Summary: Difference Between Microtubules
Microtubule
Microtubules (micro- + tube + -ule) are a component of the cytoskeleton, found throughout the cytoplasm. These tubular polymers of tubulin can grow as long as 50 micrometres and are highly dynamic. The outer diameter of a microtubule is about 24 nm while the inner diam…
What is the difference between microtubules and microfilaments?
Main Differences Between Microtubules and Microfilaments
- Microtubules are the long, shaped hollow fiber present in the cytoskeleton of the cell. ...
- Microtubules are shaped as a hollow tubes, while Microfilaments are shaped as two strands revolving around each other.
- Microtubules are created by tubulin, while Microfilaments are made up of actin.
What are some examples of intermediate filaments?
Type IV
- Alpha-internexin
- Neurofilaments - the type IV family of intermediate filaments that is found in high concentrations along the axons of vertebrate neurons.
- Synemin
- Syncoilin
What is the main function of microtubules?
The Function Of Microtubules.Microtubules are hollow, fibrous shafts whose main function is to help support and give shape to the cell.They also serve a transportation function, as they are the routes upon which organelles move through the cell.
What are the functions of microtubules and microfilaments?
- Giving shape to cells and cellular membranes.
- Cell movement, which includes contraction in muscle cells and more.
- Transportation of specific organelles within the cell via microtubule "roadways" or "conveyor belts."
- Mitosis and meiosis: movement of chromosomes during cell division and creation of the mitotic spindle.

What a the difference between microfilaments and microtubules?
They contribute to the cell's movement on a surface. The main difference between microtubules and microfilaments is that microtubules are long, hollow cylinders, made up of tubulin protein units whereas microfilaments are doublestranded helical polymers, made up of actin proteins.
Are intermediate filaments and microtubules the same?
Intermediate filaments bear tension and anchor the nucleus and other organelles in place. Microtubules help the cell resist compression, serve as tracks for motor proteins that move vesicles through the cell, and pull replicated chromosomes to opposite ends of a dividing cell.
What is the function of microfilaments and microtubules?
Microfilaments and microtubules are key components of the cytoskeleton in eukaryotic cells. A cytoskeleton provides structure to the cell and connects to every part of the cell membrane and every organelle. Microtubules and microfilaments together allow the cell to hold its shape, and move itself and its organelles.
What is the difference between microtubules and microfilaments quizlet?
Microtubules are hollow rods of the protein tubulin that interact with motor proteins to create movement within the cell. Microfilaments are the thinnest cytoskeletal structures.
What is intermediate filaments and its function?
Intermediate filaments, in contrast to actin filaments and microtubules, are very stable structures that form the true skeleton of the cell. They anchor the nucleus and position it within the cell, and they give the cell its elastic properties and its ability to withstand tension.
What functions do microtubules actin filament and intermediate filaments perform in the cell?
The cytoskeleton of a cell is made up of microtubules, actin filaments, and intermediate filaments. These structures give the cell its shape and help organize the cell's parts. In addition, they provide a basis for movement and cell division.
What is the main function of the microtubules?
Introduction. Microtubules, together with microfilaments and intermediate filaments, form the cell cytoskeleton. The microtubule network is recognized for its role in regulating cell growth and movement as well as key signaling events, which modulate fundamental cellular processes.
What is the main function of microfilaments?
In association with myosin, microfilaments help to generate the forces used in cellular contraction and basic cell movements. The filaments also enable a dividing cell to pinch off into two cells and are involved in amoeboid movements of certain types of cells.
What are the 4 functions of microfilaments?
Their functions include cytokinesis, amoeboid movement and cell motility in general, changes in cell shape, endocytosis and exocytosis, cell contractility and mechanical stability.
What is the function of microfilaments and microtubules quizlet?
Microtubules help to maintain cell shape, provide tracks for vesicles and other cargo inside of cells, and make up the spindles that attach to chromosomes during cell division. Microfilaments also help to maintain cell shape and associate with myosin to cause muscle contraction.
What are the three main cytoskeletal proteins and their functions?
Three major types of filaments make up the cytoskeleton: actin filaments, microtubules, and intermediate filaments. Actin filaments occur in a cell in the form of meshworks or bundles of parallel fibres; they help determine the shape of the cell and also help it adhere to the substrate.
