
- The Commutative property states that " changing the order of the operands does not change the result."
- The commutative property for addition is A + B = B + A
- The commutative property for multiplication is A × B = B × A
Full Answer
What daily activity is an example of a commutative property?
What daily activity is an example of a commutative property? Essentially nothing in real life ever commute, but sometimes the non-commutativity is small enough that we can ignore it with little consequence. The example given by Jake is obviously an extremely good one and a very classical one.
Would you please Show Me an example of commutative property?
They are the commutative, associative, multiplicative identity and distributive properties. Commutative property: When two numbers are multiplied together, the product is the same regardless of the order of the multiplicands. For example 4 * 2 = 2 * 4
What are some examples of commutative properties?
What are the three properties of multiplication?
- Commutative Property.
- Associative Property.
- Distributive Property.
How do you use the commutative property?
Properties of Addition: Properties, Examples, Problems
- Define Properties of Addition. Properties of addition are defined for the different conditions and rules of addition. ...
- Rules for Addition. Suppose two positive or two negative integers/numbers are added. ...
- Properties of Addition. ...
- Solved Example Problems on Properties of Addition. ...
- Summary. ...
- Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) on Properties of Addition. ...

What is the commutative property simple definition?
This law simply states that with addition and multiplication of numbers, you can change the order of the numbers in the problem and it will not affect the answer.
What is an example of a commutative property in math?
Commutative property of multiplication: Changing the order of factors does not change the product. For example, 4 × 3 = 3 × 4 4 \times 3 = 3 \times 4 4×3=3×44, times, 3, equals, 3, times, 4. Associative property of multiplication: Changing the grouping of factors does not change the product.
What is the definition of commutative property class 7?
The commutative property states that the numbers on which we operate can be moved or swapped from their position without making any difference to the answer. The property holds for Addition and Multiplication, but not for subtraction and division.
What is the meaning of commutative in math?
: being a property of a mathematical operation (as addition or multiplication) in which the result does not depend on the order of the elements The commutative property of addition states that 1 + 2 and 2 + 1 will both have a sum of 3.
What is the commutative property for kids?
The commutative property of multiplication says that you can multiply numbers in any order and the answer will always be the same.
What is associative property example?
The associative property of multiplication states that the product of three or more numbers remains the same regardless of how the numbers are grouped. For example, 3 × (5 × 6) = (3 × 5) × 6. Here, no matter how the numbers are grouped, the product of both the expressions remains 90.
What is commutative property maths class 8?
In Mathematics, a commutative property states that if the position of integers are moved around or interchanged while performing addition or multiplication operations, then the answer remains the same.
How do you write commutative property?
The commutative property states that the change in the order of two numbers in an addition or multiplication operation does not change the sum or the product. The commutative property of addition is written as A + B = B + A. The commutative property of multiplication is written as A × B = B × A.
What is associative property maths class 8?
This property states that when three or more numbers are added (or multiplied), the sum (or the product) is the same regardless of the grouping of the addends (or the multiplicands).
What is commutative property addition?
The commutative property of addition says that changing the order of addends does not change the sum. Here's an example: 4 + 2 = 2 + 4 4 + 2 = 2 + 4 4+2=2+4.
What is the definition of associative property of addition?
What is Associative Property of Addition? To “associate” means to connect or join with something. According to the associative property of addition, the sum of three or more numbers remains the same regardless of how the numbers are grouped.
Q.1. What is commutative property? Explain it by an example.
Ans: The sum or the product of two numbers is said to be commutative for addition or multiplication if their sum or the product remains the same ev...
Q.2.What is the formula for commutative and associative property?
Ans: The formula for the commutative property over addition is A+B=B+A when A and B are operands. The formula for the commutative property over mul...
Q.3.What is the commutative property of addition?
Ans: According to the commutative property, if the sum of two numbers is said to be commutative for addition if their sum remains the same even if...
What is Commutative Property?
The sum or the product of two numbers is said to be commutative for addition or multiplication if their sum or the product remains the same even if the order of the addition or multiplication is changed, respectively.
Commutative Property Over Addition
Commutative property over addition says the sum of two numbers is said to be commutative for addition if their sum remains the same even if the order of the addition is changed. Consider the following table where A and B are natural numbers,
Commutative Property Over Addition Formula
The commutative property says if A and B be the operands, then changing its position does not change the result of the addition. Therefore, A + B = B + A.
