Weathering is not a prerequisite for mass movement although it aids mass movements. Mass movements are very active over weathered slopes. Mass Movement can be grouped under two classes
What is the difference between weathering erosion and mass wasting?
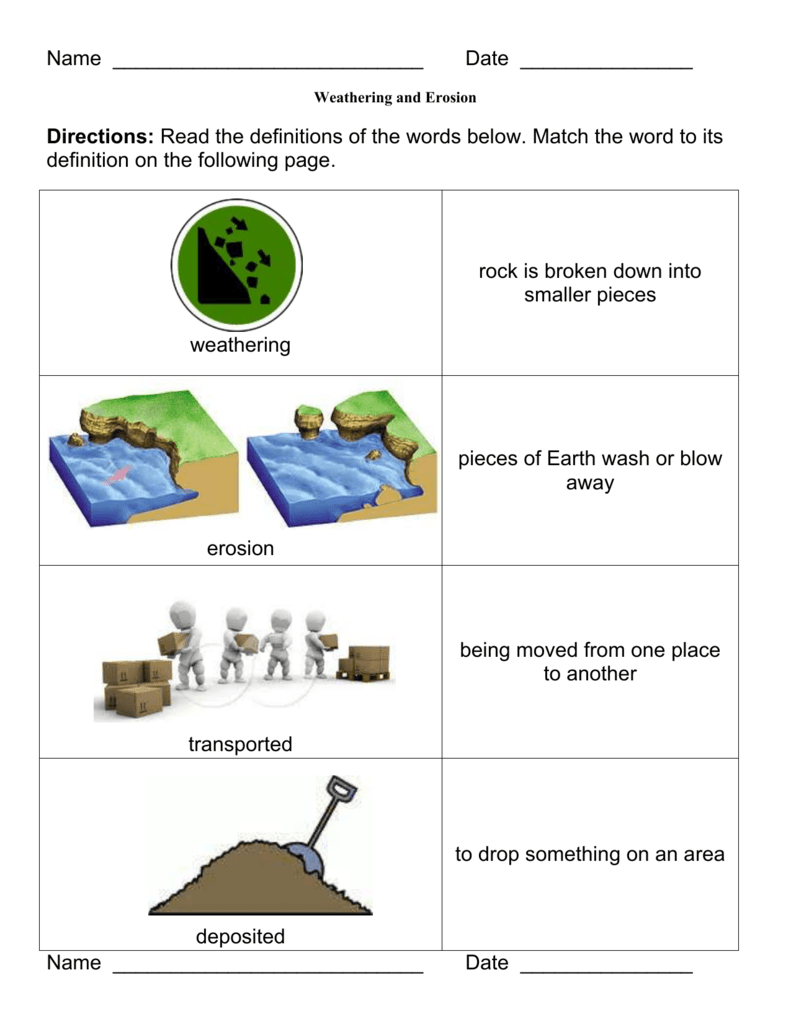
Weatheringis the physical disintegration or chemical alteration of rocks at or near the Earth‟s surface. Erosionis the physical removal and transportation of weathered material by water, wind, ice, or gravity. Mass wasting is the transfer or movement of rock or soil down slope primarily by gravity.
What is mass wasting and mass movement in geography?
MASS WASTING / MASS MOVEMENT : Mass movement is the movement of weathered material down a slope due to gravitational forces. 1. Soil Creep: This is a slow, gradual but more or less continuous movement of soil down the hill slopes. It is shown on the figure to the right.
Why do weathering rates vary from rock to rock?
Weathering rates will not only vary depending on the type of weathering process, whether it is mechanical, chemical, or biological, but they will also vary depending on the rock material that is being weathered. Some rocks are harder than other rocks, and will weather slower than softer rocks.
What do you mean by mechanical weathering?
Physical or mechanical weathering.: Mechanical weathering is the physical disintegration of a rock by the actual prising apart of separate particles. It takes place in a number of ways. (a) Repeated temperature change: In deserts, rocks exposed to the blazing sun during the day are intensely heated.
Is weathering a mass movement?
