Difference Between White Matter and Gray Matter
- The basic colourations of both tissues have been the basis for the naming, and their colours can be considered to distinguish the two.
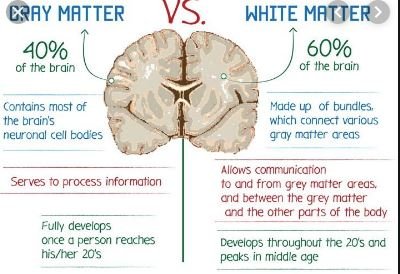
- Gray matter forms the processing units of sensory function while white matter forms the connections among gray matter units.
- The white matter is slightly more prominent (60%) than gray matter (40%) in the quantity.
Why does white matter appear different from gray matter?
White matter is a white nerve tissue in the central nervous system that is composed of myelinated nerve fibers or axons. Grey matter is a greyish nerve tissue in the central nervous system that is composed of nerve cell bodies and dendrites. The white matter looks different because the nerve cells are covered in myelinated coloring casing that help the nerve cells to communicate
Is grey matter or white matter more important for IQ?
They found that people with high IQ scores had significantly more grey matter in 24 of the regions than people with lower scores. Why is white matter important? The white matter is white because of the fatty substance (myelin) that surrounds the nerve fibers (axons). This myelin is found in almost all long nerve fibers, and acts as an electrical insulation.
What does gray white matter differentiation mean?
Grey-white differentiation refers to the appearance of the interface between cerebral and cerebellar white matter and grey matter on brain CT and MRI.. The term is most often used when trying to differentiate cytotoxic from vasogenic oedema. cytotoxic oedema (see ionic oedema), where there is a loss of grey-white differentiation (i.e. inability to distinguish white matter from grey matter ...
Is the cerebellum white matter or grey matter?
The white matter of the cerebellum is also present in its deep part. In the cerebellum, the white matter contains four cerebellar nuclei: dentate nucleus, globose nucleus, emboliform nucleus, and fastigial nucleus. In the spinal cord, the white matter is present on the superficial side and the grey matter is in the center of white matter.

What are the two main differences between grey matter and white matter?
What is the function of gray matter and white matter? Gray matter largely functions to receive information and regulate outgoing information, as it contains the cell bodies of neurons. White matter, which is largely composed of axons, serves to transmit signals to other regions of the brain, spinal cord, and body.
What is the function of grey matter and white matter?
Together, the gray and white matter of your brain and spinal cord help form spinal tracts. These pathways send nerve signals from your brain to the rest of your body. Knowing the most common tracts can help you discern the source of your injury.
What is more important grey or white matter?
The central nervous system is made up of grey matter and white matter. However, grey matter plays the most significant part in allowing humans to function normally daily.
What is the difference between white matter and gray matter quizlet?
The Gray Matter is a gray-colored zone that surrounds the hollow central cavity of the CNS. A mixture of neuron cell bodies of interneurons and motor neurons and neuroglia. Synapses occurs in gray matter. The White Matter contains no neuron cell bodies but millions of axons and neuroglia.
What happens if you have too much gray matter?
Grey Matter Disorders If the plaque continues to grow, this can cause a significant decline in cognitive functions and a loss of memory, known as Alzheimer's disease. Aside from a loss in cognitive functioning, grey matter decline can lead to motor function issues such as losing control of fine motor skills.
What is white matter in the brain responsible for?
Function. White matter essentially functions in affecting learning and brain functions, modulating the distribution of action potential, and coordinating communication between the different brain regions.
What kills grey matter?
Grey matter decreases when neurons die. A common cause is a stroke or brain hemorrhage. Neurons also die naturally with age, although they are the longest living cells in the body. Unnatural causes of neuronal death include Parkinson's disease, Alzheimer's disease, and traumatic brain injury.
What happens if your white matter is damaged?
White matter disease is an umbrella term for damage to your brain's white matter caused by reduced blood flow to the tissue. It can cause issues with memory, balance and mobility. People who have risk factors for cardiovascular disease also have a greater risk of developing white matter disease.
