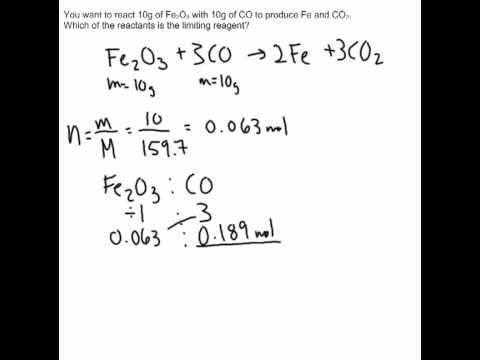
An excess reactant is a substance that is not wholly consumed or entirely reacted in a chemical reaction. It is also known as an excess reagent
Reagent
A reagent /riˈeɪdʒənt/ is a substance or compound added to a system to cause a chemical reaction, or added to see if a reaction occurs. The terms reactant and reagent are often used interchangeably—however, a reactant is more specifically a substance consumed in the cours…
Full Answer
How do you find the excess reagent?
- Firstly find the relative number of moles of each component in the balanced equation.
- Then convert the data given in the question under study into moles.
- Now by inspection see which one of the components will completely react and which one will be in excess.
How to calculate amount of excess reactant?
- Write balanced eq
- Find ratios between reactants
- Find molar amounts from given, eq. (#1), and ratios (#2)
- Reactant with most moles is in excess
- Very simplified test. May involve other factors…
Why do we use excess reactants in a chemical reaction?
Excess reactants. A good way to ensure that one reactant fully reacts is to use an excess of the other reactant. This is financially efficient when one of the reactants is very cheap.
What does excess reactant mean in chemistry?
The excess reactant is the reactant in a chemical reaction with a greater amount than necessary to react completely with the limiting reactant. It is the reactant(s) that remain after a chemical reaction has reached equilibrium. What if there is no excess reactant? When there is no limiting reactant in a chemical equation, that means the reaction goes to completion.

What is the reactant in excess?
The excess reactant is the reactant in a chemical reaction with a greater amount than necessary to react completely with the limiting reactant. It is the reactant(s) that remain after a chemical reaction has reached equilibrium.
How do you find the excess reactant?
The reactant that produces a lesser amount of product is the limiting reagent. The reactant that produces a larger amount of product is the excess reagent. To find the amount of remaining excess reactant, subtract the mass of excess reagent consumed from the total mass of excess reagent given.
What is the excess reactant quizlet?
Excess Reactant. The substance that is not used up completely in a reaction, it is only partially consumed.
What is an example of a limiting reactant?
Examples of Limiting Reagent If two moles of H2 react with one mole of N2, then all N2 will not be used since there is not enough H2 in the reaction. Therefore, hydrogen is the limiting reagent.
How do you find the limiting reactant quickly?
1:163:32How to Find Limiting Reactant (Quick & Easy) Examples ... - YouTubeYouTubeStart of suggested clipEnd of suggested clipSo first step we're going to convert the reactants in the most by dividing by the molar mass. We'reMoreSo first step we're going to convert the reactants in the most by dividing by the molar mass. We're going to divide by the molar mass of sf4 which is 108. Point zero seven. And then the molar mass of
What is the difference between a limiting reactant and an excess reactant quizlet?
Solution. A limiting reactant is the reactant that is completely consumed and which determines the amount of product formed. An excess reactant is the reactant present in a greater amount than necessary to react with all the limiting reactant.
What is limiting reagent and excess reagent?
In a chemical reaction, reactants that are not used up when the reaction is finished are called excess reagents. The reagent that is completely used up or reacted is called the limiting reagent, because its quantity limits the amount of products formed.
What is a limiting reactant quizlet?
Limiting reactant. The reactant that controls the amount of product able to be produced by a chemical reaction because it is used up completely. Excess reactant. The reactant that is not used up completely in a chemical reaction.
What is an excess reactant?
An excess reactant is a substance that is not wholly consumed or entirely reacted in a chemical reaction. It is also known as an excess reagent. Th...
Are excess reactants present in all reactions?
No, an excess reactant is not present in all reactions. It is present in stoichiometrically imbalanced reactions.
What is a limiting reactant?
The reactant that is fully consumed or entirely reacted in a reaction is known as a Limiting Reactant.
Give examples of excess reactants?
When a candle is burned in the air, i.e. oxygen, the amount of product formed is independent of oxygen. Thus oxygen is an excess reactant here. Whe...
Ammonia reacts with oxygen to produce nitric oxide. Find out limiting reactants and excess reactants.
To calculate the limiting and excess reactant, firstly, we will write a balanced chemical equation. 4NH 3 + 5O 2 → 4NO + 6H 2 O We can see from t...
What is excess reactant?
Updated July 25, 2019. The excess reactant is the reactant in a chemical reaction with a greater amount than necessary to react completely with the limiting reactant. It is the reactant (s) that remain after a chemical reaction has reached equilibrium.
What happens if a reaction involves one or more reactants with low solubility in a solvent?
If the reaction involves one or more reactants with low solubility in a solvent, there's a good chance this will affect the identities of the excess reactants. Technically, you'll want to write the reaction and base the equation on the projected amount of dissolved reactant.
What is the total mass of reactants?
Total mass, so that total mass of reactants=total mass of products
What is the principal reaction in alcohol fermentation?
As an example, consider the principal reaction in alcohol fermentation: conversion of glucose to ethanol and carbon dioxide:
What is conversion in chemistry?
Conversion is the fraction or percentage of a reactant converted into products. 4.
