What are the three levels of Health Promotion?
First, the central concepts are defined and the logical relations between them are spelt out. A preliminary conclusion is that there is a logical difference between health and disease, which makes health promotion and disease prevention two distinct endeavours. However, since disease is defined in relation to health, as those kinds of internal processes and states that typically …
What are the three levels of disease prevention?
As a discipline, preventive medicine has traditionally been described to encompass primary, secondary, and tertiary prevention. The fields of preventive medicine and public health share the objectives of promoting general health, preventing disease, and applying epidemiologic techniques to these goals. This paper discusses a conceptual approach between the overlap …
What is the primary level of Health Promotion?
Oct 18, 2017 · Effective prevention requires data, critical thinking, engineering, enforcement, and clear instruction. Health promotion is a process of enabling the community to create capacity enhancement in ways that extend beyond repair and risk reduction. Enhanced capacity makes it easier to repair.
What are the three levels of prevention?
Mar 16, 2020 · Defined by the World Health Organization, health promotion is: Disease prevention differs from health promotion because it focuses on specific efforts aimed at reducing the development and severity of chronic diseases and other morbidities. Wellness is related to health promotion and disease prevention.

What is health promotion and disease prevention?
Health promotion is the process of improving and protecting the health of the public, including individuals, populations, and communities. Health promotion and disease prevention can be achieved through planned activities and programs that are designed to improve population health outcomes.
What is the main difference between prevention and promotion?
Prevention is essentially a medical action that deals with the individual or risk groups as well as the observance of physical health. In contrast with this, health promotion is concerned with the whole population in its daily life and not only selected individuals or groups (von Troschke 2004).
How does health promotion health education and disease prevention differ?
Health promotion is concerned with promoting a healthy lifestyle and preventing illness and it includes social, psychological, political, and educational factors. Health education is concerned with informing people about health issues.
What is the meaning of health promotion?
Health promotion is the process of enabling people to increase control over, and to improve, their health. It moves beyond a focus on individual behaviour towards a wide range of social and environmental interventions.
What are the prevention of diseases?
Primary prevention refers to actions aimed at avoiding the manifestation of a disease (this may include actions to improve health through changing the impact of social and economic determinants on health; the provision of information on behavioral and medical health risks, alongside consultation and measures to ...
What are examples of health promotion?
Promoting Health for AdultsHelping People Who Smoke Quit.Increasing Access to Healthy Foods and Physical Activity.Preventing Excessive Alcohol Use.Promoting Lifestyle Change and Disease Management.Promoting Women's Reproductive Health.Promoting Clinical Preventive Services.Promoting Community Water Fluoridation.More items...
What is the difference between health and health promotion?
Health education involves voluntary changes in behavior through awareness, knowledge, skills, beliefs, attitudes, and values, whereas health promotion utilizes approaches that compel individuals to change their behaviors.Sep 28, 2021
What is the difference between health promotion and hygiene promotion?
The difference between Hygiene Promotion and health promotion; Hygiene Promotion is more specific and more targeted than health promotion. It focuses on the reduction – and ultimately the elimination – of diseases and deaths that originate from poor hygiene conditions and practices.
What is the difference between health promotion and health communication?
Usually, in a public health perspective, health promotion is the goal, communication is the tool to reach the goal.
Why health promotion and disease prevention is important nursing?
The Importance of Health Promotion and Disease Prevention. Preventive health is growing in popularity as people seek to improve their overall health and wellness by making better choices. Nurse practitioners are greatly involved with this effort, since preventive health can reduce and prevent disease.
What are the 3 types of prevention?
Primary Prevention—intervening before health effects occur, through.Secondary Prevention—screening to identify diseases in the earliest.Tertiary Prevention—managing disease post diagnosis to slow or stop.
What is the importance of disease prevention?
Disease prevention involves actions to reduce or eliminate exposure to risks that might increase the chances that an individual or group will incur disease, disability, or premature death.
How does disease prevention differ from health promotion?
Disease prevention differs from health promotion because it focuses on specific efforts aimed at reducing the development and severity of chronic diseases and other morbidities. Wellness is related to health promotion and disease prevention.
What is health promotion?
