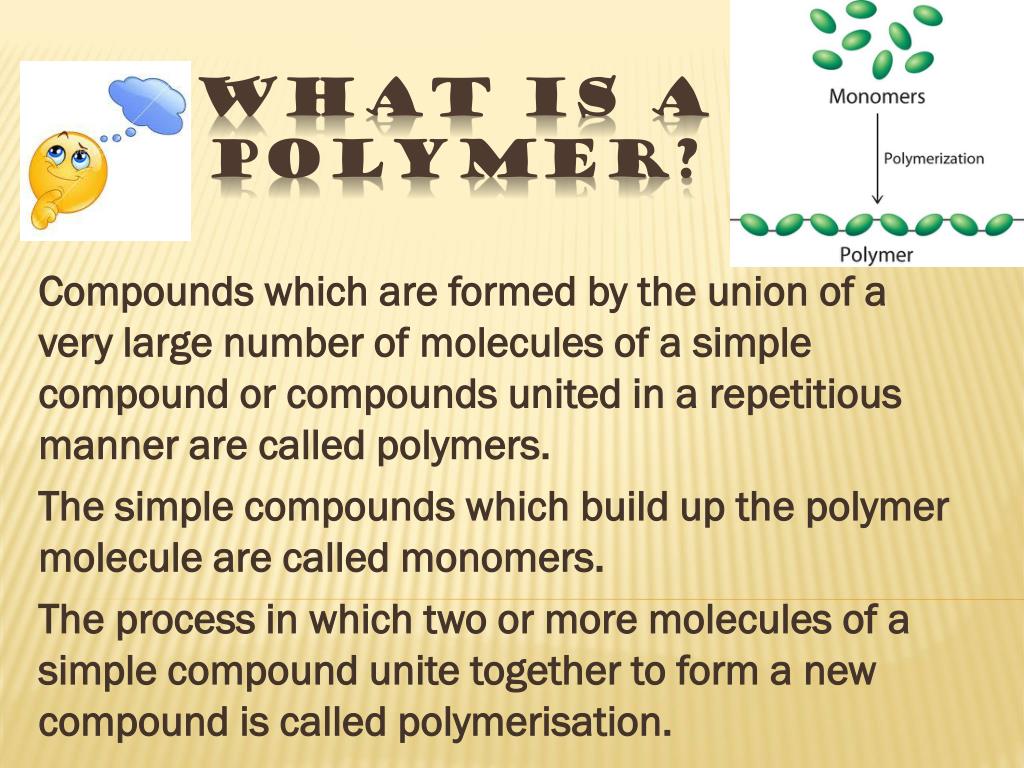
What is a polymer and what is it made of?
Polymers are materials made of long, repeating chains of molecules. There are natural and synthetic polymers, including proteins and rubber, and glass and epoxies.
What are facts about polymers?
- Oil paints consist of a suspension of pigment (colorant) in a drying oil such as linseed oil.
- Oil varnishes consist of a polymer, either natural or synthetic, dissolved in a drying oil together with the necessary additives such as catalyst that promotes crosslinking of the drying oil.
- Enamels are oil varnishes with pigment added.
What is the relationship between a polymer and a monomer?
Monomers and Polymers - Key takeaways
- Monomers are simple molecules and the smallest repeating units in polymers.
- Polymers are very large molecules (macromolecules) that are made from single repeating units (monomers).
- There are three categories of monomers: monosaccharides, amino acids, and nucleotides.
What is an everyday example of polymer?
- Polycarbonate (PC) is one of the polymers which have high impact strength. ...
- HIPS ( High Impact Polystyrene) made by adding butadiene to polystyrene also possess high impact strength.
- Polyamides ( family of nylons) have excellent tensile strength. ...

What is meant by polymer meaning?
Definition of polymer : a chemical compound or mixture of compounds formed by polymerization and consisting essentially of repeating structural units.
What is a polymer example?
