Prokaryote
A prokaryote is a unicellular organism that lacks a membrane-bound nucleus, mitochondria, or any other membrane-bound organelle. The word prokaryote comes from the Greek πρό "before" and κάρυον "nut or kernel". Prokaryotes are divided into two domains, Archaea and Bacteria. Species wit…
Prokaryote
A prokaryote is a unicellular organism that lacks a membrane-bound nucleus, mitochondria, or any other membrane-bound organelle. The word prokaryote comes from the Greek πρό "before" and κάρυον "nut or kernel". Prokaryotes are divided into two domains, Archaea and Bacteria. Species wit…
What is one defining characteristic of a prokaryotic cell?
Prokaryotic cells are the unicellular cells that lack a well-defined nucleus, i.e. genetic material is not enclosed by a nuclear membrane. These cells are very minute in size 0.1 to 5.0 μ m. Common prokaryotic cell is a bacterial cell. Our body has over 100 trillion bacterial cells.
What are the main features of prokaryotic cells?
Key Terms
- eukaryotic: Having complex cells in which the genetic material is organized into membrane-bound nuclei.
- prokaryotic: Of cells, lacking a nucleus.
- nucleoid: the irregularly-shaped region within a prokaryote cell where the genetic material is localized
What are some facts about prokaryotic cells?
Prokaryotes Facts for Kids
- Prokaryotes are thought to be the oldest organisms on earth.
- Prokaryotes have cytosol that looks very grainy. ...
- Prokaryote DNA floats freely but is usually found in concentration in or around what they call the “nuclear region.”
What do you mean by prokaryotic cells?
What do you mean by prokaryotic cell? A prokaryotic cell is a unicellular organism that lacks a membrane-bound nucleus (karyon), mitochondria, or any other membrane-bound organelle. The word prokaryote comes from the Greek πρό (pro) "before" and κάρυον (karyon) "nut or kernel".

What is in a prokaryotic cell?
All prokaryotic cells have a nucleoid region, DNA and RNA as their genetic material, ribosomes that make proteins, and cytosol that contains a cytoskeleton that organizes cellular materials. However, prokaryotic organisms are a very diverse group of organisms and come in many different shapes and sizes.
What is a prokaryotic cell your answer?
Prokaryote definition Prokaryotes are unicellular organisms that lack membrane-bound structures, the most noteworthy of which is the nucleus. Prokaryotic cells tend to be small, simple cells, measuring around 0.1-5 μm in diameter. The key structures present in a prokaryote cell.
What are prokaryotic cell in one word?
A prokaryote is a single-celled organism that doesn't have a nucleus. Bacteria are one familiar type of prokaryote. If you take a biology class, you're likely to learn about prokaryotes, tiny organisms without a distinct nucleus bound by a membrane, like most other living things.
What are prokaryotes easy definition?
prokaryote, also spelled procaryote, any organism that lacks a distinct nucleus and other organelles due to the absence of internal membranes. Bacteria are among the best-known prokaryotic organisms. The lack of internal membranes in prokaryotes distinguishes them from eukaryotes.
What is prokaryotic cell with example?
Prokaryotes are single celled, microscopic entities. They neither have specialized organelles nor a prominent nucleus with a membrane. Examples of prokaryotes include cyanobacteria, E. coli, mycoplasma etc.
What is prokaryotic cell explain with example?
Prokaryotic cells are single-celled microorganisms known to be the earliest on earth. Prokaryotes include Bacteria and Archaea. The photosynthetic prokaryotes include cyanobacteria that perform photosynthesis. A prokaryotic cell consists of a single membrane and therefore, all the reactions occur within the cytoplasm.
What is a prokaryotic cell example?
Prokaryotes are single celled, microscopic entities. They neither have specialized organelles nor a prominent nucleus with a membrane. Examples of prokaryotes include cyanobacteria, E. coli, mycoplasma etc.
What are 5 examples of prokaryotic cells?