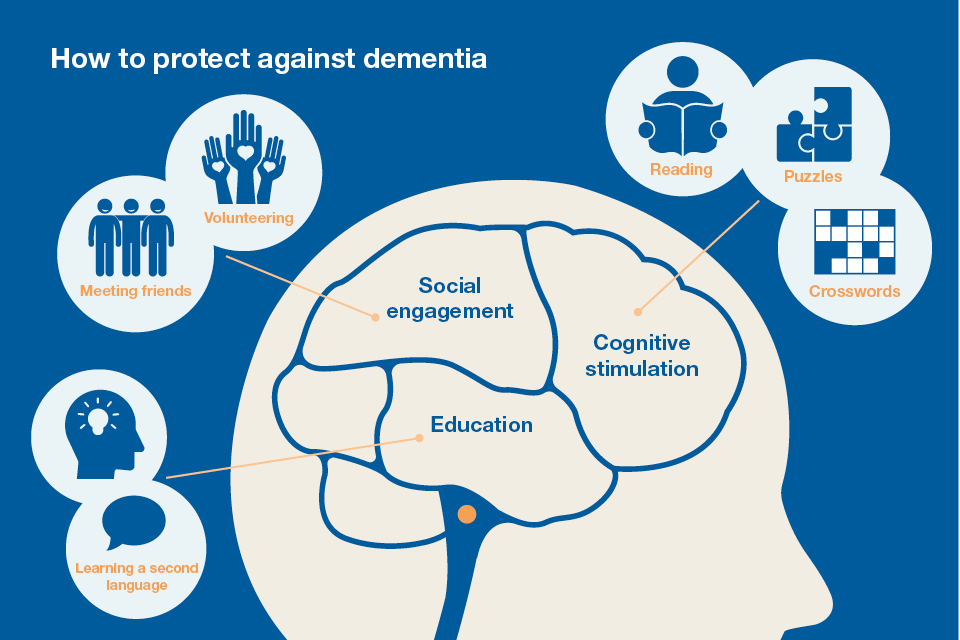
Health promotion programs aim to engage and empower individuals and communities to choose healthy behaviors, and make changes that reduce the risk of developing chronic diseases and other morbidities. Defined by the World Health Organization , health promotion:
What is the National Prevention Strategy?
Provides information on the National Prevention Strategy – a comprehensive plan with evidence-based recommendations for building healthy and safe environments, expanding access to quality care, empowering people to make healthier choices, and eliminating health disparities.
What are the social determinants of health?
Social determinants of health are the economic, social, cultural, and political conditions in which people are born, grow, and live that affect health status. Modifiable risk behaviors include, for example, tobacco use, poor eating habits, and lack of physical activity, which contribute to the development of chronic disease.
What is social and environmental health?
It covers a wide range of social and environmental interventions that are designed to benefit and protect individual people’s health and quality of life by addressing and preventing the root causes of ill health, not just focusing on treatment and cure.
What is health promotion?
The terms "health promotion" and "disease prevention" refer to professional activities . But a "health promoter" has also come to denote a profession, with an alternative agenda compared to that of traditional public health work, work that by some is seen to be too medically oriented, too reliant upon prevention, risk-elimination and health-care. But is there really a sharp distinction between these activities and professions? The main aim of the paper is to investigate if these concepts are logically different, or if they are just two extremes of one dimension. The central concepts, health promotion and disease prevention, are defined, and it is concluded that health promotion and disease prevention are logically distinct concepts, although they are conceptually related through a causal connection. Thus, logically, it is possible to promote health without preventing disease, even if this is not so common, in practice, but it is not possible to prevent disease without promoting health. Finally, most health promoting interventions target basic health, not manifest health, and often also thereby reduce future disease.
What are ethical issues in health promotion?
One important ethical issue for health promotion and public health work is to determine what the goals for these practices should be. This paper will try to clarify what some of these goals are thought to be, and what they ought to be. It will specifically discuss two different approaches to health promotion, viz., behavior change and empowerment. The general aim of this paper is, thus, to compare the behavior-change approach and the empowerment approach, concerning their immediate (instrumental) goals or aims, and to morally evaluate the strengths and weaknesses of these two goal models, in relation to the ultimate goal of health promotion. The investigation shows that the behavior-change approach has several moral problems. First of all, it is overly paternalistic and often disregards the individual’s or group’s own perception of what is important – something that also increases the risk of failed interventions. Furthermore, it risks leading to ‘victim blaming’ and stigmatization, and to increased inequalities in health, and it puts focus on the ‘wrong’ problems, i.e., behavior instead of the ‘causes of the causes’. It is thereafter shown that the empowerment approach does not have any of these problems. Finally, some specific problems for the empowerment approach are discussed and resolved, viz., the idea that empowering some groups might lead to power over others, the objection that the focus is not primarily on health (which it should be), and the fact that empowered people might choose to live lives that risk reducing their health.
