How are somatic reflexes activated?
To produce the action, the somatic reflex arc is activated when a signal from the stimulus is sent to the muscle cells, passing through afferent neurons to the CNS, and finally, to the efferent neurons. The most common categories of somatic reflexes include the stretch reflex, the inverse stretch reflex, and the withdrawal reflex.
What are the different types of somatic reflexes?
There are several somatic reflexes, with the most common categories of somatic reflexes including the stretch reflex, inverse stretch reflex, and the withdrawal reflex. The stretch reflex, or tendon reflex, is one of the simplest monosynaptic reflexes (reflexes that have only one synapse between the afferent and efferent neurons ).
What are the effector target cells in reflexes?
For example, in the patella-tendon reflex, the effector target cells are muscle cells located near the knee. The effector targets are the cells that act. They are often muscle cells, and are the terminal cells in reflex arcs. Picmonic's rapid review multiple-choice quiz allows you to assess your knowledge.
What is the stretch reflex?
The stretch reflex, or tendon reflex, is one of the simplest monosynaptic reflexes (reflexes that have only one synapse between the afferent and efferent neurons ). The stretch reflex occurs when muscle spindles, or afferent neurons along the length of skeletal muscles, are stretched, causing muscle contraction.
What is the effector in a reflex action?
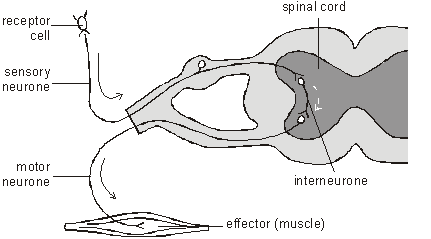
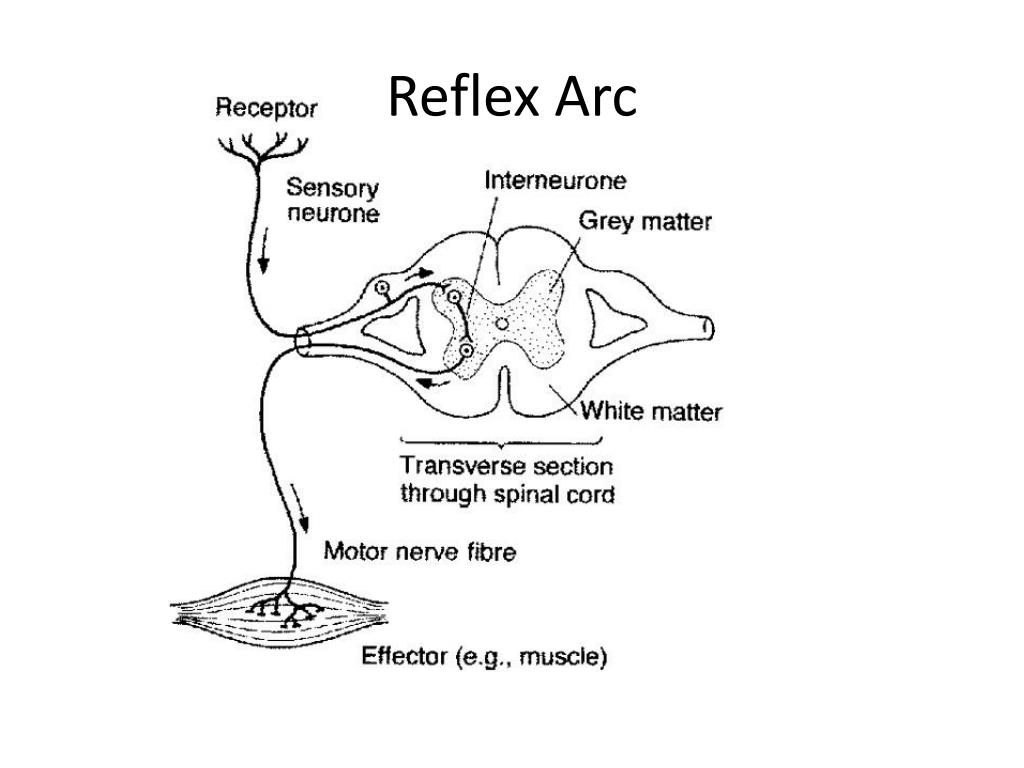
The primary components of the reflex arc are the sensory neurons (or receptors) that receive stimulation and in turn connect to other nerve cells that activate muscle cells (or effectors), which perform the reflex action.
