:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/what-you-need-to-know-about-thyroid-storm-3232981_final-f6b75fd80c824233bced2cd5972526ce.jpg)
Which gland in the human body produces the hormone thyroxine?
Thyroxine is the main hormone secreted into the bloodstream by the thyroid gland . It is the inactive form and most of it is converted to an active form called triiodothyronine by organs such as the liver and kidneys . Thyroid hormones play vital roles in regulating the body’s metabolic rate, heart and digestive functions, muscle control ...
What is the action of thyroxine in the cells?
Thyroxine stimulates oxygen utilization and heat production by many different populations of body cells. It causes increased utilization of carbohydrates, increased protein catabolism, as indicated by a greater excretion of nitrogen, and greater oxidation of fats as suggested by loss in body weight.
What are the symptoms of too much thyroxine?
These are the most common symptoms:
- fatigue and tiredness
- increased awareness of the cold
- dry and coarse skin
- dry and thinning hair
- hoarse or croaky voice
- constipation
- muscle weakness, cramps and aches
- pins and needles in the fingers and hands (carpal tunnel syndrome)
- heavier and longer periods
- fertility problems
What does high levels of thyroxine mean?
What does it mean if your Free Thyroxine result is too high? Elevated free thyroxine levels may indicate hyperthyroidism, thyroid hormone resistance syndrome, or thyroxine toxicosis. Elevated free thyroxine may cause symptoms of hyperthyroidism including excessive appetite, anxiety, heart palpitations, sweating, shortness of breath, weight loss, and intolerance to heat.
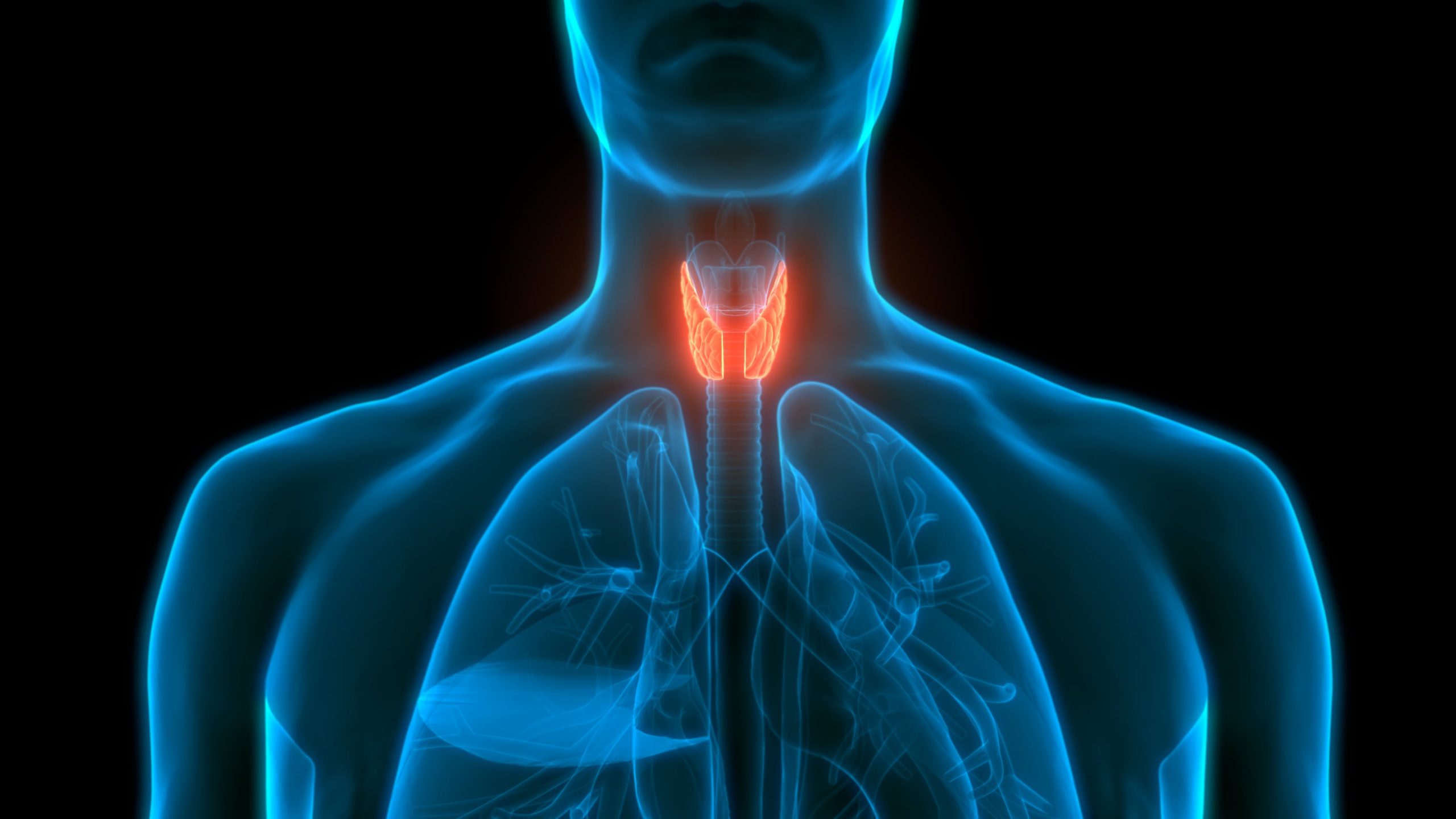
What is the main function of thyroxine hormone?
