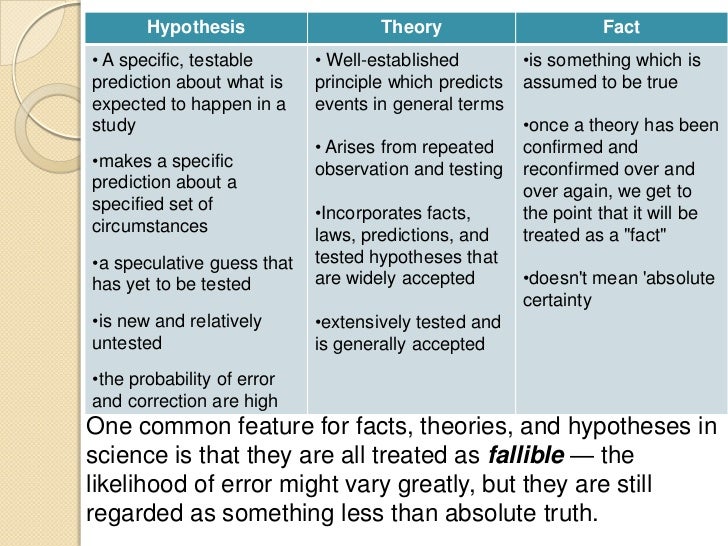
In scientific reasoning, a hypothesis is an assumption made before any research has been completed for the sake of testing. A theory on the other hand is a principle set to explain phenomena already supported by data. Theories will pull together experimental results to provide full explanations such as "The Big Bang Theory."
What is the difference between a hypothesis and a theory?
What to Know In scientific reasoning, a hypothesis is an assumption made before any research has been completed for the sake of testing. A theory on the other hand is a principle set to explain phenomena already supported by data. Theories will pull together experimental results to provide full explanations such as "The Big Bang Theory."
What is the difference between a theory and a principle?
A theory on the other hand is a principle set to explain phenomena already supported by data. Theories will pull together experimental results to provide full explanations such as "The Big Bang Theory."
What is a theory in science?
A theory, in contrast, is a principle that has been formed as an attempt to explain things that have already been substantiated by data. It is used in the names of a number of principles accepted in the scientific community, such as the Big Bang Theory.
What is the difference between a theory and evidence?
A theory, on the other hand, is supported by evidence: it's a principle formed as an attempt to explain things that have already been substantiated by data. Toward that end, science employs a particular vocabulary for describing how ideas are proposed, tested, and supported or disproven.

What is the difference between a theory and a hypothesis?
In scientific reasoning, a hypothesis is an assumption made before any research has been completed for the sake of testing. A theory on the other hand is a principle set to explain phenomena already supported by data. Theories will pull together experimental results to provide full ...
What is hypothesis in argument?
A hypothesis is an assumption, something proposed for the sake of argument so that it can be tested to see if it might be true.
What is a Theory?
A theory, in contrast, is a principle that has been formed as an attempt to explain things that have already been substantiated by data. It is used in the names of a number of principles accepted in the scientific community, such as the Big Bang Theory. Because of the rigors of experimentation and control, its likelihood as truth is much higher than that of a hypothesis.
What is the name of the theory that the solar system is formed by the condensation of the atmosphere?
Laplace's popular version of his astronomy, the Système du monde, was famous for introducing what came to be known as the nebular hypothesis, the theory that the solar system was formed by the condensation, through gradual cooling, of the gaseous atmosphere (the nebulae) surrounding the sun. Louis Menand, The Metaphysical Club, 2001.
What is a tentative hypothesis?
A hypothesis is usually tentative, an assumption or suggestion made strictly for the objective of being tested.
Why are theories considered the basis of scientific reasoning?
While theories are never completely infallible, they form the basis of scientific reasoning because, as Miller said "to the best of our ability, we’ve tested them, and they’ve held up."
Is evolution a theory or a fact?
The distinction has come to the forefront particularly on occasions when the content of science curricula in schools has been challenged—notably, when a school board in Georgia put stickers on textbooks stating that evolution was "a theory, not a fact, regarding the origin of living things." As Kenneth R. Miller, a cell biologist at Brown University, has said, a theory "doesn’t mean a hunch or a guess. A theory is a system of explanations that ties together a whole bunch of facts. It not only explains those facts, but predicts what you ought to find from other observations and experiments.”
What is the Difference Between Theory and Principle?
A theory is a scientifically credible general principle that explains a phenomenon. A principle, on the other hand, is a basic truth, rule or law. It can also refer to a value or a code of conduct that guides behavior. Moreover, while a theory explains a phenomenon, a principle can explain a phenomenon as well as guide the behavior of people.
Why is it important to know that theories stem from principles?
Therefore, it is important to note that theories stem from principles. This is because a theory stems from a general principle that can be proven through evidence. While theories are capable of various phenomena, principles direct the entire society as they are behind every law and system.
What is a Principle?
A principle is a basic rule, law or concept. Oxford dictionary defines principle as “a fundamental truth or proposition that serves as the foundation for a system of belief or behaviour or for a chain of reasoning” while American Heritage dictionary defines it as a “basic truth, law, or assumption”.