What is the topic of health claims substantiation?
The topic of "Health Claims Substantiation for Probiotic and Prebiotic Products " was discussed at the 8 (th) annual International Scientific Association for Probiotics and Prebiotics (ISAPP) meeting. The topic is especially timely considering that the regulatory review process for health benefit claims on probiotic and prebiotic products in Europe has not resulted in a single claim being approved (120 negative opinions on probiotic claims and 19 negative opinions on prebiotic claims through February 2011). This situation in Europe and elsewhere has driven companies to seek clarity on a research path that would stand up to scientific scrutiny as well as satisfy regulatory demands for health claim substantiation. It can be challenging to negotiate rigid regulatory distinctions, such as between health and disease, when these states are more realistically represented by continua. One research approach focused on improved homeostasis is explored as a statistically robust approach to measuring physiological parameters in healthy populations, which are the required target for food and supplement claims. Diverse global regulatory frameworks complicate this issue, and harmonization of different approaches globally would simplify requirements for industry, decrease consumer confusion and improve the scientific framework for the research community to set up appropriate research pathways. This report highlights key points from this discussion.
How does health promotion help in old age?
Health promotion is considered to contribute to quality of life in old age. Programs are designed to encourage physical activities and lifestyle changes. They are, however, unlikely to achieve their aims if they fail to understand how they interfere with quality of life as it is perceived by older persons. This chapter summarizes the findings of 49 studies that investigated how older persons promote their health or try to prevent diseases and how they experience programs aimed at supporting them in this matter. Health promotion programs are likely to succeed if their focus is not restricted on disease prevention and physical fitness. When older persons participate in such programs their desire for physical activity and physical integrity always involves the satisfaction of their social, identity related and developmental needs. Programs that fail to address these needs are unlikely to meet the needs of their target group.
What is the current trend in patients' disease management?
Background: The current trend in patients’ disease management is mostly aimed at addressing their present health complaints; the focus is thus purely curative. As the limits of curative medicine become apparent and the cost of medical care escalates, disease prevention is gaining prominence. Factors that contribute to unreliable delivery of an integrated health care service are worth investigation. This study explores the extent to which health promotion and disease prevention services are integrated to curative health care and identifies the factors associated with not reliably providing the services. Methods: A cross-sectional quantitative study using an exploratory and descriptive design was used to explore and describe the extent of health promotion, preventive, and curative health care services provision, and investigated factors related to low performance. Phase I of the study examined the degree of promotive and preventive health care provision at hospitals and health centers while investigating the staffing and equipment and supply status of the facilities. Phase II, using the Delphi consensus-seeking process, focused on the validation of the findings from Phase I. Results: Of all patients who attended health facilities, only 2.4% (n=20) received optimal health promotion services. Disease prevention services were optimally provided to only 3.6% (n=30) patients. Integrated health promotion and disease prevention services were provided to only 0.8% (n=7) patients. The main reasons for not providing an integrated health care service were shortage of skilled health staff, equipment, medication, protocols, and guidelines, and high service cost, poor patient awareness, and health professionals’ focus on curative health care. Conclusion: Health service providers were not routinely conducting patient-specific health promotion, disease prevention, and integrated health care services, losing the opportunities of patient’s presence for health promotion and diseases prevention purposes. Addressing barriers can help with integrating health promotion and disease prevention services to the curative health care services. Keywords: integrated health service, disease prevention, health promotion, curative care, non-communicable diseases
How effective is mental health promotion?
