The fundamental quantities by definition they are physical quantities that receive that name because they cannot be defined in terms of others; that is, they are independent and from them, as many magnitudes of different kinds are obtained or derived.
What are the 7 fundamental units?
What are the seven fundamental units of Measurement?
- Mass –. The basic fundamental unit of mass is “ Kg”. ...
- Time –. The basic fundamental unit of Time is “Sec (s)”. ...
- Electric Current –. The basic fundamental unit of Electric Current is “Ampere (A)”.
- Amount of Substance –. Amount of Substance is a dimensionless expression of the number of particles in a particle or object.
- Illumination. ...
- Distance. ...
- Temperature. ...
What is fundamental quantity in physics?
The quantities which can be measured by an instrument and by means of which we describe the laws of physics are called physical quantities. “Those physical quantities which are independent of each other and cannot be expressed in terms of one another, are known as fundamental quantities, Absolute or Base Quantities.”
What are the basic physical quantities?
Physical quantities examples
- Mass
- Length
- Time
- Electric current
- Volume
- Area
- Density
- Force
- Energy
- Power
What are the fundamental units?
The units in which they are measured are thus called fundamental units. In this textbook, the fundamental physical quantities are taken to be length, mass, time, and electric current. (Note that electric current will not be introduced until much later in this text.)

What are fundamental qualities?
Fundamental Qualities are qualities that make the financial statement useful to the users. The Fundamental Qualities are Relevance and Faithful Representation, the Enhancing Qualities are Completeness, Timeliness, Verifiability and Understandability.
Why are they called fundamental quantities?
Length is called a fundamental quantity because the length of an object does not change.
What is fundamental quantities and unit?
Fundamental quantities are physical quantities whose dimensions and units are not usually derived from other physical quantities.
What are the fundamental quantities answers?
There are seven fundamental quantities – length, mass, temperature, time, electric current, luminous intensity and amount of substance.
What are fundamental quantities write their name?
There are seven fundamental (basic) physical quantities: Length, mass, time, temperature, electric current, luminous intensity and amount of a substance and their units are fundamental units.
What are fundamental quantities Class 6?
Length, time, mass and temperature are the fundamental physical quantities. These can be measured directly, using suitable measuring instruments.
What are the main fundamental quantities?
Following are the seven fundamental quantities:Length (metre)Mass (kilogram)Time (second)Electric current (ampere)Thermodynamic temperature (kelvin)Amount of substance (mole)Luminous intensity (candela)
How many fundamental quantities are there?
seven base quantitiesThe present SI has seven base quantities: time, length, mass, electric current, thermodynamic temperature, amount of substance, and luminous intensity.
What is fundamental quantity and derived quantity with example?
Fundamental quantity: quantities which are independent on other physical quantity. ex: length, mass, time, current, amount of substance, luminous intensity, thermodynamic temperature, Derived quantity: quantities which depend on fundamental quantities.
What is the most fundamental quantity?
If the universe was two-dimensional, for example one linear space dimension and one-time dimension, then the “speed of light” would be your fundamental physical quantity. That's because it acts as a kind of scale factor to relate those two dimensions.
What are fundamental quantities Class 7?
Fundamental quantities : The quantities for which the standardized units can be decided are called fundamental quantities. e.g., the distance and time are the quantities for which standard units have been decided.
What is called fundamental physical quantity?
Basic physical quantities that do not depend upon other quantities are called fundamental physical quantities. There are seven fundamental quantities- length, mass, temperature, time, electric current, luminous intensity and amount of substance.
What is the main difference between fundamental and derived quantities?
Fundamental quantities are the base quantities of a unit system, and they are defined independent of the other quantities. Derived quantities are based on fundamental quantities, and they can be given in terms of fundamental quantities.
Which quantities are fundamental quantities?
What Are The 7 Fundamental Quantities And Their Units?Kilogram for mass.Second for time.Kelvin for temperature.Ampere for electric current.Mole for the amount of substance.Candela for luminous intensity.Metre for distance.
What does it mean to be called a derived unit?
derived unit. noun. a unit of measurement obtained by multiplication or division of the base units of a system without the introduction of numerical factors.
What do we call the gravitational force between the earth and an object?
The gravitation force between the earth and object is called weight.It is also equal to the product of acceleration due to gravity and mass of the...
Write the differences between mass and weight of an object.
MassWeight1. The mass of an object is the quantity of matter contained in it.1. The weight of an object is the force with which it is attracted tow...
A motorboat, whose speed in 15 km/hr in still water goes 30 km downstream and comes back in a total ...
Let the speed of the stream be \\(x\\) \\(km/hr\\)Speed downstream \\(=(15+x)km/hr\\)Speed upstream \\(=(15-x)km/hr\\)Distance travelled downstream...
Why do we need standard unit measurement?
We need standard unit for measurement to make our judgement more reliable and accurate. For proper dealing, measurement should be same for everybod...
What do you mean by fundamental & derived quantities? Give the derived unit of Force.