What is function of gray matter?
The grey matter serves to process information in the brain. Structures within the grey matter process signals generated in the sensory organs or other areas of the grey matter. This tissue directs sensory (motor) stimuli to nerve cells in the central nervous system where synapses induce a response to the stimuli.
What is a white matter?
White matter is found in the deeper tissues of the brain (subcortical). It contains nerve fibers (axons), which are extensions of nerve cells (neurons). Many of these nerve fibers are surrounded by a type of sheath or covering called myelin. Myelin gives the white matter its color.
What is gray matter made up of?
Gray matter consists primarily of neuronal cell bodies, or soma. This a spherical structure that houses the neuron's nucleus.
What do grey and white matter in brain represent?
The white matter refers to those parts of the brain and spinal cord that are responsible for communication between the various gray matter regions and between the gray matter and the rest of the body. In essence, the gray matter is where the processing is done and the white matter is the channels of communication.
What is the function of gray matter in the spinal cord?
The gray matter of the spinal cord is a vital part of the central nervous system and is involved in muscle movement, sensory information like fine touch, proprioception and vibration, and more.
How is grey matter and white matter distribution in brain?
In the cerebrum and cerebellum, white matter is predominantly found in deeper areas – with gray matter coating the white matter - see figure 1. Other gray matter structures, like the basal ganglia, are embedded within this white matter core. The brain's fluid-filled ventricles are also found within the white matter.
What is the function of white matter quizlet?
White matter in brain is known as the cerebral white matter. The white matter deep to the cortical gray matter is responsible for communication between cerebral areas and between the cerebral cortex and lower CNS.
What is the function of white matter in the brain?
White matter in the brain serves to connect regions of the same hemisphere, opposite hemisphere, lower brain centers, or spinal cord. In doing so,...
What is the difference between gray matter and white matter?
The difference between gray and white matter has to do with the presence or absence of myelin in the nervous tissue. Myelin is a fatty substance wh...
What is the function of gray matter and white matter?
Gray matter largely functions to receive information and regulate outgoing information, as it contains the cell bodies of neurons. White matter, wh...
Difference Between Gray and White Matter
The terms white matter and gray matter refer to different components of nervous tissue found in the brain and spinal cord, which make up the central nervous system (CNS). Neurons, specialized cells which send and respond to electrical impulses, make up a large portion of the nervous system and are responsible for forming the basis of the CNS.
Location of Gray Matter and White Matter
Within the CNS, gray and white matter are localized in distinct regions. The gray matter of the spinal cord is found deep to the white matter, and in cross section, resembles a butterfly or the letter H. The brain stem shows a similar organization, with additional gray matter nuclei, or neuron cell bodies, distributed within the white matter.
Gray Matter vs White Matter Function
Along with differences in myelination, gray and white matter in the brain and spinal cord have different functions. The cerebrum consists of an outer layer of grey matter called the cerebral cortex, which surrounds an inner mass of white matter.
What is gray matter?
Gray matter, named for its pinkish-gray color, is home to neural cell bodies, axon terminals, and dendrites, as well as all nerve synapses. This brain tissue is abundant in the cerebellum, cerebrum, and brain stem. It also forms a butterfly-shaped portion of the central spinal cord.
What is the white matter of the brain?
White Matter in the Brain and Spinal Cord. The white matter of your brain and spinal cord is composed of bundles of axons. These axons are coated with myelin, a mixture of proteins and lipids, that helps conduct nerve signals and protect the axons. White matter's job is to conduct, process, and send nerve signals up and down the spinal cord.
What are the gray and white matter of the brain and spinal cord?
Together, the gray and white matter of your brain and spinal cord help form spinal tracts. These pathways send nerve signals from your brain to the rest of your body. Knowing the most common tracts can help you discern the source of your injury. Those tracts include:
How does damage to the white matter of the brain affect the ability to move?