What is the theory of a phenomenon?
A theory is a scientifically acceptable general principle that can explain a phenomenon. Oxford dictionary defines it as “a supposition or a system of ideas intended to explain something, especially one based on general principles independent of the thing to be explained” while American Heritage dictionary defines it as a “set ...
What is a theory in science?
Thus, a theory always explains a specific phenomenon. Moreover, a theory stems from a hypothesis, which is proven with valid evidence. We mostly encounter theories in the field of science. Quantum theory, theory of evolution, theory of general relativity, theory of special relativity are some examples of scientific theory.
What is the difference between moral and scientific principles?
Moral principles are the values that guide the conduct of people in a particular society. Legal principles are the fundamental source of laws whereas scientific principles are the rules or concepts that give rise to theories.
Is the Generic Theory of Relativity universally accepted?
Figure 01: Generic Theory of Relativity. However, it also important to note that theory may not be universally accepted. When new evidence comes into the light with the advancement of technology and passage of time, scientists sometimes have to revise or replace theories.
Who uses a hypothesis?
Scientists and researchers may use hypotheses to guide their work and provide direction for their studies. Students and academic scholars also use hypotheses when writing research papers. After creating a hypothesis, these individuals can begin initial research to find out if their prediction is correct. Depending on what they find, they can either support or falsify their original hypothesis with evidence.
What is a theory?
A theory is a principle used to explain a phenomenon or occurrence with supported data. Theories are well-established explanations often accepted by a wide group of scientists and researchers because of the results of multiple tests and experiments. Theories can help society describe aspects of the natural world. An example of a theory is Albert Einstein's general relativity theory, which describes the law of gravitation and its relationship to other natural forces.
Who uses a theory?
Both researchers and scientists use theories to describe findings from their studies, and investigators prepare the results to make provable claims. These theories are then guides for why certain actions or incidents occur. Another type of professional that uses theories often is a psychologist who uses them to help understand client behavior and tendencies.
What is the difference between a hypothesis and a theory?
A hypothesis is an educated guess based on certain data that acts as a foundation for further investigation. It is based on extensive data. It is based on limited data. A theory is proven and tested scientifically.
Can a hypothesis change as the test occurs?
From the above differences, we can infer that a hypothesis might change significantly as the testing occurs. A hypothesis can either be right or wrong. When a hypothesis is tested and proved true, it becomes a theory. At BYJU’S, learn more differences like the difference between asteroid and comet.
What is Einstein's theory?
Einstein's theory breaks down when you apply it to quantum mechanics, which deals with the behavior of tiny subatomic particles. As a result, many scientists are throwing new hypotheses about gravity into the ring. But that doesn't mean Einstein was wrong.
Is it a fact or a fact?
In science, a fact is an observation that's been confirmed so many times that scientists can, for all intents and purposes, accept it as "true." But everything in science comes with a level of uncertainty, so nothing is ever scientifically "true" beyond a shadow of a doubt. You could say that "all swans are white" is a fact, but there's always the chance you could see a black swan and throw that fact out the window. Likewise, you could say it's a fact that every time you let go of a pencil, it will drop to the floor, but science leaves room for the vanishingly, infinitesimally small chance that it might not.
Is Newton's law of universal gravitation a theory?
You might expect "theory" to be the next natural step in this path to scientific truth (and to be fair, we did kind of prime you for that with the headline), but you'd be wrong. That's not to say a law is inferior to a theory; it's just a different thing altogether. In science, a law is a detailed description of how some aspect of the natural world behaves, usually involving math. Newton's law of universal gravitation, as quoted above, describes the way matter behaves with impressive precision. It makes it easy to predict how a moon will act if it's very big and close to its planet versus very small and far away. But how is all it describes — it doesn't explain why.
Is gravity a theory?
You may have heard someone disparage evolution because it's "just a theory." Gravity, on the other hand, must be 100 percent real — it's a "law," after all. It's so thoroughly proven, you might even call it a "scientific fact." Unfortunately, all of these common impressions aren't quite right. The words "fact," "hypothesis," "theory," and "law" have very specific meanings in the world of science, and they don't exactly match the ones we use in everyday language.
Is evolution a theory?
A theory is the granddaddy of all scientific statements, which is why it makes no sense to say that evolution is "just a theory." As Joe Hanson puts it in his video for It's Okay to Be Smart, "Stop saying it like a bad thing. Calling it a theory means it's passed the toughest tests that we can throw at it, and evolution has been tested maybe more than any theory that we know of."
What is the difference between a theory and a principle?
The main difference between Principle and Theory is that the Principle is a rule that has to be followed or is an inevitable consequence of something , such as the laws observed in nature and Theory is a contemplative and rational type of abstract or generalizing thinking, or the results of such thinking. A principle is a concept or value that is ...
What is a theory?
Theory. A theory is a contemplative and rational type of abstract or generalizing thinking, or the results of such thinking. Depending on the context, the results might, for example, include generalized explanations of how nature works. The word has its roots in ancient Greek, but in modern use it has taken on several related meanings.
