Joint probability is a measure of how likely it is that two (or more) things will both occur. Conditional probability is a measure of how likely one thing is to happen if you know that another thing has happened. Joint probability is the probability of two events occurring simultaneously.
Which one is better joint or conditional probability?
Feb 18, 2022 · Joint probability is a measure of how likely it is that two (or more) things will both occur. Conditional probability is a measure of how likely one thing is to happen if you know that another thing has happened. Joint probability is the probability of …
How do you calculate a joint probability?
Feb 04, 2020 · Joint probability is a measure of how likely it is that two (or more) things will both occur. Conditional probability is a measure of how likely one thing is to happen if you know that another thing has happened.
What is the formula for joint probability?
Broadly speaking, joint probability is the probability of two things* happening together: e.g., the probability that I wash my car, and it rains. Conditional probability is the probability of one thing happening, given that the other thing happens: e.g., the probability that, given that I wash my car, it …
How to determine conditional probability?
As you can see in the equation, the conditional probability of A given B is equal to the joint probability of A and B divided by the marginal of B. Let’s use our card example to illustrate. We know that the conditional probability of a four, given a red card equals 2/26 or 1/13.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/JointProbabilityDefinition2-fb8b207be3164845b0d8706fe9c73b01.png)
What is the difference between prior probability and conditional probability?
What is meant by conditional probability?
How do you find conditional probability and joint probability?
What is joint probability and examples?
How do you find joint probability?
What is the main difference between conditional probability and mutually exclusive events?
The simplest example of mutually exclusive are events that cannot occur simultaneously. In other words, if one event has already occurred, another can event cannot occur. Thus, the conditional probability of mutually exclusive events is always zero.
Is joint probability the same as intersection?
How do you find the joint probability of three events?
- Calculate the probability of A.
- Find the probability of B.
- Determine the probability that both A and B will occur by multiplying them.
- Use the formula: P(A ∪ B) = P(A) + P(B) − P(A ∩ B) ,
What does a joint probability measure quizlet?
Which of the following is a conditional probability?
How do you find the conditional?
What is meant by joint probability distribution?
What is conditional probability?
The conditional probability concept is one of the most fundamental in probability theory and in my opinion is a trickier type of probability. It defines the probability of one event occurring given that another event has occurred (by assumption, presumption, assertion or evidence).
Why is robability important in data science?
P robability plays a very important role in Data Science, as Data Scientist regularly attempt to draw statistical inferences that could be used to predict data or analyse data better.
What is marginal distribution?
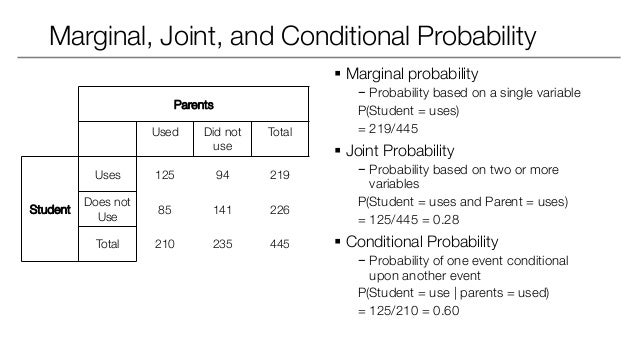
In probability theory and statistics, the marginal distribution of a subset of a collection of random variables is the probability distribution of the variables contained in the subset. It gives the probabilities of various values of the variables in the subset without reference to the values of the other variables ( Source: Wikipedia) — If that was too much jargon, to put it simply, the marginal probability is the probability of an event irrespective of the outcome of another variable — P (A) or P (B).

Event
Probability
Joint Probability
- Joint probability is the likelihood of more than one event occurring at the same time P(A and B). The probability of event A and event B occurring together. It is the probability of the intersection of two or more events written as p(A ∩ B). Example: The probability that a card is a four and red =p(four and red) = 2/52=1/26. (There are two red fours in a deck of 52, the 4 of hearts and the 4 …
Conditions For Joint Probability
- One is that events X and Y must happen at the same time. Example: Throwing two dice simultaneously.
- The other is that events X and Y must be independent of each other. That means the outcome of event X does not influence the outcome of event Y. Example: Rolling two Dice.
- If the following conditions met, then P(A∩B) = P(A) * P(B).
Conditional Probability
- The conditional probability of an event B is the probability that the event will occur given the knowledge that an event A has already occurred. It is denoted by P(B|A). So now, The joint probability of two dependent events becomes P(A and B) = P(A)P(B|A)
Bayes Theorem
- We know that, P(A and B) = P(A)P(B|A) andP(B and A) = P(B)P(A|B) When we equate this we will get, P(A)P(B|A) = P(B)P(A|B), then P(A|B) = P(A) P(B|A) / P(B) This is the Bayes theorem It tells: how often A happens given that B happens, written P(A|B), When we know: how often B happens given that A happens, written P(B|A) and how likely A is on its own, written P(A) and how likely B …
Prior & Posterior Probability
- Posterior probability is the probability an event will happen after all evidence has been taken into account.
- Prior probability is the probability an event will happen before you take any new evidence into account.
- You can think of posterior probability as an adjustment on the prior probability
- Posterior probability is the probability an event will happen after all evidence has been taken into account.
- Prior probability is the probability an event will happen before you take any new evidence into account.
- You can think of posterior probability as an adjustment on the prior probability
- Posterior = ( Likelihood * Prior ) / Evidence
Hypothesis, Evidence & Likelihood
- The hypothesis is your “guess” at what will occur. It is a testable assertion.
- Evidence will support or oppose the hypothesis.
- The Likelihood is the chance or probability that one thing will happen.