Fundamental quantity: quantities which are independent on other physical quantity. ex: length, mass, time, current, amount of substance, luminous i...
The unit of Stefan's constant \\(\sigma\\) is
Stefan's law is \\(E=\sigma (T^4)\\)\\(\Rightarrow \sigma =\dfrac{E}{T^4}\\)where,\\(E=\dfrac{Energy}{Area \times Time}=\dfrac{Watt}{m^2}\\)\\(\sig...
What are the differences between the mass of an object and its weight?
Mass is the measure of the amount of matter in a body. Weight is the measure of the amount of force acting on a mass due to the acceleration due to...
Which of the following is not the fundamental quantity,
We know that the fundamental quantities are mass, length and time. velocity = \\(\dfrac{displacement}{time}\\)hence velocity is derived quantity
What are the difference between the mass of an object and its weight?
Mass is the actual amount of material contained in a body and is measured is kg, gm, etc. Whereas weight is the force exerted by the gravity on tha...
Which of the following is a fundamental unit?
Fundamental quantities are those quantities which do not depend on other quantities for their measurement. Current is a fundamental quantity and do...
What are fundamental quantities?
FUNDAMENTAL QUANTITIES: “Those physical quantities which are independent of each other and cannot be expressed in terms of one another, are known as fundamental quantities, Absolute or Base Quantities.”. So, certain physical quantities have been chosen arbitrarily and their units are used for expressing all other physical quantities.
What are derived quantities?
DERIVED QUANTITIES: Physical quantities which can be expressed as combination of base quantities are called as derived quantities. For example : Speed, velocity, acceleration, force, momentum, pressure, energy etc.
How to measure a physical quantity?
In order to measure a physical quantity, it has to be expressed in terms of a certain reference standard of measurement of that physical quantity which is called a unit. The magnitude of physical quantity is expressed in terms of the number of times of the physical quantity contains that unit.
What is the unit of distance in which the size of a nucleus is measured?
Fermi is a unit of distance in which the size of a nucleus is measured. 1 Fermi = 10 – 15 m. Atomic Mass Unit : It is a unit of mass equal to 1/12th mass of carbon (12) nucleus and is used in measuring the masses of nuclei. 1 atomic mass unit = 1.67 × 10 – 27 kg.
What is fundamental quantity?
1. fundamental quantity - one of the four quantities that are the basis of systems of measurement. fundamental measure. quantity, measure, amount - how much there is or how many there are of something that you can quantify.
What is the definition of temperature?
temperature - the degree of hotness or coldness of a body or environment (corresponding to its molecular activity) mass - the property of a body that causes it to have weight in a gravitational field. length - the linear extent in space from one end to the other; the longest dimension of something that is fixed in place;
Is luminous flux a photometric quantity?
However, there is nothing wrong with photometric quantities such as luminous flux, which is the most fundamental quantity, to measure light. The case for luminous flux. The Hubble constant is a fundamental quantity that measures the current rate at which our universe is expanding.
What is fundamental unit?
A fundamental unit is a unit adopted for measurement of a base quantity. A base quantity is one of a conventionally chosen subset of physical quantities, where no subset quantity can be expressed in terms of the others.
What is derived quantity?
Define derived quantities and their units - definition. The Fundamental Quantity is independent Physical Quantity that is not possible to express in other Physical Quanitity. It is used as pillars for other quantities aka Derived Quantities. In Physics, Length, Mass, Time, Electric Current, Thermodynamic Temperature, ...
What are the fundamental quantities in the study of thermal fluctuations in fluids?
The fundamental quantities in the study of thermal fluctuations in fluids are space and time-dependent correlation functions . These functions are the natural quantities for theoretical analyses as well as laboratory measurements. They are well defined for a wide variety of physical systems, and they possess both macroscopic properties and interpretations at the microscopic level.
What is the fundamental quantity of transport theory?
The fundamental quantity in the transport theory approach is the total specific intensity, L, which is a function of position r → for light in the direction given by a unit vector s ˆ and its units are W . cm−2 . s−1. The equation of transfer satisfied by L can be written as
Fundamental Quantities
Fundamental quantities are quantities which do not depend upon other quantities for their complete identification ( definition ) . There are 7 fundamental quantities.
Derived Quantities
Derived quantities are those quantities that can be expressed in terms of fundamental quantities by means of the mathematical symbols of multiplication and division only (no addition or subtraction or any other sign). Basically they may be divided into two categories. The first group consists of derived quantities , which have proper units.