Thyroxine is the main hormone secreted into the bloodstream by the thyroid gland. It plays vital roles in digestion, heart and muscle function, brain development and maintenance of bones.
What is the function of thyroxine hormone Class 8?
Solution : Thyroxine hormone regulates the carbohydrate, protein and fat metabolism in the body so as to provide the best growth balance.
What are the functions of thyroid hormones Class 11?
The thyroid hormones are secreted by the thyroid gland, which is located in front of the neck. These hormones are integral in the regulation of many functions and aspects of the human body, such as temperature regulation, energy levels, weight, hair, nail growth and more.
Where thyroxine is produced?
the thyroid glandThyroid hormones are made by the thyroid gland. The thyroid gland makes and releases two thyroid hormones: thyroxine (T4) and triiodothyronine (T3).
What are hormones for Class 8?
Answer: Hormones are chemical substances that are secreted by the ductless glands or endocrine glands and released directly into the blood stream. They are responsible for regulating growth, development, behaviour and reproduction.
What are the 3 functions of the thyroid gland?
What does the thyroid gland do? The thyroid gland produces hormones that regulate the body's metabolic rate controlling heart, muscle and digestive function, brain development and bone maintenance. Its correct functioning depends on a good supply of iodine from the diet.
Is caused due to deficiency of thyroxine hormone Class 8?
Goitre is caused by the deficiency of thyroxine in the body.
What conditions are related to abnormal thyroid hormone levels?
Several conditions can result from or cause abnormal thyroid hormone levels. Thyroid disease is very common, with an estimated 20 million people in the United States having some type of thyroid condition. A person assigned female at birth is about five to eight times more likely to have a thyroid condition than a person assigned male at birth.
When should I see my doctor about my thyroid hormone levels?
Abnormal thyroid hormone levels usually cause noticeable symptoms. Since thyroid hormone is responsible for controlling the speed of your metabolism, too much thyroid hormone can make it faster than normal and too little thyroid hormone can slow it down. These imbalances cause certain symptoms, including:
What hormone is made in the thyroid gland?
Thyroxine is a hormone made in the thyroid gland for the regulation of metabolism, body heat production, blood pressure, and the normal development of the skeletal and nervous systems. Thyroxine is an amino acid-based hormone that targets the genes involved in the metabolism of glucose in the body. Iodine in the blood is a key component of making thyroxine, and if not enough iodine is present, it can lead to the development of abnormal growths called goiters.
What is the first test for thyroid problems?
When a patient is diagnosed with potential thyroid problems, one of the first tests is to check the TSH levels in the blood. If not enough TSH is being made, which is known as hypothyroidism, the patient is prescribed synthetic TSH in pill form. If too much TSH is detected, which is known as hyperthyroidism, further tests are conducted and treatments may include surgical removal of the thyroid gland or taking radioactive iodine to slow down the gland's activity.
What is the name of the hormone that is produced by the body?
Thyroxine is one of two hormones that together form what's referred to collectively as the thyroid hormone. Thyroxine travels through the blood to the target cells and is then converted to triiodothyronine, shortened to T3; think of T4 as the messenger, and T3 as the worker that carries out the order. T3 is the active form of thyroid hormone and is primarily responsible for your metabolism, which is the process by which your cells break down food and other substances into smaller molecules they can use.
What is the role of thyroxine in the body?
Thyroxine is a component of thyroid hormone which regulates metabolism, body heat, blood pressure, certain tissue development, and reproductive functions. Explore the importance of this hormone to the endocrine system and other bodily functions. Updated: 11/27/2021
How does thyroid hormone work?
