What does cell body do in the nervous system?
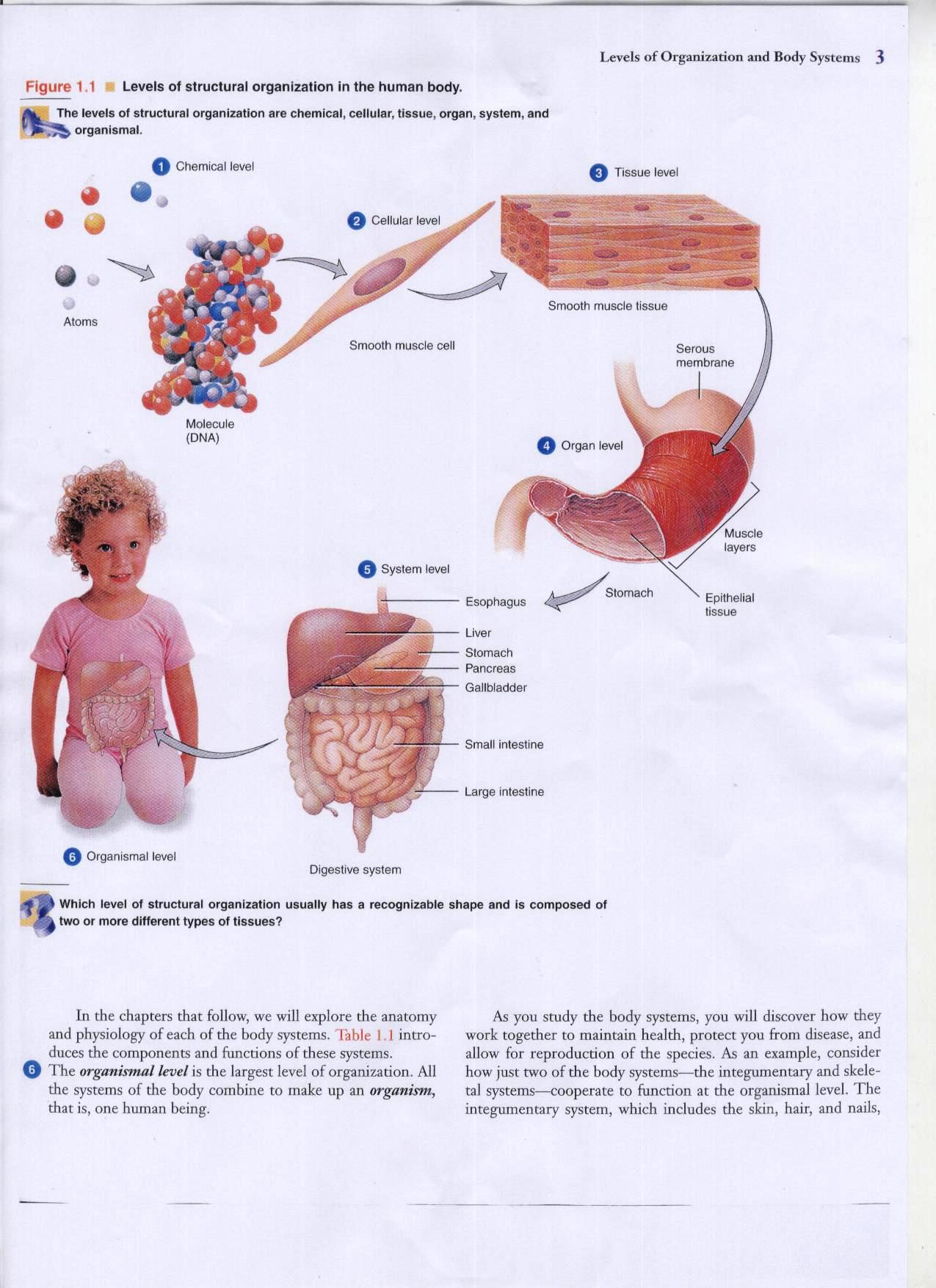
The human body is made up of trillions of cells. Cells of the nervous system, called nerve cells or neurons, are specialized to carry "messages" through an electrochemical process. The human brain has approximately 86 billion neurons. To learn how neurons carry messages, read about the action potential.