How are microtubules and microfilaments dynamic?
Microtubules, like actin filaments, are dynamic structures: they can grow and shrink quickly by the addition or removal of tubulin proteins. Also similar to actin filaments, microtubules have directionality, meaning that they have two ends that are structurally different from one another.
What do microfilaments microtubules and intermediate filaments have in common?
2:514:06Microfilaments vs Microtubules vs Intermediate Filaments - YouTubeYouTubeStart of suggested clipEnd of suggested clipAnd one more thing is their sub cellular distribution both microfilaments and microtubules are foundMoreAnd one more thing is their sub cellular distribution both microfilaments and microtubules are found in cytoplasm whereas intermediate filaments are found in both cytoplasm.
How are microtubules different from other cytoskeletal filaments?
How are microtubules different from the other cytoskeletal filaments? Microtubules are large bundles composed of the protein myosin. They are generally 15 nanometers in size. Microtubules are the smallest cytoskeletal element with a diameter of 5 nanometers and they are composed of the protein actin.
What are intermediate filaments made of?
Whereas actin filaments and microtubules are polymers of single types of proteins (actin and tubulin, respectively), intermediate filaments are composed of a variety of proteins that are expressed in different types of cells.
Which of the following is a major difference between microtubules and actin filaments?
The key difference between actin filaments and microtubules is that actin filaments are the smallest type of filamentous proteins made from actin while microtubules are the largest type of filamentous proteins made from tubulin..
What is the difference between microtubules and microfilaments?
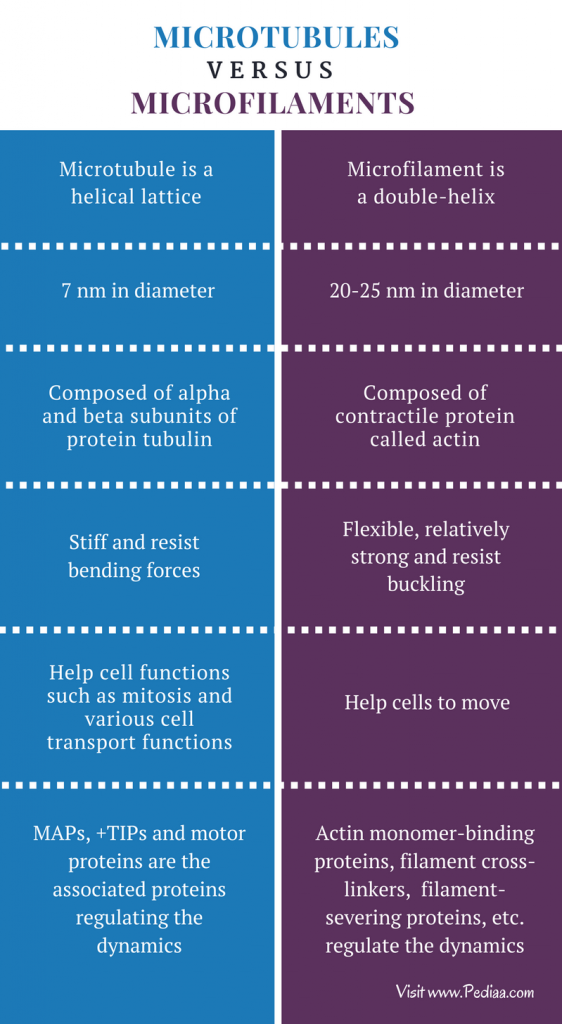
The main difference between microtubules and microfilaments is that microtubules are long, hollow cylinders, made up of tubulin protein units whereas microfilaments are double-stranded helical polymers, made up of actin proteins . 1. What are Microtubules.
What are the two components of the cytoskeleton?
Micro tubules and microfilaments are two components of the cytoskeleton of a cell. The cytoskeleton is formed by microtubules, microfilaments, and intermediate filaments. Microtubules are formed by the polymerization of tubulin proteins. They provide mechanical support to the cell and contribute to the intracellular transport.
What is the thinnest fiber in the cytoskeleton?