Why is temperature important in chemical reactions?
Temperature is an important parameter for chemical reactions because a constant reaction rate is related to the temperature of the reaction. The reaction rate constant increases with an increase in temperature. The relation of the temperature and reaction rate constant can be described by the Arrhenius equation. Reactants are needed for the energy to obtain products. This energy is called activation energy. Reactants have higher kinetic energy at a higher reaction temperature. Activation energy is provided by the kinetic energy of the reactant particles. When temperature increases, the kinetic energy of the reacting particles is increased; hence the reaction rate increases [23,24].
What are the limits of flammability of a mixture?
These weak and rich mixture limits of flammability in air lie at 5 and 15 volumetric per cent of fuel vapour (34.3 to 10.2 air/fuel mass ratio) for methane , and reduce progressively through the hydrocarbon gases to almost constant values of 1 and 5 (22 to 4 air/fuel ratio) for the petroleum liquids ranging widely from aviation gasoline to residual fuel oil2.
Is esterification a reversible reaction?
The esterification of oleic acid with methanol is a reversible reaction. Oleic acid conversions were obtained as 27% and 52% for the molar feed ratios of 3:1 and 6:1, respectively, at 4 h. As the molar feed ratio increased to 9:1, the conversion of oleic acid decreased to 46%. The results confirmed that using excess methanol led to incremental oleic acid conversion. On the other hand, a methanol–oleic acid ratio greater than 6:1 caused a decrease in the oleic acid conversion. Therefore, a 6:1 M ratio was determined to be the optimum molar ratio for this reaction [15,16].
What is excess reagent?
An excess reagent is one that is present in large enough quantities that it does not restrict the outcome of the reaction.
What are the two reactants in a stoichiometric set up?
In a stoichiometric set-up, in reference to either a synthesis or combustion chemical reaction, there are two reactants: The limiting reactant, and the excess reactant. The limiting reactant is the reactant (of the two/more) that is completely reacted up, or used up, before any other reactant is. When solved for, it is the reactant with the least amount of moles found to be used. The excess reactant is the opposite: It is the reactant that, after the limiting reactant is used up, still has more of that substance left over
Why is excess reactant important?
This is financially efficient when one of the reactants is very cheap. When one reactant is in excess, there will always be some left over. The other reactant becomes a limiting factor and controls how much of each product is produced. While using excess reactants can help to increase percentage yields, this is at the expense of atom economy.
How many moles of magnesium react with two moles of acid?
The equation shows that one mole of magnesium will react with two moles of acid. Use the information in the question to calculate how many moles of each reactant are present. For all of the magnesium to be used up, we would need twice the number of moles of acid and this is not the case.
Can excess reactants increase yield?
While using excess reactants can help to increase percentage yields, this is at the expense of atom economy . A balance between the economic and environmental value of the use of excess reactants must be established.
Excess Reactant
Consider going grocery shopping for a meal that must be prepared for dinner. There will always be some ingredients left over and some that will be totally consumed once the dish is created, no matter how well planned it is. This situation can be compared to chemical processes that occur all around us.
Limiting and Excess Reactants
In the above example of assembling a bicycle, it can be seen that while one frame was left over, all of the wheels were used up in the process. As a result, the number (or quantity) of wheels determined how many final products (bicycles) could be manufactured, i.e. the wheels set the limit.
How to Find Excess Reactant
Assume a reaction that commences with 10 moles of hydrogen gas (H2) and 7 moles of oxygen gas (O2). The coefficients of a balanced equation for water formation, {eq}2H_2 + O_2 \rightarrow 2H_2O {/eq} , reveal that one mole of H2 and half a mole of O2 are spent for every one mole of water produced.
What is Excess Reactant?
An excess reactant is the reactant that is present in excess in a reaction mixture. Therefore, after the completion of the reaction, some amount of this reactant still remains since it is in excess. We can observe the presence of excess reactant at the beginning of the reaction, at the progression, and at the end as well. Sometimes the presence of an excess reactant is important in determining an unknown amount of a particular substance that can react with this excess reactant. For example, in titrimetric methods, we use an excess reactant with a known amount and after the completion of the reaction. Here, we can determine the amount of excess reactant still present in the reaction mixture, to determine how much of this reactant reacted with the unknown.
Why is excess reactant important?
Sometimes the presence of an excess reactant is important in determining an unknown amount of a particular substance that can react with this excess reactant. For example, in titrimetric methods, we use an excess reactant with a known amount and after the completion of the reaction.
What is the Difference Between Limiting Reactant and Excess Reactant?
The key difference between limiting reactant and excess reactant is that the limiting reactant can limit the amount of final product produced, whereas excess reactant has no effect on the amount of final product.
What is a limiting reactant?
Limiting reactant is the reactant of a particular chemical reaction which can limit the formation of the final product. Therefore, it decides how much product we can yield from the completion of the chemical reaction. Moreover, this reactant is completely consumed during the reaction. The reaction stops when all the limiting reactant is consumed.
What is a reactant in chemistry?
A reactant is a compound that is consumed during a chemical reaction. A chemical reaction involves reactants – some reactants in excess and some in limited amounts. The limiting reactant always decides the amount of final product formed after the completion of the reaction. That means, the limiting reactant limits the amount of final product, ...
Why does a reaction stop when one reactant is missing?
The reaction stops when all the limiting reactant is consumed. It is because the reaction stops when one reactant is missing. By looking at the stoichiometric relationship between this reactant and the final product in a chemical equation, we can determine how much product is going to be formed.