What do the cells do in a human body?
The majority of the cells in our body use glucose to break down and use for energy. The organ that metabolizes the fructose we eat is the liver. By clicking “Check Writers’ Offers”, you agree to our terms of service and privacy policy. We’ll occasionally send you promo and account related email
What is the definition of cell body in psychology?
Psychology Definition of CELL BODY: n. that part of the neuron (nerve cell) including the nucleus and its surrounding cytoplasm, but excluding the axon and dendrites.
What cells are the body cell of an organism?
Types of Cells in the Human Body. Adult human beings are made up of around 37 trillion individual cells, and approximately 200 different types of cells. Some key cell types of the human body include stem cells, muscle cells, blood cells, bone cells, nerve cells, fat cells, sperm cells, and egg cells. The human body contains about 200 different ...
What's the best definition of a cell?
What is a cell? A cell is a mass of cytoplasm that is bound externally by a cell membrane. Usually microscopic in size, cells are the smallest structural units of living matter and compose all living things. Most cells have one or more nuclei and other organelles that carry out a variety of tasks.
What is an example of a cell body?
For example, A tire can be a cell body because it is sturdy and able to contain fluid (as long as it is laying flat).
What is another word for body cells?
somatic cell Add to list Share. A somatic cell is any cell that makes up an organism, except for a reproductive cell. For example, the cells that make up your skin are all somatic cells.
How many cells are in our body?
37.2 trillion cells. This is not a final number, but it's a very good start. While it's true that people may vary in size–and thus vary in their number of cells–adult humans don't vary by orders of magnitude except in the movies.
What are the 4 types of cells?
The Four Main Types of CellsEpithelial Cells. These cells are tightly attached to one another. ... Nerve Cells. These cells are specialized for communication. ... Muscle Cells. These cells are specialized for contraction. ... Connective Tissue Cells.
What are the cell types?
There are two distinct types of cells: prokaryotic cells and eukaryotic cells. Though the structures of prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells differ (see prokaryote, eukaryote), their molecular compositions and activities are very similar. The chief molecules in cells are nucleic acids, proteins, and polysaccharides.
Is the term for the cells of the body?
Somatic Cells Somatic cells are the cells in the body other than sperm and egg cells (which are called germ cells).
What is the other name of new cell?
Answer and Explanation: The name given to new cells created at the end of cell division is daughter cells. At the end of cell division, the parent cell (dividing cell) will undergo each of the mitotic stages in order to produce two genetically identical (containing the same DNA as the parent cell) daughter cells.
What makes up the cell body?
A cell consists of a nucleus and cytoplasm and is contained within the cell membrane, which regulates what passes in and out. The nucleus contains chromosomes, which are the cell's genetic material, and a nucleolus, which produces ribosomes.
What are the parts of the cell body?
A cell consists of three parts: the cell membrane, the nucleus, and, between the two, the cytoplasm. Within the cytoplasm lie intricate arrangements of fine fibers and hundreds or even thousands of miniscule but distinct structures called organelles.
Which of the following is a part of cell body?
The cell body contains cytoplasm and nucleus. Dendrites are the smaller branches arising from the cell body. They connect with dendrites of other cells and transfer the signal. The axon carries the nerve impulses away from the cell body.
What is difference between cell body and cytoplasm?
The cytoplasm is mainly composed of water, salt, and proteins. In Eukaryotic cells, all organelles are located in cytoplasms such as the nucleus, endoplasmic reticulum, and mitochondria....Difference Between Cytoplasm and Protoplasm.CytoplasmProtoplasmThe cytoplasm is a part of the Protoplasm.Cytoplasm is included in protoplasm.9 more rows
What are the parts of a cell called?
Cells have many parts, each with a different function. Some of these parts, called organelles, are specialized structures that perform certain tasks within the cell. Human cells contain the following major parts, listed in alphabetical order:
Which organelle processes the cell's genetic instructions to create proteins?
Ribosomes are organelles that process the cell’s genetic instructions to create proteins. These organelles can float freely in the cytoplasm or be connected to the endoplasmic reticulum (see above).