The thinnest fibers in the cytoskeleton are microfilaments. The monomer, which forms the microfilament is called globular actin subunit (G-actin). One filament of the double-helix is called filamentous actin (F-actin). The polarity of the microfilaments is determined by the binding pattern of myosin S1 fragments in the actin filaments. Therefore, the pointed end is called the (-) end and the barbed end is called the (+) end. The structure of the microfilament is shown in figure 3.
What are the filaments made of actin called?
The filaments which are made up of actin filaments are known as microfilaments . Microfilaments are a component of the cytoskeleton. They are formed by the polymerization of actin protein monomers. A microfilament is around 7 nm in diameter and composed of two strands in a helical nature.
How are microfilaments resistant to fractures?
Microfilaments are strong and relatively flexible. They are resistant to fractures by tensile forces and buckling by multi-piconewton compressive forces. The motility of the cell is achieved by the elongation of one end and contraction of the other end.
Why are microfilaments so strong?
Microfilaments: Microfilaments are flexible and relatively strong. They resist buckling due to compressive forces and filament fracture by tensile forces.
What is the structure of a microtubule?
Structure of Microtubules. Eukaryotic microtubules are long and hollow cylindrical structures. Inner space of the cylinder is referred to as the lumen. The monomer of the tubulin polymer is α/β-tubulin dimer.
What is the difference between intermediate filaments and microfilaments?
Summary: Difference Between Intermediate Filaments and Microfilaments is that Intermediate filaments are the structures that form a network around the nucleus and extend to the periphery of the cell. While Microfilaments are long and fine threadlike structures with a diameter of about 3 to 6 nm. These filaments are made up ...
How many nm are in a filament?
Diameter of each filament is about 10 nm. The intermediate filaments are formed by ropelike polymers, which are made up of fibrous proteins.
Which is more abundant, myosin or actin?
Actin is more abundant than myosin. Microfilaments are present throughout the cytoplasm. The microfilaments present in ectoplasm contain only actin molecules and those present in endoplasm contain both actin and myosin molecules.
What are intermediate filaments?
Intermediate filaments are in the form of rods which are composed of varieties of alpha-helical segmanets such as 1A, 1B, 2A and 2B. They reinforces and support cell shape and may fix organelle position therefore more permanent than the rest.
What are microtubules made of?
Microtubules are a component of the cytoskeleton made of globular proteins called tubulin,...
What is the function of microtubules?
Microtubules are a component of the cytoskeleton made of globular proteins called tubulin, combined together to form a straight hollow tubes. It produces spindle fiber during cell division which eventually helps in contraction of the cell forming and cleavage.
What are Microtubules?
Microtubules are long, hollow cylindrical structures made up of globular proteins consisting of dimers of α- and β-tubulin subun its arranged side by side around a core. They are the largest elements of the cytoskeleton. Each tube has a diameter of 25 nm, and contains a ring of 13 protein protofilaments. Each protofilament constitutes of α- and β-tubulin globular protein subunits through the polymerization process. The functions of microtubules are governing intracellular transport, separation of chromosomes during mitosis, movement of flagella and cilia, and positioning of cellulose molecules during cell wall synthesis in plants.
What are Microfilaments?
Microfilaments are the thinnest fibers in the cytoskeleton. They are made of globular actin protein subunits. Each filament has two protein chains loosely twisted together. Each chain is made of ‘pearl’ like globular protein subunits. The diameter of a microfilament is about 7 nm. Moreover, microfilaments possess polarity, so they have plus (+) and minus (-) ends and they represent the growth & direction of microfilaments.
What are the Similarities Between Microtubules and Microfilaments?
Both microtubules and microfilaments are fibers of the cytoskeleton of the eukaryotic cells.
What are microtubules and microfilaments?
Summary – Microtubules vs Microfilaments. Microtubules and microfilaments are two types of long fibers that make the cytoskeleton. Microtubules are long hollow cylindrical structures made of dimers of α- and β-tubulin subunits arranged side by side around a core. On the other hand, microfilaments are the thinnest fibers made ...
What are the two types of fibers that make up the cytoplasm?
Microtubules and microfilaments are two types of fibers that occur in the cytoplasm of every eukaryotic cell. These fibers are basically responsible for making the criss-cross networks known as ‘cytoskeleton’ of the cytoplasm. The cytoskeleton is a dynamic system which helps to maintain the shape of the cell and anchor the cell organelles in ...