Another, more common example of weathering by water and gravity is mass movement or landslides. Mass movement occurs when soil is saturated with water, which makes it heavy, and the force of gravity overcomes the resistance of the slope.
What is the difference between mass movement and erosion?
Erosion is the gradual removal of the topsoil while mass movement is the movement of loose rock materials down slope. 2. Agents of erosion are running water, winds, waves and glaciers while that of mass movement entails the force of gravity.
What is the difference between weathering and weathering?
Erosion and weathering are the processes in which the rocks are broken down into fine particles....Erosion vs Weathering.ErosionWeatheringWind, water, ice and human activities are some of the causes of erosion.Weathering is caused due to atmospheric factors like air pressure.3 more rows
What are the types of weathering and mass movement?
Mechanical, biological and chemical weathering can all happen in river landscapes. Mechanical weathering is the breakdown of rock without any changes in its chemical composition. An example of mechanical weathering is freeze-thaw. Freeze-thaw weathering occurs when the temperature alternates above and below freezing.
What do you mean by mass movement?
Definition of mass movement noun. an organized effort by a large number of people, especially those not forming part of the elite of a given society, to bring about pervasive changes in existing social, economic, or political institutions, frequently characterized by charismatic leadership.
What is the difference between weathering and erosion?
When the smaller rock pieces (now pebbles, sand or soil) are moved by these natural forces, it is called erosion. So, if a rock is changed or broken but stays where it is, it is called weathering. If the pieces of weathered rock are moved away, it is called erosion.
What is difference between mass and weathering soil?
Weathering is the physical disintegration or chemical alteration of rocks at or near the Earth's surface. Erosion is the physical removal and transportation of weathered material by water, wind, ice, or gravity. Mass wasting is the transfer or movement of rock or soil down slope primarily by gravity.
What is an example weathering?
Weathering is the wearing away of the surface of rock, soil, and minerals into smaller pieces. • Example of weathering: Wind and water cause small pieces of rock to break off at the side of a mountain. • Weathering can occur due to chemical and mechanical processes.
Which term describes weathering?
1. Weathering is a term which describes the general process by which rocks are broken down at the Earth's surface into such things as sediments, clays, soils and substances that are dissolved in water. 2. The process of weathering typically begins when the earth's crust is uplifted by tectonic forces.
What is the link between weathering and mass movement?
The broken rock fragments (as a result of weathering) move down the slope through mass movements . These can be rapid, such as landslides or slow as with soil creep: Landslides are occasional, rapid movements of a mass of earth or rock sliding along a steep slope.
What is the relationship between weathering and mass movement quizlet?
What is the relationship between weathering and mass movement? Weathering prepares material for mass movement.
Why is weathering and mass movement important?
These processes affect the earth by lowering the relief (landforms) by breaking down rock material at the earth's surface. The landforms get lower and often – but not always – smoother! These are general processes that wear down or rearrange landforms: weathering, mass movement, erosion, transportation, and deposition.
What are the features of river erosion and mass movement?
Explanation. — Agents of erosion are running water, winds, waves and glacier while that of mass movement entails the force of gravity. —Erosion involves scratching, polishing and plucking of loose, rock surfaces while mass movement involves creeping, flowing, slumping, sliding and falling. — Interlocking spurs.
What is the difference between soil erosion and landslides?
Landslides are a type of soil erosion which transports soil at a short time and very large volume. While causes of soil erosion are rainfall, soil, slope, vegetation, and humans. Landslides and erosion are being related to the soil.
What is the difference between mass wasting and landslides?
A landslide is defined as the movement of a mass of rock, debris, or earth down a slope. Landslides are a type of "mass wasting," which denotes any down-slope movement of soil and rock under the direct influence of gravity.
What are the types of mass movement?
Types of Mass Movement: Creep; Fall, Slip, Flow; Solifluction; Rock Glaciers; Slumping (Earthflow); Mudflow (lahar); Debris Flow, Debris Slide, Debris Avalanche; Rockslide; Rockfall; Debris Fall.
What causes chemical weathering?