What is the function of the nucleus?
The nucleus serves as the cell’s command center, sending directions to the cell to grow, mature, divide, or die. It also houses DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid), the cell’s hereditary material. The nucleus is surrounded by a membrane called the nuclear envelope, which protects the DNA and separates the nucleus from the rest of the cell.
What is the cytoplasm made of?
Within cells, the cytoplasm is made up of a jelly-like fluid (called the cytosol) and other structures that surround the nucleus.
Which apparatus packages molecules processed by the endoplasmic reticulum to be transported out of the cell?
The Golgi apparatus packages molecules processed by the endoplasmic reticulum to be transported out of the cell.
Which organelle converts food into energy?
Mitochondria. Mitochondria are complex organelles that convert energy from food into a form that the cell can use. They have their own genetic material, separate from the DNA in the nucleus, and can make copies of themselves.
What are the building blocks of all living things?
Cells are the basic building blocks of all living things. The human body is composed of trillions of cells . They provide structure for the body, take in nutrients from food, convert those nutrients into energy, and carry out specialized functions. Cells also contain the body’s hereditary material and can make copies of themselves.
What is the cell body?
The Cell Body. The cell body, also called the soma, is the spherical part of the neuron that contains the nucleus. The cell body connects to the dendrites, which bring information to the neuron, and the axon, which sends information to other neurons. When information is received from another neuron, the dendrites pass the signal to the cell body.
What are the building blocks of a cell?
Proteins are the building blocks of the cell. They allow neurons to build new axons and dendrites to make new connections with other neurons, and they make the chemicals that neurons need to send signals. The cell body is the manufacturing plant for these very important compounds. A.
What Is a Neuron?
Your brain is made up of millions of cells called neurons. Neurons make connections with each other to create pathways that control all aspects of life, such as bodily functions, emotions, and movement. Each neuron is composed of three parts: the cell body, dendrites, and an axon. Today, we'll look more closely at the cell body.
What organelle makes ribosomes?
The nucleus also contains the nucleolus, which makes ribosomes needed for protein production. In addition to ribosomes, the cell body also contains the endoplasmic reticulum and the Golgi apparatus. These organelles all work together to help make, package, and sort proteins to the other parts of the cell.
Which organelle connects information to the neuron and the axon?
Dendrites: connects information to the neuron and the axon. Axon: the connector of information to other neurons. Organelles: tiny organs in cells with specific job duties. Nucleus: the important organelle that holds a cell's DNA. Bipolar neurons: cell body in the middle with an axon and a dendrite on each end.
What is the most important organelle in the cell?
The most important organelle in the cell body is the nucleus . The nucleus contains the cell's DNA and regulates all processes in the cell. The cell needs DNA to act as a blueprint to direct cellular activity. The nucleus also contains the nucleolus, which makes ribosomes needed for protein production.
Which organelle contains the DNA?
The nucleus is the most important organelle and contains the cell's DNA and regulates all processes in the cell. The cell body also contains the endoplasmic reticulum and the Golgi apparatus. There are more than one type of neuron and, thus, more than one type of cell body. Some types of neurons include:
What is the Cell Body?
The cell body (AKA the soma) is one of the three main parts of a nerve cell (or neuron ). It’s the rounded, bulbous part of the cell that houses the nucleus, along with other key organelles like the endoplasmic reticulum, ribosomes, mitochondria, and Golgi apparatus.
Which part of the cell is responsible for receiving electrical signals from other neurons?
The cell body is connected to the dendrites, which project outwards from the soma and receive chemical signals from other neurons. They convert these chemical signals to electrical impulses before transmitting them to the cell body. The axon is a long extension that carries nerve impulses away from the cell body.
What organelle controls the firing of signals?
These organelles carry out all the functions necessary for the survival of the neuron, including protein synthesis, respiration, and other key metabolic functions. At one end of the soma is a specialized structure called the axon hillock. This connects the nerve cell body to the axon and controls the firing of signals (or action potentials) ...
What is the role of neurons in the human body?