There is a growing evidence-base that mental health promotion, delivered by trained facilitators, is effective in promoting self-awareness and self-care to prevent the damaging effects of ongoing stress in one’s life and to promote early detection of any possible emerging mental health problems. Within Australia, however, few clinicians or school staff are confident or trained in mental health promotion. Aims: This paper reports the results of a two-day professional development experience designed for prospective facilitators of a mental health program for secondary-school students. The goal was to develop facilitators’ knowledge and understanding of best practice in youth mental health promotion and to increase their confidence in delivering the program. Design: A mixed methods evaluation was designed to assess the impact that a solution-focused training program had on participating facilitators. Methods: A questionnaire was created for the study and included eight quantitative items and one open ended, qualitative question. Twenty-seven nurses and guidance officers from central Queensland were recruited via convenience sampling and data were analysed using descriptive statistics and thematic analysis. Results: The evaluation revealed that participants’ perception of their ability to facilitate a youth mental health program significantly improved after completing the professional development. Qualitative data indicated that participants found the professional development experience to be valuable, provide useful and transferable skills, and believed it to be necessary for mental health promotion work. Conclusion: By providing detailed description of the program’s content and processes, other mental health professionals may be inspired to further develop engaging and effective learning experiences.
Is heart disease a public health problem?
Globally, heart disease is still a major public health problem. In developed countries, this is due to an ageing population, and in developing countries, like Uganda, it is due to increasing negative lifestyles. Many women in Uganda move from rural to urban areas, thereby changing their diet, reducing their level of physical activity, and increasing their weight as well as their risk of myocardial infarction. Method The qualitative method was used in this study. Twelve women aged over 40 years, who within 10 years had moved from the countryside, into the city of Kampala, were interviewed by the use of a semi-structured question guide. Data were analyzed by means of Burnard’s content analysis method and by using the Theory of Reasoned Action.The aim was to examine women’s experiences and perceptions of body image, lifestyles and overweight in relation to a change of living conditions, and, furthermore, to examine their knowledge of the risks of heart disease. The results showed the following themes: body image, overweight, physical inactivity, culture, transition, women’s needs, concerns and lack of knowledge about the risk of heart disease. The core finding was that in spite of an income increase, a reduced health situation was described. All the interviewees reported increased body weight, encouraged by their surroundings. Lack of knowledge about nutrition and risk factors for heart disease, i.e., overweight and inactivity, and the fact that being obese was perceived, by themselves and others, as beautiful, were reported. Conclusion Important knowledge gained for public health measures was that interventions increasing women’s heart health should be geared towards women’s empowerment. Strategies ought to raise knowledge and awareness of forces and structures in Ugandan women’s surroundings that keep them inactive and make them increase their body weight. It is important to give the women support in taking charge of their own body and health.
What is health promotion?
Health promotion is the process of adoption of healthy behaviour and a positive attitude for maintaining a healthy lifestyle. Health promotional activities are environmental modification, health education, nutritional intervention, lifestyle and behavioural changes.
Why is primary prevention important?
Primary prevention based on the “positive health” concept, It encourages achievement and maintenance of the health of every individual and enables him to lead a socially and economically productive life.
What is primordial prevention?
Primordial prevention. The primordial prevention strategy is applied to reduce the development of risk factors before their appearance. Adequate attention is given to prevent chronic disease. The main action in primordial prevention is providing health education and awareness to people on how to live a healthy lifestyle.
How can chronic conditions like diabetes, hypertension and obesity be prevented?
Chronic conditions like diabetes, hypertension and obesity are preventable through the adoption of a healthy lifestyle. A child can be made habitual to a healthy lifestyle from the beginning. Parent, teacher, peer group and society play a major role in changing the lifestyle of a child. “Genes load the gun.
What is the purpose of the disability stage?
This stage aims at disability limitation and rehabilitation. Disability is the prevention of the transition of the disease process from impairment. Despite taking measures, if any type of disability occurs, rehabilitation is required to retain the individuals highest level of functioning.
What are the objectives of secondary prevention?
Objectives of secondary prevention. Completely cure or cease the progression of the disease. Preventing the spread of disease by providing treatment to known cases. Prevent complication. Reduces the degree of disability by shortening the period. This prevention is taken up by early diagnosis and screening.
Does lowering blood pressure reduce cardiovascular risk?
For example, A study has shown that the average reduction in blood pressure and cholesterol level reduces the risk of cardiovascular disease. In population strategy, a mass of the population will be made aware of the effectiveness of behavioural and lifestyle changes for the risk of cardiovascular disease.