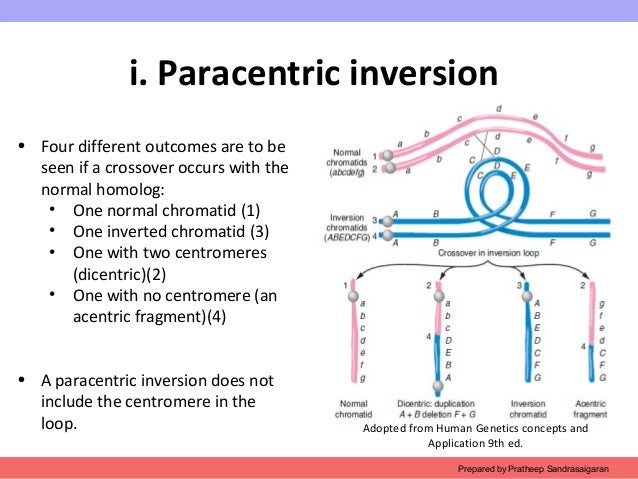
Genetic anomalies involve one gene and Chromosomal anomalies involve more than one gene and may involve thousands of genes. How are Genetic and Chromosomal Disorders confirmed? They are confirmed by analysis of the child's body tissues. Amniocentesis may be able to detect some genetic and chromosomal abnormalities before birth.
What is the difference between chromosomal and genetic disorders?
Genetic disorders arise due to the changes occur in the genome of an organism. There are three types of genetic disorders including single gene mutations, complex disorders and chromosomal disorders. Hence, chromosomal disorders are a type of genetic disorders.
What is the difference between a normal and an abnormal gene?
A single gene defect usually does not cause the chromosome structure or number to be abnormal. Similarly, a person can have normal genes; however, if the person has extra copies of genes due to a chromosome abnormality, then those extra copies can cause the genes to not work properly. This is an important distinction to make.
What is chromosomal abnormality?
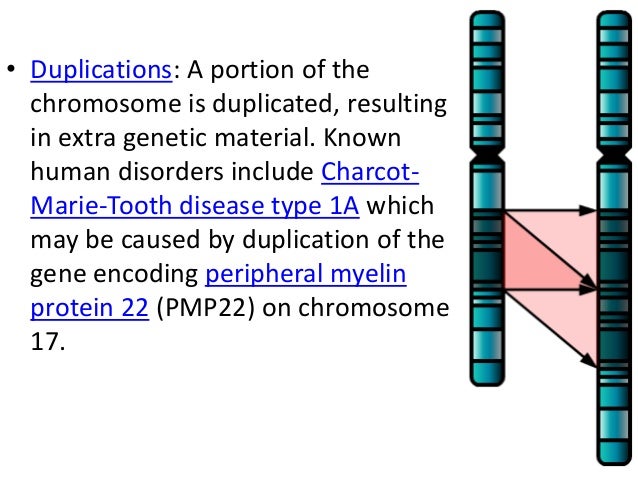
A chromosomal abnormality affects an entire chromosome and many or all of the genes that make it up. The most common chromosomal abnormalities are duplications, where an individual has an extra copy of a chromosome. Deletions are when an individual is missing a chromosome or piece of chromosome.
What is the difference between a genome and a chromosome?
A genome is the complete set of genes, arranged in chromosomes, for a particular species. Genetic defects and chromosomal abnormalities are both sometimes called "genetic conditions" or "genetic disorders," but the difference lies in how much of the DNA is actually affected. Deoxyribonucleic acid, or DNA, is the protein molecule that forms genes.
What is the difference between genetic and chromosomal?
Any condition caused by a gene change is called a genetic condition (also called a genetic disorder). Some types of genetic conditions are caused by problems in one or more chromosomes. Chromosomes are the structures that hold genes. Each person has 23 pairs of chromosomes, or 46 in all.
Are all chromosomal abnormalities genetic?
Although it is possible to inherit some types of chromosomal abnormalities, most chromosomal disorders (such as Down syndrome and Turner syndrome) are not passed from one generation to the next. Some chromosomal conditions are caused by changes in the number of chromosomes.
What are genetic abnormalities?
Genetic abnormalities are conditions caused by changes to the genes or chromosomes. Inherited disorders are caused by gene mutations. These include disorders such as cystic fibrosis, sickle cell disease, and Tay-Sachs disease.
What are examples of genetic abnormalities?
Genetic DisordersGenetic Disorders. Sickle Cell Disease.Cystic fibrosis. Cystic Fibrosis Liver Disease.Brain, Nerves and Spine. Huntington's Disease.Cleft lip and palate. Cleft Lip and Palate.
