
Limiting Factor Definition A limiting factor is a resource or environmental condition which limits the growth, distribution or abundance of an organism or population within an ecosystem.
Full Answer
What resources would be considered a limiting factor?
Space, food, oxygen, and water are limiting factors. Temperature and precipitation determine the climate of an ecosystem, which impacts the organisms that can live in an ecosystem. An ecosystem can support only so large of a population.
What are some examples of limiting factors?
You can also have limiting factors (or density-dependent factors) for populations:
- light
- food availabilty
- predators
- disease etc.
What does a limiting factor mean in science?
What does limiting factors mean in science? A limiting factor is anything that constrains a population’s size and slows or stops it from growing. Some examples of limiting factors are biotic, like food, mates, and competition with other organisms for resources.
What does limiting factor mean?
Limiting Factors A limiting factor is any factor that slows down the rate of photosynthesis if there is not enough of it. It is called a limiting factor because it “limits” the reaction from taking place.

What is a simple definition of limiting factor?
A limiting factor is anything that constrains a population's size and slows or stops it from growing. Some examples of limiting factors are biotic, like food, mates, and competition with other organisms for resources.
What is the definition of a limiting factor in photosynthesis?
A limiting factor is something that is limiting the rate of photosynthesis e.g. if there isn't enough light for the reaction to occur, light is the limiting factor. As the intensity of light increases, so does the rate of photosynthesis.
Whats the definition of limiting?
Definition of limiting 1a : functioning as a limit : restrictive limiting value. b : being an environmental factor (such as a nutrient) that limits the population size of an organism. 2 : serving to specify the application of the modified noun this in "this book" is a limiting word.
What is the definition of limiting factor in chemistry?
Within stoichiometry, limiting factors are the reactants or reagents within a chemical reaction that are consumed by the reaction before other reactants. The limiting factor is the reactant or reagent that has the lowest supply regarding its needed ratio compared to other reactants within the system.
What is a limiting factor GCSE?
So a limiting factor can be defined as something present in the environment in such short supply that it restricts life processes. There are three main factors which limit the rate of photosynthesis: Temperature. Light intensity. Carbon dioxide concentration.
What is a limiting factor for plants?
The major limiting factors in this process are light intensity, temperature, and carbon dioxide levels. For both light intensity and temperature, if the level is too low or too high, the rate of photosynthesis declines rapidly.
What are the types of limiting factors?
The common limiting factors in an ecosystem are food, water, habitat, and mate. The availability of these factors will affect the carrying capacity of an environment. As the population increases, food demand increases as well. Since food is a limited resource, organisms will begin competing for it.
What are biotic limiting factors?
Biotic or biological limiting factors are things like food, availability of mates, disease, and predators. Abiotic or physical limiting factors are non-living things such as temperature, wind, climate, sunlight, rainfall, soil composition, natural disasters, and pollution.
What are the 4 limiting factors of an ecosystem?
Space, food, oxygen, and water are limiting factors. Temperature and precipitation determine the climate of an ecosystem, which impacts the organisms that can live in an ecosystem. An ecosystem can support only so large of a population.
What is a limiting reactant chemistry GCSE?
A reaction finishes when one of the reactants is all used up. The other reactant has nothing left to react with, so some of it is left over: the reactant that is all used up is called the limiting reactant - it sets a limit on how much product can form.
What is limiting and excess reactant?
In a chemical reaction, reactants that are not used up when the reaction is finished are called excess reagents. The reagent that is completely used up or reacted is called the limiting reagent, because its quantity limits the amount of products formed.
How do you find the limiting factor of a reaction?
Calculate the number of moles of each reactant by multiplying the volume of each solution by its molarity. Determine which reactant is limiting by dividing the number of moles of each reactant by its stoichiometric coefficient in the balanced chemical equation.
What is a Limiting Factor?
Within many studies or fields, there are variables within systems that determine and result in a measurable change in the system's output. These variables are called limiting factors because they are factors that limit the output, outcome, value, or product a system can produce.
What Does Limiting Factor Mean in Chemistry?
Within the field of chemistry, limiting factors are regarding stoichiometry, or the relationship between the masses of the reactants and products prior to, during, and resulting from a chemical reaction.
What does Limiting Factor Mean in Biology?
Within the field of biology, limiting factors have different applications and meanings. A biological limiting factor is a variable that determines the carrying capacity an ecosystem has for a certain population or species. I.e., limiting factors determine or limit population sizes.
What is limiting factor?
A limiting factor is a resource or environmental condition which limits the growth, distribution or abundance of an organism or population within an ecosystem. These can be either physical or biological factors which can be identified through a response of increased or decreased growth, abundance, or distribution of a population, ...
What are the limiting factors of an organism?
Resources such as food, water, light, space, shelter and access to mates are all limiting factors. If an organism, group or population does not have enough resources to sustain it, individuals will die through starvation, desiccation and stress, or they will fail to produce offspring.
What are the limiting factors of the human population?
Density dependent limiting factors such as decreased availability of space due to defore station is a global issue, causing decline and extinctions in many populations. Resources are also increasingly scarce due to hunting and leaching of nutrients from soil, which causes intraspecific and interspecific competition within and between populations. Removal of predators has also disturbed the balance of natural biotic, cycle of predators and prey; in some cases, prey animals have been able to thrive in the absence of predators, exceeding the carrying capacity of ecosystems and causing environmental damage. Predators have also been introduced as invasive species into ecosystems, putting pressure on prey populations and thus on the prey’s natural predators.
What are the limiting factors for Cordyceps fungus?
