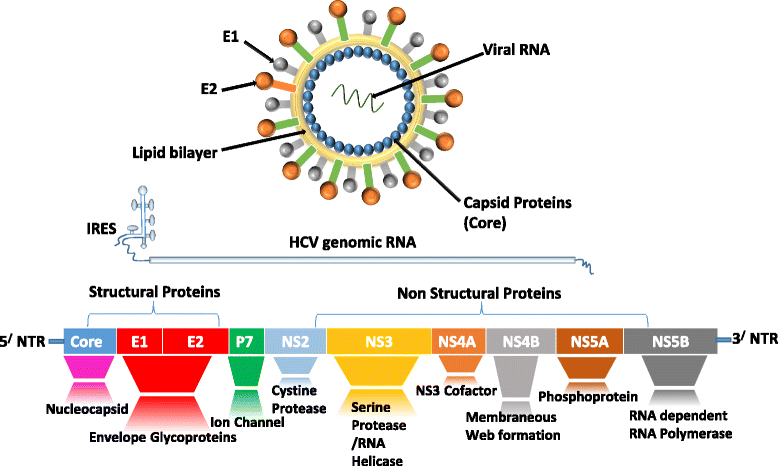
What is HBV protein?
The seven main proteins of HBV include Core, pre-Core, Small S, Middle S, Large S, Polymerase, and the critical HBV-encoded regulatory protein hepatitis B virus X protein (HBx).
Where can HBV protein be found?
Dietary sources In general, proteins from animal sources have a higher biological value than proteins from plant sources. Animal sources of protein are meat, poultry, fish, eggs, milk, cheese and yogurt, and they provide high biological value proteins.
Is Hep B a protein?
Hepatitis B vaccines contain one of the proteins from the surface of the hepatitis B virus (HepB surface antigen, or HBsAg). This protein is made by inserting the genetic code into yeast cells, which removes any risk of viral DNA getting into the final product.
What is functional cure of HBV?
Functional cure of hepatitis B is defined as sustained undetectable circulating HBsAg and HBV DNA after a finite course of treatment.
What is an example of a HBV protein?
HBV foods: meat, poultry, cheese, soya beans, milk, quinoa, eggs, fish, yogurt, quark, soya beans, quinoa.
Why do we need high biological value protein?
The biological value provides a measurement of how efficient the body utilizes protein consumed in the diet. A food with a high value correlates to a high supply of the essential amino acids.
Why hepatitis B is called silent killer?
Hepatitis B and C are known as silent killers because the diseases develop very slowly over many years, and thus most patients have no symptoms and don't even know they are infected.
How does HBV leave the cell?
In contrast, it has been suggested that HBV buds into the MVB and exits the cell via an exosomal pathway (Fig. 2) (Lambert et al. 2007). Consistent with this hypothesis, HBV virions have been localized to membranes of the late endosome and large intracellular compartments (Roingeard and Sureau 1998; Falcon et al.
What is the hepatitis B vaccine called?
In November 2017, a vaccine was approved by the FDA for use in the U.S. Heplisav-B (Dynavax) is a two-dose vaccine approved for use in adults aged 18 and older. The vaccine is administered as two doses given one-month apart. Ask your doctor about the 2-dose vaccine.
What is functional cure?
A functional cure is when a virus is not completely eliminated by the body's immune system but can be controlled without medication.
Are there vaccines for HBV?
The virus, which is called hepatitis B virus (HBV), can cause lifelong infection, cirrhosis (scarring) of the liver, liver cancer, liver failure, and death. Hepatitis B vaccine is available for all age groups.
What is the latest cure for hepatitis B?
Summary. While there is no cure for HBV, many available treatments can help prevent liver damage. Approved medications to treat HBV include oral antiviral drugs and immune modulator drugs. These two treatment approaches offer different benefits and drawbacks.
How can LBV protein foods be made more valuable to the body?
Protein complementation is when two LBV proteins are eaten together. By eating two LBV proteins in the same meal, you can make up for the lacking amino acids in each, therefore giving yourself a meal with a high biological value (HBV). A common example of protein complementation would be eating beans on toast.
Whats is HBsAg?
Following infection with hepatitis B virus (HBV), hepatitis B surface antigen (HBsAg) is detectable in the serum before liver function tests become abnormal and before development of clinical features of hepatitis; HBsAg tests usually become negative shortly after illness subsides.
What is HBx hepatitis?
Chronic infection with hepatitis B virus (HBV) is a risk factor for developing liver diseases such as hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). HBx is a multifunctional protein encoded by the HBV genome; HBx stimulates HBV replication and is thought to play an important role in the development of HBV-associated HCC.