What is the Pauli exclusion principle?
"Bernoulli's Principle". "The Pauli Exclusion Principle prevents two fermions from occupying the same state.". "The principle of the internal combustion engine".
What is a principle in law?
Principle. A principle is a concept or value that is a guide for behavior or evaluation. In law, it is a rule that has to be, or usually is to be followed, or can be desirably followed, or is an inevitable consequence of something, such as the laws observed in nature or the way that a system is constructed. The principles of such ...
What is a tentative theory?
a tentative theory about the natural world; a concept that is not yet verified but that if true would explain certain facts or phenomena; "a scientific hypothesis that survives experimental testing becomes a scientific theory". "he proposed a fresh theory of alkalis that later was accepted in chemical practices".
What are some examples of principles?
Examples of principles are, entropy in a number of fields, least action in physics, those in descriptive comprehensive and fundamental law: doctrines or assumptions forming normative rules of conduct, separation of church and state in statecraft, the central dogma of molecular biology, fairness in ethics, etc.
What is the definition of theory?
Theory (noun) A doctrine, or scheme of things, which terminates in speculation or contemplation, without a view to practice; hypothesis; speculation. Theory (noun) An exposition of the general or abstract principles of any science; as, the theory of music. Theory (noun)

What Is A Hypothesis?
What Is A Theory?
- A theory, in contrast, is a principle that has been formed as an attempt to explain things that have already been substantiated by data. It is used in the names of a number of principles accepted in the scientific community, such as the Big Bang Theory. Because of the rigors of experimentation and control, its likelihood as truth is much higher tha...
Non-Scientific Use
- In non-scientific use, however, hypothesis and theory are often used interchangeably to mean simply an idea, speculation, or hunch (though theoryis more common in this regard): And sometimes one term is used as a genus, or a means for defining the other:
Incorrect Interpretations of "Theory"
- Since this casual use does away with the distinctions upheld by the scientific community, hypothesis and theoryare prone to being wrongly interpreted even when they are encountered in scientific contexts—or at least, contexts that allude to scientific study without making the critical distinction that scientists employ when weighing hypotheses and theories. The most common oc…
What Is A Theory?
What Is A Principle?
- A principle is a basic rule, law or concept. Oxford dictionary defines principle as “a fundamental truth or proposition that serves as the foundation for a system of belief or behaviour or for a chain of reasoning” while American Heritage dictionary defines it as a “basic truth, law, or assumption”. A principle can also refer to a value or a code of conduct that guides behaviour. Principles can b…
What Is The Relationship Between Theory and Principle?
- A theory is a set of principles.
- Also, scientific principles give rise to theories.
Summary – Theory vs Principle
- Theory and principle are two inter-related concepts. The key difference between theory and principle is that theory is a scientifically credible general principle that explains a phenomenon whereas principle is a basic truth, rule, or law. 1.“Principle.” Wikipedia, Wikimedia Foundation, 3 Aug. 2018. Available here 1.”Generic Theory Of Relativity 1a...
What Is A Theory?
- A theory is a principle used to explain a phenomenon or occurrence with supported data. Theories are well-established explanations often accepted by a wide group of scientists and researchers because of the results of multiple tests and experiments. Theories can help society describe aspects of the natural world. An example of a theory is Albert Ei...
What Is A Hypothesis?
- A hypothesis is a proposed explanation used to describe a phenomenon or occurrence. These are often assumptions made prior to completing research about the relationship between multiple variables. These typically are "if/then" statements, such as "If I run tomorrow, I will feel less stressed," or declarative statements, such as "Girls with pigtails are nicer." When observing con…
Theory vs. Hypothesis
- While individuals who work outside of the science field may use theory and hypothesis interchangeably to mean an idea or speculation, they have different scientific meanings. Here are some of the key differences between a theory and a hypothesis:
Types of Theories
- There are many theories to help model and understand organisms and their behavior. Some types of theories include: 1. Behavior theory:Behavior theory looks at an individual's actions to explain why they behave a particular way. 2. Cognitive theory:Cognitive theory focuses on how and what individuals think can lead to certain emotions. 3. Grand theory:Grand theories, or conceptual fra…
Examples of Theories
- Here are some examples of theories: 1. Natural selection theory:Organisms that are better adapted to the environment typically survive and reproduce more than those that aren't. 2. Germ theory:Microorganisms, referred to as germs or pathogens, can lead to disease. 3. Cell theory:Living organisms have cells that create the basic structural unit of all organisms. 4. Evolut…
Types of Hypotheses
- There are several types of hypotheses to use when trying to explain observations. Here are some types of hypotheses: 1. Alternative hypothesis:Alternative hypothesis states the occurrence of a new theory to replace a previous one. 2. Complex hypothesis:A complex hypothesis involves multiple dependents to describe the relationship between two components. 3. Empirical hypothe…
Examples of Hypotheses
- Here are some hypothetical examples of hypotheses: 1. It’s dark outside because it‘s going to rain. 2. If I get eight hours of sleep, then this may lead to a more productive worker. 3. If I put the cactus on my windowsill, then it may grow to be healthier.