Commutative Property Over Multiplication
Commutative property over multiplication says if the product two whole numbers or integers is said to be commutative for multiplication if their product remains the same even if the order of the multiplication is changed. Consider the following table where A and B are natural numbers,
Commutative Property Over Multiplication Formula
The commutative property says if A and B be the operands, then changing its position does not change the result of the multiplication. Therefore, A × B = B × A.
Commutative Property Over Subtraction
Let us see whether the commutative property is applicable to the subtraction of numbers or not.
Commutative Property Over Division
Let us see whether the commutative property is applicable to the division of numbers or not. Let’s take two integers − 2 and 4.
What is the commutative property of multiplication?
Commutative Property of Multiplication says that the order of factors in a multiplication sentence has no effect on the product. The Commutative Property of Multiplication works on integers, fractions, decimals, exponents, and algebraic equations. The word “commutative” comes from a Latin root meaning “interchangeable”.
What does "commutative" mean in math?
The word “commutative” comes from a Latin root meaning “interchangeable”. Switching the order of the multiplicand (the first factor) and the multiplier (the second factor) does not change the product. What is 4 × 5 4 × 5? The answer is 20 20.
What is the commutative property of integers?
As we already discussed in the introduction, as per the commutative property or commutative law, when two numbers are added or multiplied together, then change in their positions does not change the result. This is one of the major properties of integers.
Where did the word "commutative" come from?
The word, Commutative, originated from the French word ‘commute or commuter’ means to switch or move around, combined with the suffix ‘-ative’ means ‘tend to’.
What are the properties of addition and multiplication?
The other major properties of addition and multiplication are: 1 Associative Property 2 Distributive Property
Is division a commutative law?
Example: 4 – 3 = 1 but 3 – 4 = -1 which are two different integers. Also, the division does not follow the commutative law.
What is commutative property?
The commutative property states that the numbers on which we operate can be moved or swapped from their position without making any difference to the answer. The property holds for Addition and Multiplication, but not for subtraction and division.
Can commutative property be applied to subtraction?
However, we cannot apply commutative property on subtraction and division. If you move the position of numbers in subtraction or division, it changes the entire problem. Therefore, if a and b are two non-zero numbers, then: The commutative property of addition is:
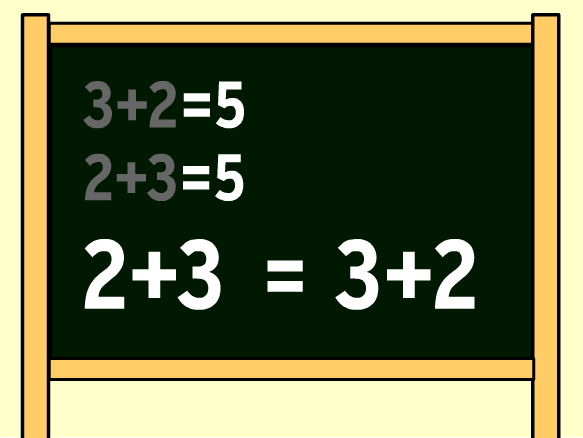
Overview
Common uses
The commutative property (or commutative law) is a property generally associated with binary operations and functions. If the commutative property holds for a pair of elements under a certain binary operation then the two elements are said to commute under that operation.
Mathematical definitions
A binary operation on a set S is called commutative if
One says that x commutes with y or that x and y commute under if
A binary function is sometimes called commutative if
Examples
• Addition and multiplication are commutative in most number systems, and, in particular, between natural numbers, integers, rational numbers, real numbers and complex numbers. This is also true in every field.
• Addition is commutative in every vector space and in every algebra.
History and etymology
Records of the implicit use of the commutative property go back to ancient times. The Egyptians used the commutative property of multiplication to simplify computing products. Euclid is known to have assumed the commutative property of multiplication in his book Elements. Formal uses of the commutative property arose in the late 18th and early 19th centuries, when mathematicians began t…
Set theory
In group and set theory, many algebraic structures are called commutative when certain operands satisfy the commutative property. In higher branches of mathematics, such as analysis and linear algebra the commutativity of well-known operations (such as addition and multiplication on real and complex numbers) is often used (or implicitly assumed) in proofs.
Mathematical structures and commutativity
• A commutative semigroup is a set endowed with a total, associative and commutative operation.
• If the operation additionally has an identity element, we have a commutative monoid
• An abelian group, or commutative group is a group whose group operation is commutative.
See also
• Anticommutative property
• Centralizer and normalizer (also called a commutant)
• Commutative diagram
• Commutative (neurophysiology)