What are the two types of fibers that occur in the cytoplasm of every eukaryotic cell?
Protein fibers are essential to carry out many functions in the living cells. Microtubules and microfilaments are two types of fibers that occur in the cytoplasm of every eukaryotic cell.
Which is larger, microfilaments or microtubules?
Microtubules have a larger diameter than microfilaments. Hence, microtubules are the largest component while microfilaments are the thinnest component of the cytoskeleton. Furthermore, microtubules are stiffer than microfilaments. Thus, this is a summary of the difference between microtubules and microfilaments.
What is the cytoskeleton of an eukaryotic cell?
Likewise, Eukaryotic Cell has a skeletal internal framework and is called the cytoskeleton as it is distributed in the cytoplasm. Cytoskeleton that consists of three main polymers: microtubules (green), intermediate filaments (purple) and actin filaments (red).
What are the cytoskeletons in Jurassic Park?
Cytoskeleton - Microfilaments, Intermediate filaments and Microtubules. We are all familiar with the film ‘Jurassic Park’. In the film, different types of dinosaurs are roaming around the jungle, some are like birds, some are gigantic, and some are like small lizards.
What is the cytoskeleton of a cell?
It is also the site for anchoring mRNA and facilitating their translation into proteins. It is also referred as cytomusculature”. Cytoskeleton is absent in bacteria.
What is a type 1 keratin?
Type I: acidic and basic keratins present in hair and nail.
What are intermediate filaments?
Intermediate filaments. They are supportive elements in the cytoplasm of the eukaryotic cells, except the plant cells and are about 10 nm thick . They are composed of non-contractile proteins. Intermediate fibers are of four types-keratin filaments, neurofibrils, gilal filaments and heterogeneous filaments (Desmin, vimentin, synemin, ...
Which protein is found in microtubules?
The presence of microtubules in plant cells were first described by Ledbetter and Porter (1963). The major protein present in the cytoskeleton are tubulin in microtubules, actin myosin and tropomyosin in microfilaments and keratins, vimentin, desmin,lamin in intermediate filaments.
Who discovered the cytoskeletal structure of the protoplasm?
History: In 1928 Koltzoff , postulated the existence of cytoskeletal structure in the protoplasm. Robertis and Franchi (1953) observed the structure microtubules in the myelinated nerve fibres and called it as neurotubules.
What are the functions of microfilaments?
Microfilaments form the dynamic cytoskeleton, which gives structural support to cells and links the interior of the cell with the surroundings to convey information about the external environment. Microfilaments provide cell motility. e.g., Filopodia, Lamellipodia. During mitosis, intracellular organelles are ...
What is the name of the subunit of microfilaments?
Individual subunits of microfilaments are known as globular actin (G-actin). G-actin subunits assemble into long filamentous polymers called F-actin. Two parallel F-actin strands must rotate 166 degrees to layer correctly on top of each other to form the double helix structure of microfilaments. Microfilaments measure approximately 7 nm in diameter with a loop of the helix repeating every 37 nm.
What are microtubules made of?
Microtubules are composed of globular proteins called tubulin. Tubulin molecules are bead like structures. They form heterodimers of alpha and beta tubulin. A protofilament is a linear row of tubulin dimers. 12-17 protofilaments associate laterally to form a regular helical lattice.
What are the components of the cytoskeleton?
Microfilaments and microtubules are key components of the cytoskeleton in eukaryotic cells. A cytoskeleton provides structure to the cell and connects to every part of the cell membrane and every organelle. Microtubules and microfilaments together allow the cell to hold its shape, and move itself and its organelles.
What are the organelles transported by during mitosis?
During mitosis, intracellular organelles are transported by motor proteins to the daughter cells along actin cables. In muscle cells, actin filaments are aligned and myosin proteins generate forces on the filaments to support muscle contraction.
What is the function of the core of a microtubule?
A core of microtubules in the neural growth cone and axon also imparts stability and drives neural navigation and guidance.
Which organelle divides the chromosomes during cell division?
Microtubules form the spindle apparatus to divide the chromosome directly during cell division ( mitosis ).