Damage to the white matter of your brain or spinal cord can affect your ability to move, use your sensory faculties, or react appropriately to external stimuli . Some people with damaged white matter suffer deficits in reflexive reactions.
What are the effects of the ventral gray horn?
A problem with the dorsal gray horn may affect your brain's ability to interpret sensory information, while issues with the ventral gray horn interfere with your body's ability to receive motor information; paralysis, tingling, and muscle weakness are often the products of damage to the ventral gray horn.
What are gray matter and white matter?
Both white matter and gray matter are terms that relate with the cells of the brain. A cross section of a brain will show these cells in their respective colours, and they are so named as white and gray matter. However, the two types of brain tissues become white and gray after being dipped in preservatives as the live colours are slightly different with the presence of blood. Gray and white matters are the two main types of brain cells and the functions of these vary from each other. Mainly, the processed signals by gray matter are being passed through white matter inside the brain.
What is gray matter?
Gray matter is the most important component of the nervous system that is composed of regions of the brain responsible for sensory perception, memory, emotions, speech, and for almost all the muscle control. Gray matter is composed of neuronal cell bodies, glial cells, and capillaries. However, the presence of the nuropil, which is composed of unmyelinated axons and dendrites, is very important to notice. It would also be important to state that most of the neurones are myelinated in gray matter except in the nuropil. The live gray matter is mainly brownish-grey in colour due to the presence of blood capillaries and neuronal cell bodies. It is very difficult to understand the mechanisms of sensory processes taking place in different regions of gray matter, yet the scientists have identified the main regions involved in hearing, seeing, muscle controlling, thinking, and speaking. Therefore, gray matter has been sometimes referred as a set of computers with different specialities.
Why do brain cells turn white and gray?
However, the two types of brain tissues become white and gray after being dipped in preservatives as the live colours are slightly different with the presence of blood. Gray and white matters are the two main types of brain cells and the functions of these vary from each other. Mainly, the processed signals by gray matter are being passed ...
What are the three major tracts of white matter?
There are three major tracts or bundles of white matter based on the regions that they connect; they are known as Projection (connect vertically between higher and lower parts), Commissural (connect between the two cerebral hemispheres), and Associate (connect different regions of the same cerebral hemisphere).
Why is the brain white?
Even though the tissue is named as white, the live colour is pinkish white due to the presence of blood. The usual preservative, formaldehyde, makes the white matter to be white.
What are the main regions of gray matter?
It is very difficult to understand the mechanisms of sensory processes taking place in different regions of gray matter, yet the scientists have identified the main regions involved in hearing, seeing, muscle controlling, thinking, and speaking.
How long is white matter?
The quantifying of white matter is mainly done by considering the total length of the composed neurones. The total length of white matter in a male is more than 175,000 kilometres while a female has almost 150,000 kilometres long white matter cells at the age of 20 years.
What is the difference between gray matter and white matter?
The difference between gray matter and white matter is that gray matter is mainly composed of cell bodies, axon ends, and dendrites while white matter is mainly composed of myelinated axons. The gray and white matter of the brain and spinal cord help build the spine. These pathways carry neurological information from your mind to the rest of your body.
What is Gray Matter?
The gray matter is essentially made out of neuronal cell bodies and unmyelinated axons. Axons are the cycles that stretch out from neuronal cell bodies, conveying signals between those bodies. In the gray matter, these axons are essentially unmyelinated, which means they are not covered by a whitish-shaded, greasy protein called myelin. Gray matter is used to process data in the mind.
What is the function of white matter?
White matter’s responsibility is to lead, process, and convey nerve messages here and they’re the spinal string. Damage to the white matter of the brain or spinal cord can affect your ability to move, use your tactile resources, or respond correctly to external improvements. Some people with the impaired white matter have insufficient reflexes.
Why is white matter called white matter?
