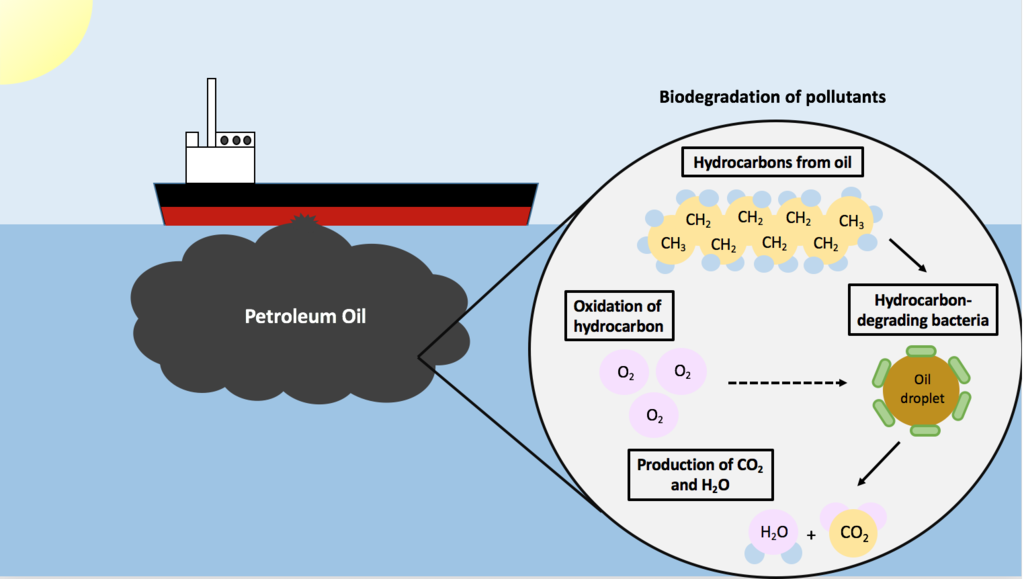
Aerobic biodegradation is done by aerobic microorganisms when the adequate supply of oxygen is available for their activity. Aerobic biodegradation is a rapid method which degrades the contaminants completely when compared to anaerobic biodegradation. Anaerobic biodegradation takes place in the absence of oxygen.
What is aerobic biodegradation?
Aerobic biodegradation is the breakdown of organic contaminants by microorganisms when oxygen is present. More specifically, it refers to occurring or living only in the presence of oxygen; therefore, the chemistry of the system, environment, or organism is characterized by oxidative conditions.
What is anaerobic biodegradable waste?
Anaerobic Biodegradation Anaerobic digestion occurs when the anaerobic microbes are dominant over the aerobic microbes. Biodegradable waste in landfill degrades in the absence of oxygen through the process of anaerobic digestion.
What is the pathway of anaerobic biodegradation?
Anaerobic biodegradation takes place in the absence of oxygen. Its pathway has four major steps: hydrolysis, acidogenesis, acetogenesis and methanogenesis. Organic substances are subjected to anaerobic digestion and converted into carbon dioxide and methane.
What is the difference between aerobic and anaerobic wastewater treatment?
Aerobic wastewater treatment is carried out by aerobic microorganisms. Aerobic microorganisms require oxygen; hence, oxygen is supplied for aerobic wastewater treatment tanks. Anaerobic wastewater treatment is carried out by anaerobic microorganisms. Thus, anaerobic wastewater treatment process occurs without an oxygen supply.

What is aerobic biodegradation?
Enhanced aerobic biodegradation is the practice of adding oxygen to saturated soil and groundwater to increase the number and vitality of indigenous microorganisms able to perform biodegradation. Oxygen is considered by many to be the primary growth-limiting factor for hydrocarbon degrading bacteria.
Does anaerobic biodegradation require oxygen?
Anaerobic digestion is a process through which bacteria break down organic matter—such as animal manure, wastewater biosolids, and food wastes—in the absence of oxygen.
What are the types of biodegradation?
There are four biodegradation environments for polymers and plastic products: soil, aquatic, landfill and compost. Each environment contains different microorganisms and has different conditions for degradation. In soil, fungi are mostly responsible for the degradation of organic matter including polymers.