The key role of neurons is to receive information from cells (via their dendrites) and pass this information on to other cells (through the axon ). There are three different types of nerve cells in the human body. These are the sensory neurons, motor neurons, and interneurons. There are three types of neurons in the human body.
Which cell contains the DNA blueprints of all the cell's proteins?
The nerve cell body contains the nucleus and, therefore, all the genetic information of the neuron. The nucleus directs all cellular activity and contains the DNA blueprints of all the cell’s proteins.
What is the axon?
The axon is a long extension that carries nerve impulses away from the cell body. The information is transmitted to other neurons, muscle cells, and organs via the axon terminals at the end of the axon. The cell body is one of the three main parts of a nerve cell.
What is a Cell?
A cell is the structural and fundamental unit of life. The study of cells from its basic structure to the functions of every cell organelle is called Cell Biology. Robert Hooke was the first Biologist who discovered cells.
How big are cells?
Cells are the fundamental unit of life. They range in size from 0.0001 mm to nearly 150 mm across
How is the cell interior organized?
The cell interior is organised into different individual organelles surrounded by a separate membrane.
Why are cells considered the structural and functional unit of life?
Meiosis causes the daughter cells to be genetically different from the parent cells. Thus, we can understand why cells are known as the structural and functional unit of life. This is because they are responsible for providing structure to the organisms and performs several functions necessary for carrying out life’s processes.
Why is the discovery of cells important?
Discovery of cells is one of the remarkable advancements in the field of science. It helps us know that all the organisms are made up of cells, and these cells help in carrying out various life processes. The structure and functions of cells helped us to understand life in a better way.
Which cell type has a nucleus?
Eukaryotic cells are characterised by a true nucleus.
Which structure controls the exit and entry of molecules into the cell?
Cell membrane. It is a selectively permeable structure that controls the exit and entry of molecules into the cell.
How do cells work?
In order to accomplish them, they must have: A cell membrane that separates the inside of the cell from the outside. By concentrating the chemical reactions of life inside a small area within a membrane, cells allow the reactions of life to proceed much faster than they otherwise would.
Which cell type is the most modern?
Eukaryotic cells are thought to be the most modern major cell type. All multicellular organisms, including you, your cat, and your houseplants, are eukaryotes. Eukaryotic cells seem to have “learned” to work together to create multicellular organisms, while prokaryotes seem unable to do this.
How many chromosomes are in an eukaryotic cell?
Eukaryotic cells usually have more than one chromosome, which contains large amounts of genetic information. Within the body of a multicellular organism, different genes within these chromosomes may be switched “on” and “off,” allowing for cells that have different traits and perform different functions within the same organism.
What are the characteristics of all living organisms?
Defining characteristics that allow a cell to perform these functions include: A cell membrane that keeps the chemical reactions of life together.
What material is capable of passing on traits to the cell's offspring?
Genetic material which is capable of passing on traits to the cell’s offspring. In order to reproduce, organisms must ensure that their offspring have all the information that they need to be able to carry out all the functions of life.All modern cells accomplish this using DNA, whose base-pairing properties allow cells to make accurate copies of a cell’s “blueprints” and “operating system.” Some scientists think that the first cells might have used RNA instead.
Why do plants have a cell wall?
In addition to having chloroplasts, plant cells also typically have a cell wall made of a rigid sugars, to enable plant tissues to maintain their upright structures such as leaves, stems, and tree trunks.
Which cell has multiple chromosomes?
Eukaryotes – Complex cells with multiple chromosomes and internal organelles such as mitochondria, chloroplasts, and nuclei.
Why are neuron cells important?
Neurons are important because they facilitate communication throughout the bodies of animals. Neurons allow animals to detect changes in both their external and internal environment and allow for changes to movement and body function ...
What is the function of the soma cell?
The nucleus is located roughly in the center of the cell body and is surrounded by endoplasmic reticulum that is continuous with the nuclear membrane. The main function of the nucleus is to store DNA. DNA is the genetic material for the cell and holds all the information about the cells structure and function. It can be used during DNA replication which is required for cell division and during transcription, which makes the mRNA instructions needed to do translation and create proteins.
What does it mean to enroll in a course?