What is an example of a somatic effector?
The muscles are generally divided into two groupings: somatic effectors, which are the body's striated muscles (such as those found in the arm and back), and autonomic effectors, which are smooth muscles (such as the iris of the eye).
What is a somatic reflex quizlet?
• If the reflex involves the contraction of skeletal muscle as the effector it is called a somatic reflex. • If the reflex involves the contraction of smooth muscle, cardiac muscle or glands, it is called an autonomic (visceral) reflex.
What are examples of effectors?
Effectors are parts of the body - such as muscles and glands - that produce a response to a detected stimulus....For example:a muscle contracting to move an arm.muscle squeezing saliva from the salivary gland.a gland releasing a hormone into the blood.
What is an example of an effector cell?
Examples of effector cells include: The muscle, gland or organ cell capable of responding to a stimulus at the terminal end of an efferent nerve fiber. Plasma cell, an effector B cell in the immune system. Effector T cells, T cells that actively respond to a stimulus.
What is an example of an effector organ?
An effector is a part of the body which can respond to a stimulus according to the instructions sent from the nervous system (spinal cord and brain). Example: Glands and muscles.
What effectors are controlled by the somatic nervous system?
The effectors controlled by the somatic nervous system are the skeletal muscles. The efferent nerves (also known as motor nerves) of the somatic nervous system function to transport nerve impulses from the central nervous system (i.e. brain and spinal cord) to the skeletal muscles of the body.
What are somatic and visceral effectors?
Effector Organ The main difference between somatic and visceral reflex is that the somatic reflex innervates skeletal muscles while the visceral reflex innervates soft tissue organs.
What is a somatic reflex?
A somatic reflex is an involuntary response to a stimulus, such as pulling one’s hand away after touching a hot stove. The nervous system is split...
What is a somatic reflex arc?
A somatic reflex arc is the neural pathway that occurs from the initial sensing of a stimulus to the response, such as the moving of a limb. The ba...
What are the somatic reflexes?
There are several somatic reflexes, with the most common categories of somatic reflexes including the stretch reflex, inverse stretch reflex, and t...
What differentiates an autonomic reflex from a somatic reflex?
The autonomic reflex and somatic reflex often differ in their efferent branches of the reflex arc and their effector targets. In an autonomic refle...
Why are somatic reflexes routinely assessed?
It is important to assess somatic reflexes because they demonstrate the ability of nerves to respond to stimuli. Each reflex is associated with a f...
What are the most important facts to know about a somatic reflex?
A somatic reflex is an involuntary movement in response to a stimulus. To produce the action, the somatic reflex arc is activated when a signal fro...
What is the somatic reflex arc?
The somatic reflex arc is the neural pathway resulting in involuntary actions, also known as reflexes. An afferent sensory neuron receives some sort of sensory input or stimulus and transmits it toward the integration center. Interneurons integrate the signal (if there are multiple sensory inputs) and transmit the signal to ...
Where does the integration of reflexes occur?
The integration occurs in the spinal cord instead of the brain. Some reflexes have multiple interneurons, but simple reflex arcs only have one neuron separating the sensory neuron and effector neuron. 5 KEY FACTS.
What are the effector targets?
The effector targets are the cells that act. They are often muscle cells, and are the terminal cells in reflex arcs.
Where does input go in reflexes?
In normal neural pathways, all input goes to the brain for processing. However, in reflexes, the input is processed in the interneurons instead, which allows for faster response. The efferent motor neuron stimulates muscle, or any effector target, into conducting the reflex action.
Which sensory neurons receive sensory input and transmit the signal on toward the integration center?
Afferent sensory neurons receive sensory input and transmit the signal on toward the integration center.
Where are effector target cells located?
For example, in the patella-tendon reflex, the effector target cells are muscle cells located near the knee.