The Golgi apparatus of plant cells serves two major functions: it assembles and processes the oligosaccharide side chains of glycoproteins, and it synthesizes the complex polysaccharides of the cell wall matrix, the hemicelluloses and pectins. The first function is common to plant and animal cells while the second is unique to plants.
What are the functions of Golgi bodies in plant cells?
Golgi Bodies in Plant Cells. In addition, as noted earlier, glycolipids and sphingomyelin are synthesized within the Golgi apparatus. In plant cells, the Golgi apparatus serves the site at which the complex polysaccharides of the cell wall are synthesized.
What is the Golgi apparatus?
What is the Golgi apparatus? The Golgi apparatus, also called Golgi complex or Golgi body, is a membrane-bound organelle found in eukaryotic cells (cells with clearly defined nuclei) that is made up of a series of flattened stacked pouches called cisternae.
What is the role of the Golgi apparatus in lipid metabolism?
Lipid and Polysaccharide Metabolism in the Golgi In addition to its activities in processing and sorting glycoproteins, the Golgi apparatusfunctions in lipid metabolism—in particular, in the synthesis of glycolipids and sphingomyelin. As discussed earlier, the glycerol phospholipids, cholesterol, and ceramide are synthesized in the ER.

What is the function of Golgi apparatus in plant and animal cells?
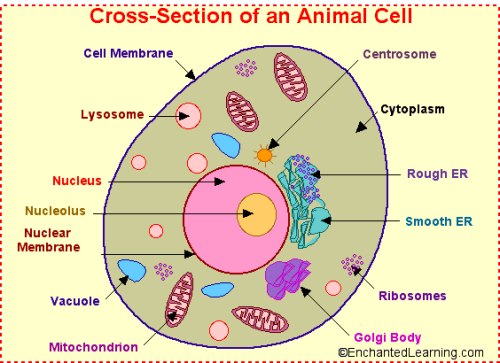
The Golgi apparatus of both higher plant and animal cells sorts and packages macromolecules which are in transit to and from the cell surface and to the lysosome (vacuole). It is also the site of oligosaccharide and polysaccharide synthesis and modification.
Do plant cells have a Golgi apparatus?
Despite the fact that plant cells have the Golgi, there remains a large difference in our knowledge of animal and plant Golgi. Whereas its role as the protein-sorting centre in the cell has been established by studies on mammalian and yeast cells, our understanding of the plant Golgi has just begun to accumulate.
What is the main function of the Golgi in a plant cell quizlet?
what is the function of the golgi apparatus? process and bundle proteins and lipids as they are synthesized - makes complicated molecules. t manufactures, processes, and transports lipids and proteins. The Golgi apparatus processes and packages proteins.
What is the difference between plant and animal Golgi?
The Golgi apparatus is found in all plant and animal cells and refers to groups of flattened disc-like structures near the endoplasmic reticulum. Animal cells have fewer but larger Golgi apparatuses. Plant cells can hold up to several hundred smaller versions.
What are the 3 main functions of the Golgi apparatus?
The three primary functions of the Golgi apparatus are the transport, sorting and modification of both protein and lipid, and the protein composition of the organelle reflects these functions.
What organelles support the plant cell and help maintain its shape?
Answer and Explanation: A central vacuole is the organelle in plant cells that stores water and helps to maintain the plant's shape.
What three organelles support the plant cell and help it to maintain its shape?
Plant cells have a rigid cell wall, a large central vacuole, and plastids.
What three organelles support the plant and help it to maintain its shape?
Plant cells have a cell wall, a large central vacuole, and plastids such as chloroplasts. The cell wall is a rigid layer that is found outside the cell membrane and surrounds the cell, providing structural support and protection. The central vacuole maintains turgor pressure against the cell wall.
How many Golgi apparatus are in plant cells?
While many types of cells contain only one or several Golgi apparatus, plant cells can contain hundreds.
Why do plants have more Golgi apparatus than animals?
Plant cells have several hundreds of Golgi bodies, unlike animal cells. In-plant cells, in addition to their normal functions, synthesize polysaccharide molecules, which constitute the making of the cell wall. For this reason, plant cells have many Golgi bodies compared to animal cells.
Which organelles are found in plant cells but not animal?
Final answer: Chloroplast is found in plant cells but not in animal cells.
Which organelle is found only in plant cell?
chloroplastsThe organelles found only in plant cells include- chloroplast, cell wall, plastids, and a large central vacuole. The chloroplasts contain a green pigment chlorophyll that is responsible for the process of photosynthesis.
What is the Golgi apparatus?
The Golgi apparatus, also known as the Golgi body or Golgi complex, is a type of organelle (i.e., a structure located in the cell) that processes a...