Examples of Prokaryotes:Escherichia Coli Bacterium (E. coli)Streptococcus Bacterium.Streptomyces Soil Bacteria.Archaea.
What is a eukaryotic cell simple definition?
eukaryote, any cell or organism that possesses a clearly defined nucleus. The eukaryotic cell has a nuclear membrane that surrounds the nucleus, in which the well-defined chromosomes (bodies containing the hereditary material) are located.
What are prokaryotes and eukaryotes?
Difference between Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic CellsProkaryotesEukaryotesCytoplasmPresent, but cell organelles absentPresent, cell organelles presentEndoplasmic reticulumAbsentPresentPlasmidsPresentVery rarely found in eukaryotesRibosomeSmall ribosomesLarge ribosomes12 more rows
What are the structural features of prokaryotic cells?
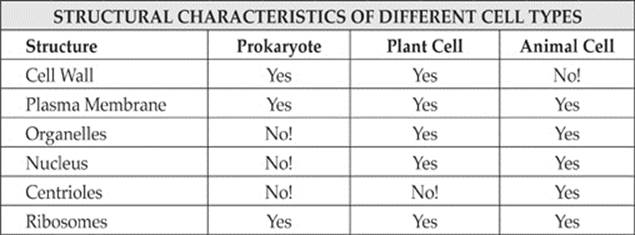
The prokaryotic cell structure is composed of: Cell wall Cell membrane Capsule Pili Flagella Ribosomes Plasmids
How is the prokaryotic cell structure different from that of the eukaryotic cell?
Prokaryotic cells lack a true nucleus. The nucleus is devoid of the nuclear membrane. On the contrary, the nucleus of the eukaryotic cells is enclo...
How does a prokaryotic cell divide?
Prokaryotic cells undergo asexual reproduction. Most prokaryotic cells divide by binary fission, where the cells divide into two daughter cells.
Why is the process of cell division in prokaryotic cells different from that in eukaryotes?
Prokaryotic cells are simpler than eukaryotic cells. They do not have a nuclear membrane surrounding their DNA, therefore, cell division is differe...
When did the prokaryotic cells evolve?
The first prokaryotic cells evolved around 3.5 billion years ago. The eukaryotic cells were formed after the prokaryotic cells and are believed to...
What are 4 examples of prokaryotic cells?
Examples of prokaryotic cells are: 1. bacterial cells like Escherichia Coli Bacterium, Streptococcus Bacterium 2. cyanobacteria, 3. archaea, 4. myc...
What is a prokaryotic cell simple definition?
Prokaryotic cell refers to the unicellular cell which lacks well-defined nucleus and other membrane bound organelles.
What are 2 examples of prokaryotic cells?
Examples of prokaryotic cells are Bacteria and cyanobacteria.
What is a prokaryotic cell example?
An example of a prokaryotic cell is a bacterial cell.
Which are prokaryotes?
Prokaryotes refers to the unicellular organisms lacking well-defined nucleus and other membrane-bound organelles.
What is a Prokaryotic Cell?
Prokaryotic cells are single-celled microorganisms known to be the earliest on earth. Prokaryotes include Bacteria and Archaea. The photosynthetic prokaryotes include cyanobacteria that perform photosynthesis.
What are the characteristics of prokaryotic cells?
The characteristics of the prokaryotic cells are mentioned below. They lack a nuclear membrane. Mitochondria, Golgi bodies, chloroplast, and lysosomes are absent. The genetic material is present on a single chromosome. The histone proteins, the important constituents of eukaryotic chromosomes, are lacking in them.
Which region of the cytoplasm is not involved in reproduction?
These are not involved in reproduction. Nucleoid Region – It is the region in the cytoplasm where the genetic material is present. A prokaryotic cell lacks certain organelles like mitochondria, endoplasmic reticulum, and Golgi bodies.
What are the components of eukaryotic chromosomes?