How many types of biodegradation are there?
Mechanisms. The process of biodegradation can be divided into three stages: biodeterioration, biofragmentation, and assimilation. Biodeterioration is sometimes described as a surface-level degradation that modifies the mechanical, physical and chemical properties of the material.
What is the difference between anaerobic digestion and composting?
The crucial difference is that composting is the decomposition of organic matter in the presence of air (oxygen) and anaerobic digestion (AD) is the decomposition of organic matter, without air (and most importantly oxygen) present.
How does an aerobic digester work?
Aerobic digestion is the degradation of the organic sludge solids in the presence of oxygen. The oxygen is introduced as fine bubbles of air into the reactor. The micro-organisms in the sludge convert the organic material to carbon dioxide and water, and the ammonia and amino species to nitrate.
What is an example of biodegradation?
Basically, organic (carbon-based) material is changed through chemical processes from complex molecules into simpler molecules, eventually returning the molecules into the environment. For example, a banana peel can be reduced from cellulose to water, carbon dioxide gas, and humus in a compost pile.
What is the difference between biodegradable waste and non-biodegradable waste?
Biodegradable wastes are those substances that degrade or break down naturally. Non-biodegradable wastes are those substances that do not degrade easily. Materials like plants, animals, their waste, paper, fruits, vegetables fall under the category of biodegradable substances.
What's the difference between biodegradable and compostable?
The main difference between the two is that biodegradable material can take an undetermined time to break down. In contrast, Compostable materials will decompose into natural elements within a specific time frame. However, it will require certain conditions like those found in industrial composting facilities to do so.
What is the difference between bioremediation and biodegradation?
Bioremediation is the act of treating waste or pollutants by the use of microorganisms (as bacteria) that can break down the undesirable substances. The decomposition of organic materials in the environment through microbial action then it is called as Biodegradation.
What factors affect biodegradability?
The surface conditions (surface area, hydrophilic, and hydrophobic properties), the first order structures (chemical structure, molecular weight and molecular weight distribution) and the high order structures (glass transition temperature, melting temperature, modulus of elasticity, crystallinity and crystal structure ...
Which organism is most important in biodegradation?
microorganismsIn the environmental context, generally microorganisms are the most important agents of biodegradation. Although extensive degradation of some xenobiotic chemicals can occur in mammals (usually in the liver), they are not particularly important in degradation of environmental pollutants.
What is Aerobic and Anaerobic Biodegradation?
Aerobic biodegradation involves the breakdown of organic matter by micro-organisms in the presence of oxygen. Anaerobic biodegradation is the breakdown of organic matter by micro-organism where oxygen is not present.
You can make a difference!
BioGreen provides world’s best biodegradable and compostable plastics which adheres to all International and Indian standards of testing for biodegradable plastics.
What is the difference between aerobic and anaerobic respiration?
The primary difference between aerobic and anaerobic respiration is the presence or absence of oxygen during the processes. More detailed differences are between the two are as follows: Oxygen is present when this form of respiration takes place. Oxygen is absent when this form of respiration takes place. Gases are exchanged in this form of ...
Why is anaerobic respiration used?
During heavy or intensive exercise such as running, sprinting, cycling or weight lifting, our body demands high energy. As the supply of oxygen is limited, the muscle cells inside our body resort to anaerobic respiration to fulfil the energy demand.
What are the by-products of anaerobic respiration?
Consequently, the by-products of this process are lactic acid and ATP.
What is the process of respiration?
Cellular respiration is a process that takes place inside the cells where energy is released by the breakdown of glucose molecules. The process can be conveniently divided into two categories based on the usage of oxygen, namely aerobic and anaerobic respiration.
What is the process of producing the energy required by cells using oxygen?
Aerobic respiration, as the name suggests, is the process of producing the energy required by cells using oxygen. The by-product of this process produces carbon dioxide along with ATP – the energy currency of the cells.
Which organisms use aerobic respiration?
In other organisms, it occurs during heavy activities. However, it is a misconception that humans and other multicellular organisms use only aerobic respiration.
Does lactic acid occur during anaerobic respiration?