The availability of host species , which the Cordyceps fungus can parasitize, is a limiting factor for the fungus. The population density of predators and prey are limiting factors for each of these parties.
What are the factors that affect population growth?
Biotic factors. As well as resource and climatic factors affecting population growth, biotic factors such as predation, herbivory, parasitism, and interspecific and intraspecific competition, are also limiting factors; these tend to be density dependent factors.
What are the physical factors that affect the limit of abiotic factors?
Physical factors or abiotic factors include temperature, water availability, oxygen, salinity, light, food and nutrients; biological factors or biotic factors, involve interactions between organisms such as predation, competition, parasitism and herbivory.
What is the limiting resource in an ecosystem?
The limiting resource within an ecosystem determines the carrying capacity (indicated in ecology by the letter, “K”), which is the maximum number of individuals in a population that a habitat can support without environmental degradation.
Limiting Factor Defined
Do you like to cook? Well, cooking is a lot like chemistry! To cook, we often follow a detailed recipe (experimental procedure) that brings together two or more ingredients (reactants) to make something new (final product).
A Molecular Representation of the Limiting Factor
For a deeper understanding of the limiting factor, we can study a molecular representation of the reaction between oxygen gas (Osub2) and hydrogen gas (Hsub2) to yield water (Hsub2O), shown below in Figure 1.
Applications of the Limiting Factor
The limiting factor plays a critical role in chemical experimentation and reaction planning. If we know the amounts of reactants present, we can use simple calculations based on the relative number of moles or molecules to determine which reactant is limiting.
How To Determine the Limiting Factor of a Reaction
Consider the balanced chemical equation for the reaction between nitrogen gas (Nsub2) and hydrogen gas (Hsub2) to yield ammonia gas (NHsub3):
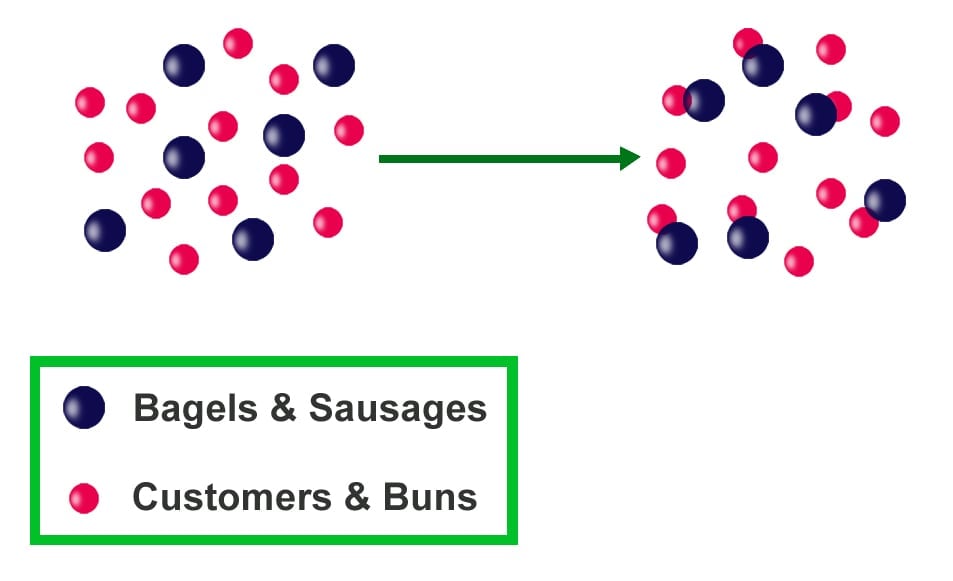
Limiting Factor Definition
Types of Limiting Factor
- Density Dependent Factors
Density dependent factors are those factors whose effect on a population is determined by the total size of the population. Predationand disease, as well as resource availability, are all examples of density dependent factors. As an example, disease is likely to spread quicker throu… - Density Independent Factors
A density independent limiting factor is one which limits the size of a population, but whose effect is not dependent on the size of the population (the number of individuals). Examples of density independent factorsinclude environmentally stressful events such as earthquakes, tsunamis, an…
Examples of Limiting Factors
- Resources
Resources such as food, water, light, space, shelter and access to mates are all limiting factors. If an organism, group or population does not have enough resources to sustain it, individuals will die through starvation, desiccation and stress, or they will fail to produce offspring. In the case of ph… - Environmental Conditions
Limiting factors are also present as environmental conditions. Two of the most prominent examples are temperature and precipitation; these are widely affected by the climate, and seasonal changes within the climate. The effect that each factor has on a particular organism i…
Related Biology Terms
- Resources– A substance within an environment, which is required by an organism for growth, maintenance and reproduction.
- Carrying Capacity– The number of populations or organisms within a population, which an environment can sustain indefinitely without environmental degradation.
- Fundamental Niche– The total range of environmental conditions that is suitable in order for …
- Resources– A substance within an environment, which is required by an organism for growth, maintenance and reproduction.
- Carrying Capacity– The number of populations or organisms within a population, which an environment can sustain indefinitely without environmental degradation.
- Fundamental Niche– The total range of environmental conditions that is suitable in order for an organism to exist, in the absence of limiting factors.
- Realized Niche– The actual amount of resources or environmental conditions that an organism is able to utilize within an ecosystem.
Quiz
- 1. Which of these limiting factors would be density independent? A. A food source B. Intraspecific competition C. A volcanic eruption D.Light 2. Temperature is an example of a: A. Density dependent factor B. An abiotic limiting factor C. A resource D.An environmental limiting factor 3. The carrying capacity (K), of an environment is reached when: A. Food resources are plentiful B. …