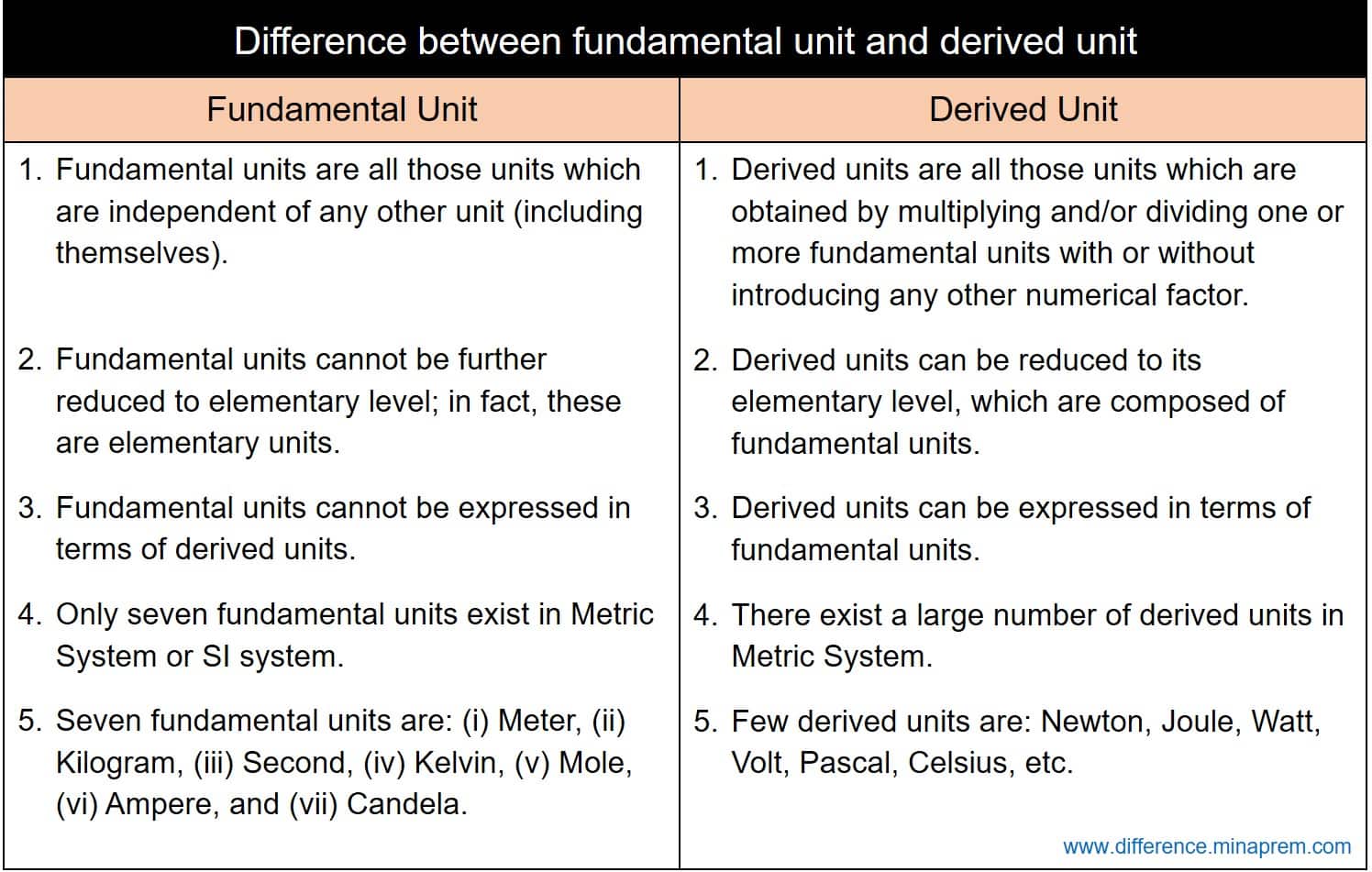
Difference between Fundamental and Derived quantities
1 . Fundamental quantities are base quantities, these quantities doesn’t depend on other quantities while derived quantities depend on Fundamental quantity. 2 . Fundamental quantities can not be further reduce to elementary level , but derived quantities can be reduced in elementary level .. 3 .
What are the fundamental magnitudes?
The fundamental quantities, according to the International System of Units (SI) are the following: length, time, mass, intensity of electric current, temperature, amount of substance (mol) and light intensity. Therefore, there are seven fundamental quantities.
Length
Meter (m). The meter is the distance traveled by light in a vacuum in 1 / 299,792,458 seconds. Pattern established in 1883.
Weather
Seconds). It is the duration of 9,192,631,770 periods of radiation corresponding to the transition between the hyperfine levels of the ground state of cesium-133. Pattern established in 1967.
Dough
Kilogram (kg). The kilogram is the mass of a platinum-iridium alloy cylinder deposited with the International Bureau of Weights and Measures. Pattern established in 1887. However, currently its exact value is defined from Planck's constant.
Electric current intensity
Ampere (A). The ampere or ampere is the constant current intensity that, remaining in two parallel, rectilinear conductors, of infinite length, of negligible circular section and located at a distance of one meter from each other in a vacuum, would produce a force equal to 2 · 10 -7 newton per meter of length.
Temperature
Kelvin (K). The kelvin is the fraction 1 / 273.16 of the triple point temperature of water.
Amount of substance
Mol (mol). The mole is the amount of a substance in a system that contains as many elemental units as there are atoms in 12 grams of carbon-12.