What are the three types of genetic abnormalities?
There are three types of genetic disorders:Single-gene disorders, where a mutation affects one gene. Sickle cell anemia is an example.Chromosomal disorders, where chromosomes (or parts of chromosomes) are missing or changed. ... Complex disorders, where there are mutations in two or more genes.
Can you fix chromosomal abnormalities?
In many cases, there is no treatment or cure for chromosomal abnormalities. However, genetic counseling, occupational therapy, physical therapy and medicines may be recommended.
What are the 3 most common chromosomal abnormalities?
Some of the most common chromosomal abnormalities include: Down's syndrome or trisomy 21. Edward's syndrome or trisomy 18. Patau syndrome or trisomy 13.
What can cause genetic abnormalities?
Different things can cause a genetic disorder, such as:a change (mutation) in one gene on a chromosome.a missing part of a chromosome (called a deletion)genes shifting from one chromosome to another (called a translocation)an extra or missing chromosome.too few or too many sex chromosomes.
What is the most common chromosomal abnormality?
The most common type of chromosomal abnormality is known as aneuploidy, an abnormal chromosome number due to an extra or missing chromosome. Most people with aneuploidy have trisomy (three copies of a chromosome) instead of monosomy (single copy of a chromosome).
What are the top 5 genetic disorders?
What You Need to Know About 5 Most Common Genetic DisordersDown Syndrome. ... Thalassemia. ... Cystic Fibrosis. ... Tay-Sachs disease. ... Sickle Cell Anemia. ... Learn More. ... Recommended. ... Sources.
Can you have a healthy pregnant after chromosomal abnormalities?
While parents who carry chromosomal rearrangements are at increased risk to have further miscarriages or babies born with health problems, they can also produce healthy children.
What are chromosomal abnormalities?
A chromosomal abnormality, or chromosomal aberration, is a disorder characterized by a morphological or numerical alteration in single or multiple chromosomes, affecting autosomes, sex chromosomes, or both.
Is a chromosomal disorder a genetic disorder?
Genetic disorders can be: Chromosomal: This type affects the structures that hold your genes/DNA within each cell (chromosomes). With these conditions, people are missing or have duplicated chromosome material. Complex (multifactorial): These disorders stem from a combination of gene mutations and other factors.
What is the main cause of chromosomal abnormalities?
Abnormal chromosomes most often happen as a result of an error during cell division. Chromosome abnormalities often happen due to one or more of these: Errors during dividing of sex cells (meiosis) Errors during dividing of other cells (mitosis)
Are birth defects always genetic?
For most birth defects, we think they are caused by a complex mix of factors. These factors include our genes (information inherited from our parents), our behaviors, and things in the environment. But, we don't fully understand how these factors might work together to cause birth defects.
What are the chances of having a baby with a chromosomal abnormality?
While most babies are born healthy, approximately 3-5% will be affected with certain birth defects or genetic conditions. In all pregnancies, tests are offered that can tell if the pregnancy may be at high risk for a condition called a chromosome abnormality. Decisions about testing in pregnancy are personal.
What is the difference between genetic defects and chromosomal abnormalities?
Genetic defects and chromosomal abnormalities are both sometimes called "genetic conditions" or "genetic disorders," but the difference lies in how much of the DNA is actually affected.
What is a chromosomal abnormality?
Affecting Many. A chromosomal abnormality affects an entire chromosome and many or all of the genes that make it up. The most common chromosomal abnormalities are duplications, where an individual has an extra copy of a chromosome. Deletions are when an individual is missing a chromosome or piece of chromosome.
What is the purpose of genes in science?
Education. |. Science. By Angela Libal. Genes are the instructions for building and maintaining an organism. Chromosomes are the orderly chains these genes form during cell division. A genome is the complete set of genes, arranged in chromosomes, for a particular species. Genetic defects and chromosomal abnormalities are both sometimes called ...
How many genes are in a human genome?
The typical human genome contains 46 chromosomes, or 23 pairs, half inherited from each genetic parent at conception. The DNA for all 46 chromosome resides in every cell that has a nucleus. Humans' 46 chromosomes are made up of about 25,000 individual genes.
What is abnormality in biology?
Depending on which chromosomes and component genes are affected, an abnormality may cause a disorder, with multiple physical and intellectual challenges, or simply an anomaly, with effects that may remain unnoticed for most or all of an individual's life. Additionally, each affected individual is still an individual, ...
Why is it called a single gene defect?