Examples of synthetic polymers include nylon, polyethylene, polyester, Teflon, and epoxy. Natural polymers occur in nature and can be extracted. They are often water-based. Examples of naturally occurring polymers are silk, wool, DNA, cellulose and proteins.
What are the 4 types of polymers?
Types of polymers. There are several types of polymers. Among the main ones are: natural, synthetic, addition, condensation and rearrangement.
Why is it called a polymer?
By definition, polymers are large molecules made by bonding (chemically linking) a series of building blocks. The word polymer comes from the Greek words for “many parts.” Each of those parts is scientists call a monomer (which in Greek means “one part”). Think of a polymer as a chain, with each of its links a monomer.
What are the 3 main types of polymers?
There are 3 principal classes of polymers – thermoplastics, thermosets, and elastomers. Differentiation between these classes is best defined by their behaviour under applied heat.
Is water a polymer?
Liquid water is a dynamic polydisperse branched polymer | PNAS.
What is polymer used for?
Product made from polymers are all around us: clothing made from synthetic fibers, polyethylene cups, fiberglass, nylon bearings, plastic bags, polymer-based paints, epoxy glue, polyurethane foam cushion, silicone heart valves, and Teflon-coated cookware.
Which polymer is best?
The best plastic polymer is High-density polyethylene because it is chemically inert, hard, and tough. It is a linear arrangement molecule with a high density due to the close packing structure.
What are the 2 kinds of polymer?
Types of PolymersNatural Polymers.Synthetic Polymers.
What is another name of polymer?
What is another word for polymer?plasticpolystyrenepolyethyleneacrylicPVCsynthetic polymerpolyvinyl chloridemethyl methacrylatePMMA1 more row
How is polymer made?
Polymers are formed by two main ways called addition and condensation polymerization. In addition, polymerization, an initiator (or catalyst) reacts with a starting monomer. The result of this initiation reaction is a monomer attached to the initiator with an unsatisfied bond.
Is polymer is a plastic?
All the plastics are polymer but all the polymers are not plastic which means plastic is a sub-division of polymer. Polymers are uniform molecules formed by small monomers and plastics are long-chain molecules formed by large monomers. Polymers can be either natural or synthetic but plastics are synthetic materials.
What is the most common polymer?
PolyethylenePolyethylene (PE): Low and high density polyethylene (LDPE and HDPE respectively) are the two most common and the material properties vary across the different variants.
What is a common polymer?
Some familiar household synthetic polymers include: Nylons in textiles and fabrics, Teflon in non-stick pans, Bakelite for electrical switches, polyvinyl chloride (PVC) in pipes, etc. The common PET bottles are made of a synthetic polymer, polyethylene terephthalate.
What is a polymer made of?
chemistry : a chemical compound that is made of small molecules that are arranged in a simple repeating structure to form a larger molecule. See the full definition for polymer in the English Language Learners Dictionary.
What are some examples of polymers?
Examples of polymer in a Sentence. Recent Examples on the Web They are made of durable, high-impact resistant, composite plastic polymer. — Chris Hachey, BGR, 16 June 2021 One of those drugs uses a polymer — a gel-like mixture of molecules — to ensure the active ingredient releases slowly, extending its benefits.
What is thermoplastic polymer?
Thermoplastic polymers or thermosoftening plastics are the other type of synthetic polymers. While thermoset plastics are rigid, thermoplastic polymers are solid when cool, but are pliable and can be molded above a certain temperature. While thermoset plastics form irreversible chemical bonds when cured, the bonding in thermoplastics weakens with temperature. Unlike thermosets, which decompose rather than melt, thermoplastics melt into a liquid upon heating. Examples of thermoplastics include acrylic, nylon, Teflon, polypropylene, polycarbonate, ABS, and polyethylene.
What is a synthetic polymer?
Thermoset plastics are made from a liquid or soft solid substance that can be irreversibly changed into an insoluble polymer by curing using heat or radiation. Thermoset plastics tend to be rigid and have high molecular weights.
Why do polymers have high molecular mass?
