Ultimately, marasmus can progress to the point of no return when the body's ability for protein synthesis is lost. At this point, attempts to correct the disorder by giving food or protein are futile.
How many deaths from marasmus in the US in 1995?
In 1995, there were only 228 deaths caused by marasmus in the U.S., of which only 3 were children. In 2016, the prevalence of marasmus in the United States was 0.5%. Prevalence is higher in hospitalized children, especially ones with chronic illnesses, however an exact incidence of nonfatal marasmus is not known.
Why is marasmus more common in children?
Marasmus is more commonly seen in children under the age of 5 due to that age range being characterized as one that has an increase in energy need and susceptibility to viral and bacterial infections. The World Health Organization also identifies the elderly as another population that is vulnerable to malnutrition. Because their nutritional requirement is not well defined, attempts to provide them with the necessary nutrition becomes difficult.
How many children are under 5 years old with malnutrition?
There are multiple forms of malnutrition and roughly 1/3 of the world’s population is currently experiencing one or more of them. There are around 50 million children less than 5 years old who have protein-energy malnutrition.
Where does the word "marasmus" come from?
The word "marasmus" comes from the Greek μαρασμός marasmos ("withering").
What is marasmus in children?
Marasmus occurs more often in young children and babies. It leads to dehydration and weight loss. Starvation is a form of this disorder. The symptoms of marasmus include: You’re at an increased risk for marasmus if you live in a rural area where it’s difficult to get food or an area that has a food shortage.
What causes marasmus and kwashiorkor?
Causes of marasmus and kwashiorkor. The main cause of both of these conditions is a lack of access to food. Some things that may affect a person’s access to food include: famine. a caregiver’s inability to get food due to lack of transportation or a physical inability. living in poverty.
What happens if you don't consume enough nutrients?
When you don’t consume enough nutrients, your body becomes malnourished. One type of malnourishment is protein-energy undernutrition. Protein-energy undernutrition is sometimes called protein-energy malnutrition. You have this if your body has a severe calorie or protein deficiency.
Can you get kwashiorkor if you are weaned off breast milk?
You’re at an increased risk for kwashiorkor if you live in a rural area where there’s limited access to protein-rich foods. Children who have been weaned off of breast milk are also at an increased risk if they don’t have access to protein-rich foods. Marasmus symptoms. Kwashiorkor symptoms. weight loss.
Can you get marasmus from a rural area?
You’re at an increased risk for marasmus if you live in a rural area where it’s difficult to get food or an area that has a food shortage. Babies, including babies who aren’t breast-fed, young children, or older adults also have an increased risk for marasmus.