When differentiating genetic defects from chromosomal abnormalities, it can be less confusing to call genetic defects "single-gene defects" because they involve mutations in individual genes. Though the affected gene may not give proper instructions, the individual's overall chromosome number and structure are normal.
What is a deletion in chromosomes?
Deletions are when an individual is missing a chromosome or piece of chromosome. In translocation abnormalities, different chromosomes either exchange portions with one another, or a portion of one chromosome splits off and gets stuck to another without an exchange.
How many genes are in a human chromosome?
There are approximately 25,000 genes contained on the 46 chromosomes in each cell of the human body. This means that one chromosome contains thousands of genes. A person can have normal chromosomes in number and structure, but still have a disease or condition caused by a mutation in one or more of the genes on the chromosomes.
Can a single gene defect cause a chromosome to not work?
A single gene defect usually does not cause the chromosome structure or number to be abnormal. Similarly, a person can have normal genes; however, if the person has extra copies of genes due to a chromosome abnormality, then those extra copies can cause the genes to not work properly.
What is missing in Turner syndrome?
Sometimes part of a chromosome is missing, as in Turner syndrome, where part of a female’s X chromosome is missing. Additionally, the number of “sex” chromosomes (pair 23: a boy has one X and one Y, a girl has 2 X’s) can vary and some arrangements may be more problematic than others.
What is a NIPTS test?
The NIPTS test usually looks at some of the most common chromosomal disorders. These occur when one chromosome in the pair of two is either entirely or partially duplicated. This is a “trisomy”: three copies rather than the normal two. Doctors never detect some abnormalities.
What is genetic disorder?
When people refer to genetic disorders, they are usually referring to a problem that can be traced back to one of these changes in the DNA sequence. Meanwhile, chromosomal disorders (which are also genetic disorders) often refer to full or partial chromosomes that are missing, repeated, or otherwise altered.
Why do we find out about common ones?
But for now, we find out about common ones because babies can survive with them. This gives scientists a chance to conduct research and identify the problem.
How many pairs of chromosomes are there in the human genome?
We also know that 23 pairs of chromosomes comprise the human genome. These are the physical structures containing our DNA and other structural proteins. Sometimes small problems with the DNA sequence can cause big changes. A single deleted or incorrectly assembled sequence can cause essential proteins to go unproduced.
What is chromosomal abnormality vs genetic disorder?
Chromosomal abnormality vs. genetic disorder. A genetic disorder is any difference in a someones DNA that causes a problem physically or mentally. Understanding what our DNA (i.e. the human genome) actually does is a hot topic of scientific research because we still don’t know what most of it is used for. But we do know how much DNA there is and ...
Why are forums important?
Forums can be a great outlet for sharing experiences and learning new information about the process of parenthood. But sometimes they can, unfortunately, be a vehicle for spreading misinformation. Especially when science jargon gets in the way.
What are chromosome abnormalities?
There are many types of chromosome abnormalities. However, they can be organized into two basic groups: numerical abnormalities and structural abnormalities.
What are chromosomes?
Chromosomes are the structures that hold genes. Genes are the individual instructions that tell our bodies how to develop and function; they govern physical and medical characteristics, such as hair color, blood type and susceptibility to disease.
Where are chromosomes found in the body?
Your body has many different kinds of cells, such as skin cells, liver cells and blood cells. In the center of most cells is a structure called the nucleus. This is where chromosomes are located.
How many chromosomes do humans have?
The typical number of chromosomes in a human cell is 46: 23 pairs, holding an estimated total of 20,000 to 25,000 genes. One set of 23 chromosomes is inherited from the biological mother (from the egg), and the other set is inherited from the biological father (from the sperm).
How do scientists study chromosomes?
For a century, scientists studied chromosomes by looking at them under a microscope. In order for chromosomes to be seen this way, they need to be stained. Once stained, the chromosomes look like strings with light and dark "bands," and their picture can be taken. A picture, or chromosome map, of all 46 chromosomes is called a karyotype. The karyotype can help identify abnormalities in the structure or the number of chromosomes.
What is the purpose of a comparison test?
The comparison can be used to find chromosomal abnormalities where the two samples differ. One such method is called noninvasive prenatal testing. This is a test to screen a pregnancy to determine whether a baby has an increased chance of having specific chromosome disorders.
What is a picture of all 46 chromosomes called?
A picture, or chromosome map, of all 46 chromosomes is called a karyotype. The karyotype can help identify abnormalities in the structure or the number of chromosomes. To help identify chromosomes, the pairs have been numbered from 1 to 22, with the 23rd pair labeled "X" and "Y.".