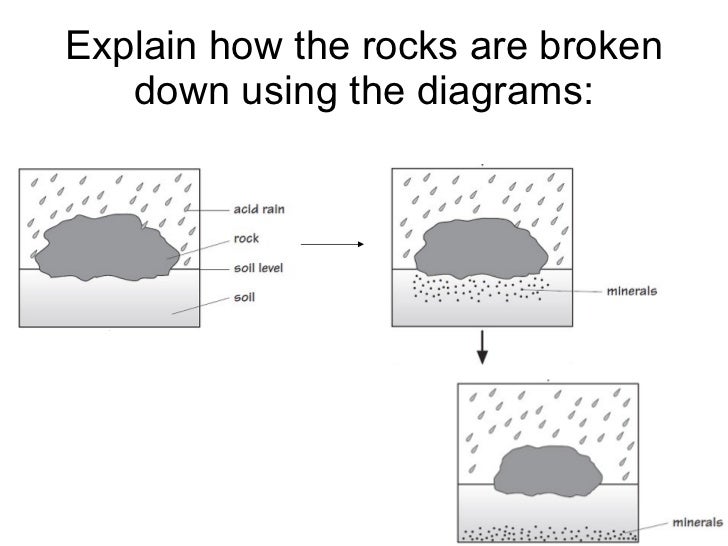
Chemical weathering is caused by the action of rainwater. Rainwater contains small amounts of acidthat attacks alkalinerock
How is weathered material carried away?
This material and weathered material is carried away by waves along the coast
What causes cracks in rocks?
Rocks have many cracks. Rain water fills the cracks. Water freezes. Expansion causes stresses and cracks are enlarged. When the ice thaws, the crack contracts. Repeated freezing and thawing happens. Rock fragments break off and collect as scree at the foot of the cliff.
Why is rain acidic?
dissolvedby rainwater. Acid rain makes rainwater more acidic than normal and is caused by greenhouse gasses dissolving in water found in clouds.
What is mechanical weathering?
Mechanical weathering is the physical disintegration of a rock by the actual prising apart of separate particles. It takes place in a number of ways. (a) Repeated temperature change: In deserts, rocks exposed to the blazing sun during the day are intensely heated.
What are the factors that influence the weathering of rock?
In addition to climate, the type of rock (lithology) and the nature and amount of fractures or other weaknesses in it are major influences on the effectiveness of the various rock weathering processes.
Why does soil weather?
This is because the soil absorbs rain-water and keeps the underlying rocks in contact with this moisture. The rain-water absorbs organic acids from the soil and thus becomes a stronger weathering agent then pure rain-water acting on bare rock. There are three major chemical, weathering processes.
What is the term for a large mass of soil or rock falling suddenly?
3. Landslides (slumping or sliding) : There are very rapid kinds of movement and occur when a large mass of soil or rock falls suddenly. Land-slides usually occur on steep slopes undercut by a river or the sea so that it falls by gravity. Slumping is particularly common where permeable debris or rock layers overlie impermeable strata such as clay. Water sinking through the permeable material is halted by the clay. The damp clay provides a smooth slippery surface over which the upper layers easily slide.
What is slumping in rock?
Slumping is particularly common where permeable debris or rock layers overlie impermeable strata such as clay. Water sinking through the permeable material is halted by the clay. The damp clay provides a smooth slippery surface over which the upper layers easily slide. Report Error or Discrepancy.
What is the process of wearing away the earth?
WEATHERING AND MASS MOVEMENT. The process of wearing away the earth causes a general lowering and levelling out of the surface. It is known as denudation and is carried out in four phases-. Weathering. Erosion.
How does vegetative cover affect soil?
4. Vegetation : Although vegetative cover can protect rock by shielding if from raindrop impact and providing roots to stabilize soil, it also produces organic acids from the partial decay of organic matter; these acids contribute to chemical weathering. Plant roots can enter crevices and break up a rock, exerting enough pressure to force rock segments apart, thereby exposing greater surface area to other weathering processes. In the complexity of nature, physical and chemical weathering processes usually operate together. Of course, in all of this, is the crucial factor, for these processes require long periods of time to operate.