This is disproven by the fact that our muscles, during vigorous exercises, undergo anaerobic respiration, where lactic acid is produced as the waste-byproduct instead of carbon dioxide. Also Read: Difference between Glycolysis and Krebs Cycle.
What are the steps of anaerobic biodegradation?
Anaerobic biodegradation takes place in the absence of oxygen. Its pathway has four major steps: hydrolysis, acidogenesis, acetogenesis and methanogenesis. Organic substances are subjected to anaerobic digestion and converted into carbon dioxide and methane.
What is the difference between biodegradation and bioremediation?
The key difference between biodegradation and bioremediation is that biodegradation is a natural process that occurs in the environment while bioremediation is an engineered technique applied by humans to clean the environment. Both processes are governed mainly by the microorganisms. 1.
How are pollutants degraded?
The majority of the pollutants are degraded completely by aerobic biodegradation in the presence of oxygen. Anaerobic biodegradation is done under oxygen-absent environments. Bioremediation is a biotechnological approach which uses biological agents to clean contaminants in the environment.
What is the ability of microorganisms to decompose organic materials in the environment?
Biodegradation is the ability of microorganisms to decompose organic materials in the environment. Bacteria and fungi are well-known decomposers in the soil which help to recycle elements in the environment. The majority of the pollutants are degraded completely by aerobic biodegradation in the presence of oxygen.
What are the two modes of biodegradation?
There are two modes of biodegradation: aerobic biodegradation and anaerobic biodegradation . Aerobic biodegradation is done by aerobic microorganisms when the adequate supply of oxygen is available for their activity. Aerobic biodegradation is a rapid method which degrades the contaminants completely when compared to anaerobic biodegradation.
What is ex situ bioremediation?
This kind of bioremediation is known as ex situ bioremediation. Bioremediation is a biotechnological approach for controlling environmental pollution. The natural biodegradable ability of biological agents such as bacteria, fungi, plants is explored in bioremediation.
What is the process of decomposing organic materials in the environment by microorganisms?
Biodegradation is the process of decomposing organic materials in the environment by microorganisms. Bioremediation is a waste management technique which uses biological agents to clean the contaminants in the environment. Nature of the Process. It’s a natural process that happens without human intervention.
What is the difference between aerobic and anaerobic wastewater treatment?
The key difference between aerobic and anaerobic wastewater treatment is that in aerobic wastewater treatment, treatment tanks are constantly supplied with oxygen while , in anaerobic wastewater treatment, gaseous oxygen is prevented from entering into the system.
How does aerobic wastewater treatment work?
Aerobic wastewater treatment tanks are constantly supplied with oxygen. It is been done by circulating air through the tanks. For effective functioning of aerobic organisms, sufficient amounts of oxygen should be present in the aerobic tanks at all times.
What is produced during anaerobic digestion?
During anaerobic digestion, methane and carbon dioxide are produced. Methane is a biogas. Hence, anaerobic digestion process can be used to produce biogas which can be utilized as electricity. Anaerobic wastewater treatment process occurs via four major steps named: hydrolysis, acidogenesis, acetogenesis, and.
What is the advantage of anaerobic digestion?
The big advantage of anaerobic digestion is it's ability to produce the renewable energy-source methane (the main constituent of biogas) which can power the process of anaerobic digestion (AD), whereas aerobic systems always require an input of energy to run them.
Why is aerobic digestion so popular?
This process is popular because it is able to stabilize the water with little biomass production. Anaerobic treatment occurs in many different stages. Aerobic digestion is present everywhere that organic matter decomposes in the open air with an abundant air circulation.
What are the two types of wastewater treatment systems?
There are 2 major types of systems used for wastewater treatment: aerobic and anaerobic systems. Each has different uses along with pros and cons. Whether it is aerobic or anaerobic treatment, each treatment system has its place in the world today.
What is the study of microorganisms?
microbiology ( the study of microorganisms) or. respiration systems in man and mammals generally. In this article we compare (1) aerobic digestion with anaerobic digestion (2), in the context of microbiology and wastewater treatment. This amounts to comparing aerobic digestion, hitherto referred to as “composting” with anaerobic digestion, ...