Because the molecules consist of many monomers, polymers tend to have high molecular masses. The word polymer comes from the Greek prefix poly -, which means "many," and the suffix - mer, which means "parts.". The word was coined by Swedish chemist Jons Jacob Berzelius (1779–1848) in 1833, although with a slightly different meaning from ...
What was the name of the polymer that was used as a surgical dressing?
When nitrocellulose was dissolved in ether and alcohol, it became collodion. This polymer was used as a surgical dressing, starting with the U.S. Civil War and afterward. The vulcanization of rubber was another big achievement in polymer chemistry.
What are some examples of synthetic polymers?
Examples of synthetic polymers include PVC (polyvinyl chloride), polystyrene, synthetic rubber, silicone, polyethylene, neoprene, and nylon. Synthetic polymers are used to make plastics, adhesives, paints, mechanical parts, and many common objects. Synthetic polymers may be grouped into two categories.
What are some examples of thermoplastics?
Examples of thermoplastics include acrylic, nylon, Teflon, polypropylene, polycarbonate, ABS, and polyethylene.
Who proposed the name macromolecules to describe polymers?
While scientists and engineers could make polymers, it wasn't until 1922 that an explanation was proposed for how they formed. Hermann Staudinger suggested covalent bonds held together long chains of atoms. In addition to explaining how polymers work, Staudinger also proposed the name macromolecules to describe polymers.
What does mer mean in a polymer?
What's a mer? — you might ask. Well, it means "part," and it works only as a suffix. Since poly- means "many," a polymer means "many parts.". You'll find polymers everywhere: they're what make spandex stretch and sneakers bounce.
What is a polymer that binds to cellulose fibers?
any of various polymers containing the urethane radical; a wide variety of synthetic forms are made and used as adhesives or plastics or paints or rubber. lignin. a complex polymer; the chief constituent of wood other than carbohydrates; binds to cellulose fibers to harden and strengthen cell walls of plants.
What is a trimer in biology?
trimer. a polymer (or a molecule of a polymer) consisting of three identical monomers. operon. a segment of DNA containing adjacent genes including structural genes and an operator gene and a regulatory gene. acrylate resin, acrylic, acrylic resin. a glassy thermoplastic; can be cast and molded or used in coatings and adhesives.
What is a bouncing putty?
a resin derived from allyl alcohol that hardens when cured; used as an adhesive. bouncing putty. a soft elastic silicone polymer that increases in elasticity with the application of force; used in the center of golf balls and as shock-absorbent padding. cDNA, complementary DNA.
What is a polyamide?
polyamide, polymeric amide. a polymer containing repeated amide groups. silicone, silicone polymer. any of a large class of siloxanes that are unusually stable over a wide range of temperatures; used in lubricants and adhesives and coatings and synthetic rubber and electrical insulation. trimer.
What is the name of the polymer that is found in the nucleus of a cell?
DNA, deoxyribonucleic acid, desoxyribonucleic acid. (biochemistry) a long linear polymer found in the nucleus of a cell and formed from nucleotides and shaped like a double helix; associated with the transmission of genetic information. RNA, ribonucleic acid.
What is synthetic resin?
synthetic resin. a resin having a polymeric structure; especially a resin in the raw state; used chiefly in plastics. copolymer. a polymer consisting of two or more different monomers.
What is the meaning of polymer?
A polymer is a larger molecule that is formed by the combination of many smaller molecules of the same kind. They are made of long repeating chains of molecules. The word polymer means many parts. Silk, hair, PVC are examples of polymers. The process by which monomers join together and form polymers is called polymerisation.
What is polypropylene made of?
Polypropylene is made up of monomer propene.
What are Polymers?
A polymer is a large molecule or a macromolecule which essentially is a combination of many subunits. The term polymer in Greek means ‘many parts’. Polymers can be found all around us. From the strand of our DNA which is a naturally occurring biopolymer to polypropylene which is used throughout the world as plastic.
How are polymers formed?