Enrolling in a course lets you earn progress by passing quizzes and exams.
What is a single cell?
A single cell is often a complete organism in itself, such as a bacterium or yeast. Other cells acquire specialized functions as they mature. These cells cooperate with other specialized cells and become the building blocks of large multicellular organisms, such as humans and other animals.
How do cells contribute to life?
It can be viewed as an enclosed vessel, within which innumerable chemical reactions take place simultaneously. These reactions are under very precise control so that they contribute to the life and procreation of the cell. In a multicellular organism, cells become specialized to perform different functions through the process of differentiation. In order to do this, each cell keeps in constant communication with its neighbours. As it receives nutrients from and expels wastes into its surroundings, it adheres to and cooperates with other cells. Cooperative assemblies of similar cells form tissues, and a cooperation between tissues in turn forms organs, which carry out the functions necessary to sustain the life of an organism.
How do cells reproduce?
Cells contain a special collection of molecules that are enclosed by a membrane. These molecules give cells the ability to grow and reproduce. The overall process of cellular reproduction occurs in two steps: cell growth and cell division. During cell growth, the cell ingests certain molecules from its surroundings by selectively carrying them through its cell membrane. Once inside the cell, these molecules are subjected to the action of highly specialized, large, elaborately folded molecules called enzymes. Enzymes act as catalysts by binding to ingested molecules and regulating the rate at which they are chemically altered. These chemical alterations make the molecules more useful to the cell. Unlike the ingested molecules, catalysts are not chemically altered themselves during the reaction, allowing one catalyst to regulate a specific chemical reaction in many molecules.
What is the basic unit of life?
Cells are the basic units of life. Encyclopædia Britannica, Inc. See all videos for this article. cell, in biology, the basic membrane-bound unit that contains the fundamental molecules of life and of which all living things are composed. A single cell is often a complete organism in itself, such as a bacterium or yeast.
Why are cell reactions so precise?
These reactions are under very precise control so that they contribute to the life and procreation of the cell. In a multicellular organism, cells become specialized to perform different functions through the process of differentiation. In order to do this, each cell keeps in constant communication with its neighbours.
What is the smallest cell in the world?
The smallest known cells are a group of tiny bacteria called mycoplasmas; some of these single-celled organisms are spheres as small as 0.2 μm in diameter (1μm = about 0.000039 inch), with a total mass of 10 −14 gram—equal to that of 8,000,000,000 hydrogen atoms. Cells of humans typically have a mass 400,000 times larger than the mass ...
Which organelle is smaller, prokaryotic or eukaryotic?
Specialized organelles are a characteristic of cells of organisms known as eukaryotes. In contrast, cells of organisms known as prokaryotes do not contain organelles and are generally smaller than eukaryotic cells. However, all cells share strong similarities in biochemical function.

What Is The Cell body?
- The cell body (AKA the soma) is one of the three main parts of a nerve cell (or neuron). It’s the rounded, bulbous part of the cell that houses the nucleus, along with other key organelles like the endoplasmic reticulum, ribosomes, mitochondria, and Golgi apparatus. The cell body is connected to the dendrites, which project outwards from the soma a...
Structure of The Cell Body
- The cell body is the spherical part of a neuron that contains the nucleus and other major organelles. It is surrounded by a plasma membrane and contains key structures common to most other cells, including cytoplasm, mitochondria, endoplasmic reticulum, ribosomes, Golgi apparatus, lysosomes, endosomes, and peroxisomes. These organelles carry out all the function…
The Function of The Cell Body
- The nerve cell body contains the nucleus and, therefore, all the genetic information of the neuron. The nucleus directs all cellular activity and contains the DNA blueprints of all the cell’s proteins. The cell body also contains ribosomes and is the site of virtually all protein production in the neuron (although some proteins are also produced in the dendrites). Therefore, the soma provid…
The Function of Neurons
- The cell body is a key structural component of neurons which are the basic functional units of the nervous system. The key role of neurons is to receive information from cells (via their dendrites) and pass this information on to other cells (through the axon). There are three different types of nerve cells in the human body. These are the sensory neurons, motor neurons, and interneurons…