The histone proteins, the important constituents of eukaryotic chromosomes, are lacking in them. The cell wall is made up of carbohydrates and amino acids. The plasma membrane acts as the mitochondrial membrane carrying respiratory enzymes. They divide asexually by binary fission.
What is the structure of a prokaryotic cell?
A prokaryotic cell structure is as follows: Capsule – It is an outer protective covering found in the bacterial cells, in addition to the cell wall. It helps in moisture retention, protects the cell when engulfed, and helps in the attachment of cells to nutrients and surfaces. Cell Wall – It is the outermost layer of the cell which gives shape ...
How many components are there in prokaryotic cells?
The prokaryotic cells have four main components:
Where do prokaryotic cells react?
A prokaryotic cell consists of a single membrane and therefore, all the reactions occur within the cytoplasm. They can be free-living or parasites.
What is a Prokaryotic Cell?
Prokaryotic cells are microorganisms that are known to be the earliest on earth.
What are the characteristics of a prokaryotic cell?
Characteristics of Prokaryotic Cell. Prokaryotic cells have no organized nucleus, i.e. their genetic material is not surrounded by a nuclear membrane and that type of nucleus is called nucleoid. The cell is surrounded by a plasma membrane. Surrounding plasma membrane is a cell wall which is usually made of carbohydrates and small proteins.
Why do prokaryotic cells have flagella?
6. Prokaryotic cells may have flagella used for locomotion and pili for attachment to surfaces or else can be passively transported by wind, water, etc. 7. Pilli can also be used to transfer DNA molecules to other bacteria.
How do flagella cells move?
These cells move by the simple beating of flagella or by gliding.
Which cell contains all the genes that code for all the proteins of the prokaryotic cell?
Nucleoid- It contains all the genes that code for all the proteins of the prokaryotic cell which have structural and functional roles. Plasmid – It may contain genes that code for proteins or enzymes that can protect the cell from toxic substances. Figure showing Nucleoid (bacterial DNA) and Plasmids. 4.
How does circular DNA replicate?
In this method of reproduction, circular DNA replicates followed by cell expansion. Due to this the duplicated DNA is pulled apart. Then there is a constriction in the middle which results in separating the two cells apart from each other, resulting in the formation of two daughter cells.
How do spores reproduce?
Their reproduction is by spore formation or binary fission.
What is a prokaryote?
Prokaryotes are single-celled organisms that are the earliest and most primitive forms of life on earth. As organized in the Three Domain System, prokaryotes include bacteria and archaeans.
How do prokaryotes reproduce?
The cell wall is dividing resulting in the formation of two cells. Janice Carr/CDC. Most prokaryotes reproduce asexually through a process called binary fission. During binary fission, the single DNA molecule replicates and the original cell is divided into two identical cells.
How is genetic variation accomplished in prokaryotic organisms?
Genetic variation within prokaryotic organisms is accomplished through recombination. In recombination, genes from one prokaryote are incorporated into the genome of another prokaryote. Recombination is accomplished in bacterial reproduction by the processes of conjugation, transformation, or transduction.
What are the environments that prokaryotes live in?
Many prokaryotes are extremophiles and can live and thrive in various types of extreme environments including hydrothermal vents, hot springs, swamps, wetlands, and the guts of humans and animals ( Helicobacter pylori ).
What is the outer covering of a bacterial cell?
Cell Wall: The cell wall is an outer covering that protects the bacterial cell and gives it shape. Cytoplasm: Cytoplasm is a gel-like substance composed mainly of water that also contains enzymes, salts, cell components, and various organic molecules.
What are the different types of cell shapes?
Prokaryotic organisms have varying cell shapes. The most common bacteria shapes are spherical, rod-shaped, and spiral.
Which cell has no nucleus?
Bacterial Cell Anatomy and Internal Structure. Jack0m/Getty Images. Prokaryotic cells are not as complex as eukaryotic cells. They have no true nucleus as the DNA is not contained within a membrane or separated from the rest of the cell, but is coiled up in a region of the cytoplasm called the nucleoid. Prokaryotic organisms have varying cell ...