Polymers are all created by the process of polymerization wherein their constituent elements called monomers, are reacted together to form polymer chains, i.e 3-dimensional networks forming the polymer bonds.
What type of monomer is present in polyethene?
Homomer: In this type, a single type of monomer unit is present. For example, Polyethene
Why are polymers stable?
These polymers are stable at high temperatures. Due to their high molecular weight, these are not destroyed even at very high temperatures. They are extensively used in the healthcare industries, for making sterilization equipment and in the manufacturing of heat and shock-resistant objects.
Why can't polymers be classified?
Classification of Polymers. Polymers cannot be classified under one category because of their complex structures, different behaviours and vast applications. We can, therefore, classify polymers based on the following considerations.
What are the different types of polymers?
Types of Polymers. On the basis of the type of the backbone chain, polymers can be divided into: Organic Polymers: Carbon backbone. Inorganic Polymers: Backbone constituted by elements other than carbon. On the basis of their synthesis: Natural Polymers.
What type of polymerization mechanism is used in biological processes?
The type of polymerization mechanism used depends on the type of functional groups attached to the reactants. In the biological context, almost all macromolecules are either completely polymeric or are made up of large polymeric chains.
How are polymers made?
These polymers are produced in various types of reactions. Most of the simple hydrocarbons, like propylene and ethylene, are transformed into polymers by adding one monomer after the other to the growing chain. Polyethylene is composed of repeating ethylene monomers and is an additional polymer. It can contain as many as 10,000 monomers joined in a long coiled chain. Polyethylene is translucent, thermoplastic, and crystalline. It means it softens when heated.
What are block copolymers?
Answer: Block copolymers contain long sequences of various monomer units. Polymers either with two or three blocks of two distinct chemical species (for example, A and B) are known as diblock and triblock copolymers, respectively. Polymers having three blocks, each of various chemical species (for example, A, B, and C) are termed as triblock terpolymers.
What are some examples of organic polymers?
For example, the solid parts of all the plants are prepared by polymers. These include lignin, cellulose, and various resins. Cellulose is a type of polysaccharide, which is a polymer, composed of sugar molecules. Lignin contains a three-dimensional complicated polymer network. Wood resins are the polymers of simple isoprene, a hydrocarbon. Rubber is another familiar isoprene polymer.
What is the name of the material that is made from a single hydrogen atom in ethylene?
If a single hydrogen atom in ethylene is replaced with a chlorine atom, it produces a vinyl chloride. This polymerizes to polyvinyl chloride (which is PVC), a hard, colourless, tough, thermoplastic material that is manufactured in a number of forms, including films, fibres, and foams. Vinyl acetate, which is produced by the ethylene and acetic acid reaction, polymerizes to amorphous, soft resins can be used as adhesives and coatings. It copolymerized with vinyl chloride to form a large family of thermoplastic materials.
What are the natural polymers of nucleotides?
Some other important natural polymers are given as proteins, which are the polymers nucleic acids and amino acids, which are the polymers of nucleotides. These complex molecules are composed of nitrogen-containing bases, phosphoric acids, and sugars. In the cell, nucleic acids carry genetic information. Starches, which are the important sources of food energy derived from plants, are the natural polymers, composed of glucose.
What are the polymers used in rubber?
Other additional polymers include polyisoprene, polychloroprene, polybutadiene, which are all essential in manufacturing synthetic rubbers. A few polymers, like polystyrene, are transparent and glassy at room temperature and are thermoplastic as well. Polystyrene can be coloured any shade, and it can be used in the manufacture of toys and some other plastic objects.
Which macromolecular material contains oxygen atoms?
Most of the important polymers contain nitrogen or oxygen atoms, along with the carbon, in the backbone chain. Among that macromolecular material with oxygen atoms are given as polyacetals. Polyformaldehyde is the simplest polyacetal, and it holds a high melting point and is crystalline and abrasion and also resistant to the action of solvents. Acetal resins are mostly the same metal as are many other plastics and they are used in machine parts manufacturing such as bearings and gears.