White matter is named for its light appearance coming about because of the lipid content of myelin. Be that as it may, the tissue of the newly sliced cerebrum seems pinkish-white to the unaided eye since the myelin is made out of lipid tissue veined with vessels. Its white tint in the pre-arranged sample is due to its typical protection in formaldehyde. The white matter of your mind and the spinal rope is made out of heaps of axons.
Where does the gray matter cycle signal come from?
The internal structure of the gray matter cycle signal is generated by the gray matter tangible organs or different spaces of the gray matter. This organization coordinates the tangible (engine) improvement of nerve cells in the focal sensory system, where the neural connections respond to the upgrade. These signs arrive at the gray matter through myelinated axons that make up the main part of the white matter in the frontal cortex, cerebellum, and spine.
What percentage of the brain is gray matter?
Gray matter accounts for 40% of the brain, and white matter accounts for 60% of the brain. m
What substance circulates the data recovered from the white matter and sends the direction back to the effector through the white?
Gray substance circulates the data recovered from the white matter and sends the direction back to the effector through the white matter.
What is the difference between grey matter and white matter?
What is the difference between grey and white matter in the brain? Alzheimer’s is a grey matter disease, and white matter has a central role in how the disease develops and progresses. The central nervous system of the brain is made up of two kinds of tissue: grey matter and white matter.
What is the grey matter?
The grey matter contains the cell bodies, dendrites and the axon terminals, where all synapses are. The white matter is made up of axons, which connect different parts of grey matter to each other.
What percentage of the brain is grey matter?
Grey matter takes up about 40 percent of the brain. The senses of the body — speech, hearing, feelings, seeing and memory — and control of the muscles are all part of the grey matter’s functions. In early or younger onset Alzheimer’s disease and atypical Alzheimer’s disease, the deterioration of white matter could be an early marker ...
Can white matter be seen on MRI?
White matter lesions from damaged white matter in the brains of elderly individuals can be seen on MRI testing. The cause of these white matter lesions are generally linked to diseases affecting the blood vessels in the brain, and identifying the specific disease leads to a particular treatment.
Does aging cause gray matter volume to decrease?
According to a study by Dr. Daryl Gress in the American Journal of Neuroradiology, normal aging was associated with declines in gray matter volume that were observed specifically in the hippocampus area of the brain in Alzheimer’s cases.
What is grey matter?
Grey matter. The grey matter consists of the soma or the cell bodies of neurons that are present in the brain and the spinal cord. It also contains dendrites, unmyelinated axons, glial cells: the astrocytes and the oligodendrocytes, and some capillaries.
How does white matter work?
It works as a relay and transfers the action potential from one part of the nervous system to another. It also plays an important role in modulating the distribution of action potential.
What is the grey column?
It is present throughout the spinal cord and is referred to as the grey column. The grey column is divided into three separate columns: anterior grey column, posterior grey column, and lateral grey column. Together these columns make an “H” shape or “butterfly” shape as previously described.
Where is grey matter found?
The chief contents of grey matter are unmyelinated neurons and neuronal cell bodies which are present in the brain, the brainstem, and the spinal cord. In the brain, the grey matter is present at the outer side of the cerebrum and the cerebellum which are called the cerebral cortex and cerebellar cortex, respectively. Grey matter is also present in the deeper parts of the brain in the form of nuclei embedded in the white matter. In the midbrain, it consists of several structures including the thalamus, hypothalamus, globus pallidus, and basal ganglia.
What are the functions of the grey matter?
The higher brain functions such as decision-making, memory, learning, and self-control are also performed in grey matter regions of the brain.
Where is the white matter in the brain?
In the brain, white matter is present in the deeper parts, while the grey matter is present in the outer superficial part. In the white matter of the brain, many important grey matter structures are embedded such as the thalamus, hypothalamus, and basal ganglia.
Does cannabis increase grey matter?
Cannabis use is also associated with an increase in grey matter volume of the cerebellum. According to some studies, 3D platformer games are associated with increased grey matter. Meditation and mind fullness techniques are also associated with changes in the grey matter structure.