Thyroid hormone works by entering a target cell's nucleus, binding to receptors, and starting transcription, or the copying of DNA, for making proteins. The target genes are the ones involved in the metabolism of glucose in your body. Thyroid hormone increases your metabolism and body heat production. In addition, the thyroid hormone also regulates blood pressure, the development of skeletal and nervous tissues, and it affects reproductive function.
Where is the thyroid gland controlled?
The thyroid gland is controlled by thyroid stimulating hormone, or TSH for short. TSH is manufactured in the pituitary gland in the brain. The pituitary gland receives information from the body about metabolism, blood pressure, and so forth, and then responds by either increasing TSH secretions, which travel to the thyroid gland and promote thyroxine production, or shutting off TSH secretions, which then decreases thyroxine production.
What is the endocrine system?
The endocrine system is one of the master systems of the body, along with the nervous system, that regulates the activities of other systems. It's structured around the manufacturing and delivery of chemical messengers called hormones.
What is the role of thyroxine in the body?
Thyroxine is a very important hormone and part of the system of hormones which help regulate thyroid function in your body.
What is the active ingredient in thyroid medications?
Thyroxine is the ACTIVE ingredient in many medications used to treat hypothyroidism . Medications that contain Thyroxine include Synthroid, levothyroxine , Tirosint, and Levoxyl. Thyroxine is also present in T3/T4 combination medications such as Natural Desiccated Thyroid hormone .
What is the cause of a deficiency in thyroid hormone?
Generally, a deficiency in thyroid hormone is the result of damage directly to your thyroid gland. Remember that your thyroid gland PRODUCES thyroid hormone, so in order for you to have sufficient thyroxine in your body, it must be produced from your thyroid gland . When damaged your thyroid gland will be LESS responsive to TSH.
How does thyroxine affect thyroid function?
Thyroxine, after being converted to T3, then acts on nuclear receptors in your cells to alter genetic transcription (3) (to change your genes). This is how your thyroid gland works! Deficiency in Thyroxine may result in symptoms which range from fatigue to weight gain to depression and so on .
What is the name of the hormone that is produced by the thyroid gland?
Thyroxine is the full and scientific name given to one of the major thyroid hormones produced from your thyroid gland. You might know Thyroxine as its more common name T4, either way, both names refer to the same biological hormone.
Why is thyroxine important?
Thyroxine is incredibly important because, without it, your body would not be able to create T3. While Thyroxine is not the most biologically active thyroid hormone, it still plays a very important role in acting as a reservoir for thyroid conversion. The most potent and biologically active thyroid hormone is T3 or Triiodothyronine, ...
What is the most active thyroid hormone?
The most potent and biologically active thyroid hormone is T3 or Triiodothyronine, but the trick here is that most of T3 in your body STEMS from T4. The process by which T3 is created from T4 is known as thyroid conversion (2). In this way, your body plays a balancing act with both T3 and T4 levels. It's hard to say that one is more important ...
What hormone is secreted by the thyroid gland?
Thyroxine. Thyroxine is the name of the hormone secreted by thyroid gland which does the work of metabolic activities. It also controls the rate of oxidation level in the cells. Thyroxine hormone contains 65% iodine which is necessary for the production of T3 and T4 (tyrosine) hormones.
How much thyroxine is in blood?
Excess of Thyroxine. In one deciliter of blood, there should be 4.5—11.2 mcg of thyroxine in blood. This is considered as standard level of this hormone and anything lesser than and higher than this normal level is dangerous.
What hormones are produced by thyroxine?
Thyroxine hormone contains 65% iodine which is necessary for the production of T3 and T4 (tyrosine) hormones. When there is deficiency of iodine it will automatically reduce the production of T3 and T4 hormones causing goiter. When there is increase in thyroxine this leads to a condition called hyperthyroidism.
What is it called when thyroxine levels are below 4.5?
Similarly, when the level is below 4.5 then this condition is called hypothyroidism, which arises due to deficiency of thyroxine.
What happens if you have low thyroxine levels?
People with low level of thyroxine will have dry skin with white patches, slow reflexes, slow pulse rate, enlarged heart and slow speech. Goiter is a condition of low thyroxine level in blood and such people will have rapid weight gain, weakness, joint pain and stiffness in joints.
What hormones are given to treat hypothyroidism?
Doctors would administer T3 and T4 hormones to treat deficiency of thyroxine. Levothyroxine is the medicine given for treating hypothyroidism.
Why is thyroid important?
Thyroid hormone is absolutely necessary for normal development of cells and they are vital in controlling the metabolism of proteins and fats in your body. In addition, it also controls various physiological activities and help in heat generation in the body.