What is a prokaryotic cell?
Prokaryotic cells are simple cells that do not have a true nucleus or other cell organelles. Bacteria and Archaea are the two domains of life that are prokaryotes. Prokaryotes can be contrasted with eukaryotes, ...
How do prokaryotes form?
Step 1 shows the prokaryote cell before the process begins. The DNA is tightly coiled. The DNA then uncoils, duplicates, and splits. A new cell wall is formed in the cell to form two separate cells. These cells then split completely from each other to become two different organisms.
Why are archaea considered the third domain of life?
Also, they were classified as the third domain of life because they have large differences in their ribosomal RNA structure from bacteria. Some archaea live in extreme conditions such as hot springs, but others are found in soil, oceans, and even the human body. There are between 18-23 phyla of archaea.
What are the different types of bacteria?
Bacteria come in many different shapes; they can be Bacilli (rod-shaped), Spirilla (spiral-shaped), Cocci (spherical), comma-shaped, or flagellated. Flagella are small whip-like structures that facilitate movement; bacteria that have flagella may have one, several, or many all over their body.
How many phyla are there in Archaea?
There are between 18-23 phyla of archaea. Most archaea have never been isolated in the laboratory, and they are only known from their nucleic acids in environmental samples. The cell membranes of archaea differ greatly from all other forms of life, and have molecules found only in archaea.
Which is more complex, eukaryotic or prokaryotic?
Prokaryotes can be contrasted with eukaryotes, which have more complex eukaryotic cells with a nucleus and organelles. Eukaryotes are the third domain of life, Eukaryota, and include all complex multicellular organisms such as plants, animals, fungi, and protozoa.
What is the mechanism of reproduction?
The mechanism of reproduction is usually binary fission, which is when one cell splits into two identical cells. It differs from mitosis, the mechanism of cell division in eukaryotes, because it does not involve a spindle apparatus while mitosis does. This figure depicts binary fission.
What is the difference between a prokaryotic and eukaryotic cell?
In 1957 Dougherty has divided cells into two types based on the organization in the nucleus of the cell. One is a prokaryotic cell (primitive cell) and the other is a Eukaryotic cell (ideal cell). Prokaryotic cells are the most primitive type and having no organized nucleus (lacking nuclear membrane, nucleolus, and nuclear reticulum ).
What are some examples of prokaryotes?
Some common Prokaryotes are Bacteria, Blue-green algae, Mycoplasma, or Pleuropneumonia like organisms (PPLO).
What type of ribosomes are in the cytoplasm?
The ribosomes present in the cytoplasm of cells are of the 70s type.
What is the function of flagella in bacteria?
Flagella: In bacterial cells, flagella are arising from the surface of the cell wall. Flagella help in the process of locomotion.
What is the cell wall?
Cell wall: It is situated just below the capsule or slime layer. The cell wall consists mainly of murein or peptidoglycan. The cell wall gives mechanical strength to the cell.
What is the layer of the plasma membrane called?
Capsule or Slime layers: The prokaryotic cell, especially the bacterial cell, is surrounded by a thick coat on the outside part of the plasma membrane called slime layer or capsule. The capsule protects the cell from external injury. The capsule-covered bacteria are contagious (Diplococcus pneumoniae causes pneumonia).
What Do Prokaryotic Cells Look Like?
Even though bacteria are very tiny, their populations are very large! They also can be found everywhere, but we get more into that later. Let's leave the inside of the cell and take a step back to see what they look like from the outside. These cells come in three shapes. The first one is circular shaped. How would you describe the next one? Some people say is it rod shaped, but I think it looks like a Twinkie! Oh, and the last one is my favorite! It is a spiral, twisted shape.
What are the parts of a cell that are not recognized by other cells?
There is no mitochondria, vacuoles, or chloroplasts. These are very, very simplistic cells, which is probably why they are also so small!
What are the two types of cells that are found in plants and fungi?
