
What is the genotypic ratio of Monohybrid cross?
Monohybrid Cross: F2 generation. Should the F 1 generation be allowed to self-pollinate, the potential allele combinations will be different in the next generation (F 2 generation). The F 2 generation would have genotypes of (GG, Gg, and gg) and a genotypic ratio of 1:2:1.
Which genotypes are (GG) and (F2)?
All genotypes are (Gg). The offspring or F1 generation are all green because the dominant green pod color obscures the recessive yellow pod color in the heterozygous genotype. Should the F 1 generation be allowed to self-pollinate, the potential allele combinations will be different in the next generation (F 2 generation).
What is a monohybrid cross?
Modern scientists now describe the cross of Mendel’s F1 generation as a monohybrid cross. The individuals in the cross all had one allele for green pods and one allele for yellow pods, making them hybrids. This cross only examined one trait, however many more traits can be observed at once. A Test Cross
What does F1 mean in genetics?
So in short, F1 means 'first filial generation'. If you are crossing two parents that are 'true breeding' - meaning they each have homozygous traits (one has dominant traits, the other has recessive traits) - the F1 generation will typically be heterozygous (having a genotype that is heterozygous and a phenotype that is dominant).
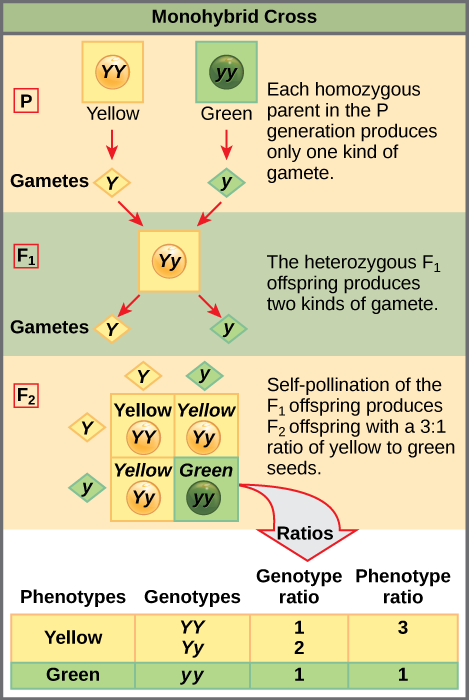
What is the F1 genotypic ratio of monohybrid cross?
1:2:1A monohybrid cross results in a phenotypic ratio of 3:1 (dominant to recessive), and a genotypic ratio of 1:2:1 (homozygous dominant to heterozygous to homozygous recessive).
What is the genotype of the F1 generation?
The offspring of the RRYY x rryy cross, which is called the F1 generation, were all heterozygous plants with round, yellow seeds and the genotype RrYy.
What is a Monohybrid F1 cross?
“A monohybrid cross is the hybrid of two individuals with homozygous genotypes which result in the opposite phenotype for a certain genetic trait.” “The cross between two monohybrid traits (TT and tt) is called a Monohybrid Cross.” Monohybrid cross is responsible for the inheritance of one gene.
What is the genotype of F2 generation in monohybrid cross?
Monohybrid Cross: F2 generation The F2 generation would have genotypes of (GG, Gg, and gg) and a genotypic ratio of 1:2:1. One-fourth of the F2 generation would be homozygous dominant (GG), one-half would be heterozygous (Gg), and one-fourth would be homozygous recessive (gg).
What is the genotype of the F1 generation quizlet?
The genotype of the F1 plants is (Gg).
What will be the F1 generation?
In basic terminology, the F1 generation is the first generation of offspring produced by a set of parents. The 'F' in F1 stands for 'filial. ' So in short, F1 means 'first filial generation'.
What will be genotype of F1 generation in the above cross?
No recessive phenotype appears in the F1 generation. This means that both parents cannot have the recessive allele for each trait. Therefore the parental genotypes must be WWdd x wwDD. As a check, this cross produces all individuals with a genotype of WwDd.
How do you calculate F1 and F2 generation?
The parents of the F1 generation are two individuals that are identically hybrid for two traits, while the parents of the F2 generation are the individuals of the F1 generation.
What is the expected genotypic outcome of the F1 generation in the cross?
Answer and Explanation: The F1 generation in this monohybrid cross would all have a heterozygous (Tt) genotype and would all display the dominant phenotype.
What are the genotypes of F1 and F2 progeny?
Homozygous tall and heterozygous tall will be in the ratio of 2:1. Thus in monohybrid cross F1 plants have similar genotype. All are heterozygous tall (Tt). In F2 generation genotypic ratio will be 1:2:1. , i.e. 1 homozygous tall: 2 heterozygous tall: 1 homozygous dwarf.
What are the genotypes and phenotypes of the F1 generation?
So, the F1 generation all have identical genotypes, heterozygous at the seed color gene, and their phenotypes are yellow seeds.
What will be the pattern of genotype of the F1 generation plants?
The genotype of the F1 generation plants is AABbCC. The number of gametes involved in the given cross can be calculated by 2n where n= 1 ( n is the number of heterozygotes). Hence there will two gametes ABC and AbC.
What is the genotype of the F2 generation?
The genotype distribution of the F2 generation is 25% homozygous dominant, 50% heterozygous, and 25% homozygous recessive.
What is Mendel's F1 generation?
The F1 generation results from cross-pollination of two parent (P) plants, and contained all purple flowers. The F2 generation results from self-pollination of F1 plants, and contained 75% purple flowers and 25% white flowers. This type of experiment is known as a monohybrid cross.
What is the F1 generation?
In basic terminology, the F1 generation is the first generation of offspring produced by a set of parents. The 'F' in F1 stands for 'filial.'. So in short, F1 means 'first filial generation'. F1 Generation Example.
Why is the F1 generation important?
The F1 generation is important because it helps us determine what genes are going to be recessive and what genes will be dominant in further crosses. We can utilize this knowledge to help 'breed out' traits in plants that we don't want. Lesson Summary. Gregor Mendel was a pioneer in the world ...
Why did Mendel cross pollinate different pea plants?
In Mendel's experiments, he would typically cross-pollinate different pea plants in hopes of getting specific and certain traits to show. When looking at his experiments, we notice the term 'F1 generation' comes up often.
What happens when you cross two purebred parents?
Crossing two purebred parents results in an F1 generation that is heterozygous for a trait, but displays only the dominant trait.
Who is the father of modern genetics?
Gregor Mendel was a pioneer in the world of genetics. Known as the 'Father of Modern Genetics', he is responsible for much of what we understand about how genetics work and how traits are passed on.
What does it mean when you cross two parents?
If you are crossing two parents that are 'true breeding' - meaning they each have homozygo us traits (one has dominant traits, the other has recessive traits) - the F1 generation will typically be heterozygous (having a genotype that is heterozygous and a phenotype that is dominant). Basically, if you have a parent with completely dominant genes ...
What is monohybrid cross?
A monohybrid cross is a breeding experiment between P generation (parental generation) organisms that differ in a single given trait . The P generation organisms are homozygous for the given trait. However, each parent possesses different alleles for that particular trait. A Punnett square may be used to predict the possible genetic outcomes ...
What happens if you cross a genotype with a homozygous recessive individual?
If the unknown genotype is heterozygous, performing a cross with a homozygous recessive individual would result in a 1:1 ratio of the phenotypes in the offspring.
What Is a Test Cross?
In this type of cross, an individual of unknown genotype is crossed with an individual that is homozygous recessive for a specific trait. The unknown genotype can be identified by analyzing the resulting phenotypes in the offspring. The predicted ratios observed in the offspring can be determined by using a Punnett square. If the unknown genotype is heterozygous, performing a cross with a homozygous recessive individual would result in a 1:1 ratio of the phenotypes in the offspring.
What are traits in DNA?
Traits are characteristics that are determined by discrete segments of DNA called genes. Individuals typically inherit two alleles for each gene. An allele is an alternate version of a gene that is inherited (one from each parent) during sexual reproduction.
Is green pod color homozygous or homozygous?
True-breeding organisms have homozygous alleles for specific traits. In this cross, the allele for green pod color (G) is completely dominant over the recessive allele for yellow pod color (g). The genotype for the green pod plant is (GG), and the genotype for the yellow pod plant is (gg).