Prokaryotic cells, on the other hand, are found in the smallest living things on Earth: bacteria! Let's shrink down and take a closer look at these tiny cells! There are two types of cells: eukaryotic and prokaryotic.
What is the shape of bacteria?
This shape of bacteria is considered rod shaped . It is one of three shapes in which bacteria can be found.
What is a prokaryotic cell?
prokaryotic cell. The form of cell composing many primitive unicellular organisms, such as bacteria. Prokaryotic cells do not have nuclei, which are partitioned by an intracellular membrane; instead the DNA forms one main coil in the cell cytoplasm. See also: cell. Medical Dictionary, © 2009 Farlex and Partners.
What are the functions of eukaryotic cells?
"For instance, the precise 3-D localization of proteins within prokaryotic cells is key to many cellular functions, including cell cycle, DNA replication, development, motility, and adhesion. Microscopes embrace hyphenation and nanotechnology: to make discoveries in different fields, ...
What hormones are produced by agrobacteria?
The hormone involved, IAA, is produced from indole-3 -acetamide, and both IAA and cytokinins can be produced by agrobacteria in rich media containing tryptophan or tyrosine. Yet mechanical force can affect both eukaryotic and prokaryotic cells.
Which cell has little internal compartmentalization?
Microbes, molecules, maladies and man. Prokaryotic cells, which are represented by the eubacteria and archaea, contain precious little internal compartmentalization and have transcriptionally coupled translation, whereas eukaryotic cells, which compose plants, fungi, algae, animals, and a widely diverse group of unicellular protists, ...
Which cell represents highly organized arrangements of the chlorophyll?
References in periodicals archive ? As opposed to prokaryotic cells in which pigment molecules are attached to peripheral membranes of the cell, the chloroplast represents highly organized arrangements of the chlorophyll, and the other pigment molecules are arranged in specific double membrane layers called thylakoids.
Can mechanical force affect both eukaryotic and prokaryotic cells?
Yet mechanical force can affect both eukaryotic and prokaryotic cells. At this workshop, Gillespie described how a mechanically sensitive hair bundle serves the hair cell in mechano-electrical transduction.
What is a prokaryotic cell simple definition?
A prokaryote is a simple, single-celled (unicellular) organism that lacks an organized nucleus or any other membrane-bound organelle. The cell wall acts as an extra layer of protection, helps the cell maintain its shape, and prevents dehydration.
What is the definition of eukaryotic cell in biology?
Eukaryote, any cell or organism that possesses a clearly defined nucleus. The eukaryotic cell has a nuclear membrane that surrounds the nucleus, in which the well-defined chromosomes (bodies containing the hereditary material) are located.
What are the two types of bacteria?
Types Spherical: Bacteria shaped like a ball are called cocci, and a single bacterium is a coccus. Examples include the streptococcus group, responsible for “strep throat.” Rod-shaped: These are known as bacilli (singular bacillus). Spiral: These are known as spirilla (singular spirillus).
Which one is a prokaryote?
Only the single-celled organisms of the domains Bacteria and Archaea are classified as prokaryotes—pro means before and kary means nucleus. Animals, plants, fungi, and protists are all eukaryotes—eu means true—and are made up of eukaryotic cells.
What are the two major types of eukaryotic cells?
Eukaryotic cells may be classified into two groups based on the number of cells that make an individual organism: (1) unicellular eukaryotic cells and (2) multicellular eukaryotic cells. Unicellular eukaryotes include the protists. Multicellular eukaryotes include a variety of plant, fungal, and animal species.
What is difference between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cell?
The primary distinction between these two types of organisms is that eukaryotic cells have a membrane-bound nucleus and prokaryotic cells do not. The nucleus is where eukaryotes store their genetic information. Prokaryotes, on the other hand, have no membrane-bound organelles.
What type of cell is bacteria?
Bacteria are single celled microbes. The cell structure is simpler than that of other organisms as there is no nucleus or membrane bound organelles. Instead their control centre containing the genetic information is contained in a single loop of DNA.