Where is the Golgi apparatus located?
The Golgi apparatus is a series of stacked membranes that are located within the cytoplasm (i.e., gel-like fluid held in the cell membrane) in all...
What is the function of the Golgi apparatus?
The function of the Golgi apparatus is processing and packaging proteins that have exited the rough endoplasmic reticulum to be further transported...
What are the most important facts to know about the Golgi apparatus?
The Golgi apparatus, also known as the Golgi body or Golgi complex, is an organelle that processes and packages proteins and lipid molecules (i.e.,...
What is the function of the Golgi apparatus?
The function of the Golgi apparatus is processing and packaging proteins that have exited the rough endoplasmic reticulum to be further transported inside and/or outside the cell. In plant cells, the Golgi body also serves as the site for the synthesis of complex polysaccharides.
Where is the Golgi apparatus located?
The Golgi apparatus is a series of stacked membranes that are located within the cytoplasm (i.e., gel-like fluid held in the cell membrane) in all eukaryotic cells (i.e., complex cells). It can typically be found adjacent to the nucleus and rough endoplasmic reticulum (an organelle involved in protein synthesis).
What are the most important facts to know about the Golgi apparatus?
The Golgi apparatus, also known as the Golgi body or Golgi complex, is an organelle that processes and packages proteins and lipid molecules (i.e., fat molecules) that are later exported to other cell compartments or secreted from the cell. The Golgi body has Golgi stacks, which are involved in modifying proteins and other complex polysaccharides. Transport vesicles pick up the molecules from the rough endoplasmic reticulum and transport them to the cis face of the Golgi stacks, where they fuse with the Golgi membrane and are sorted. They are then moved through the Golgi cisternae and undergo remodeling and other modifications. The modified protein or lipid molecules then depart from the trans face of the Golgi stacks where they are either secreted from the cell, or transported to another cell compartment.
What is the Golgi apparatus?
The Golgi apparatus is an organelle in eukaryotic organisms that moves molecules from the endoplasmic reticulum to their destination. The organelle also modifies products of the endoplasmic reticulum to their final form. The Golgi apparatus is comprised of a series of flattened sacs that extend from the endoplasmic reticulum.
How does the Golgi apparatus work?
In secretory cells, or cells which produce large amounts of a substance that your body needs, the Golgi apparatus will be very large. Consider the cells in your stomach that secrete acid. The acid is produced by reactions in the endoplasmic reticulum and is modified as is goes through the Golgi apparatus. Once to the trans side of the Golgi apparatus, the acid is packaged in a vesicle and sent towards the cell’s surface. As the vesicle joins with the plasma membrane, the acid is released into the stomach, so it can digest your food.
What is the function of the lysosome?
The lysosome delivers raw ingredients to the endoplasmic reticulum.
What are the products of eukaryotes?
Some products are meant for the endoplasmic reticulum or the Golgi appar atus itself and travel in the opposite direction of most vesicles. While the endoplasmic reticulum produces most of the products and bases used, it is the Golgi apparatus that is responsible for the final presentation and assembly of products. Often, the environment must be slightly different from that present in the endoplasmic reticulum to obtain certain end products. The many sacs of the Golgi apparatus function to provide many different areas in which reactions can take place in the most favorable of conditions.
What is the trans face of the Golgi apparatus?
The side furthest from the endoplasmic reticulum is known as the trans face of the Golgi apparatus, and this is where products are headed. After having any modifications or additions to their structure, the products are packaged in vesicles and tagged with markers that indicate where the vesicle needs to end up.
What is the rough endoplasmic reticulum?
The rough endoplasmic reticulum has a number of ribosomes, which assemble proteins from instructions contained in messenger RNA . Throughout the rest of the endoplasmic reticulum, these protein products are folded and modified. As they reach the Golgi apparatus, more modifications are made.
What is the function of the Golgi?
The Golgi also has important functions in tagging vesicles with proteins and sugar molecules, which serve as identifiers for the vesicles so they can be delivered to the proper target. The organelle is also called the Golgi complex or Golgi body.
What is the function of the Golgi apparatus?
The Golgi apparatus, or Golgi complex, functions as a factory in which proteins received from the ER are further processed and sorted for transport to their eventual destinations: lysosomes, the plasma membrane, or secretion. In addition, as noted earlier, glycolipids and sphingomyelin are synthesized within the Golgi.
How do proteins move through the Golgi apparatus?
One possibility is that transport vesicles carry proteins between the cisternae of the Golgi compartments. However, there is considerable experimental support for an alternative model proposing that proteins are simply carried through compartments of the Golgi within the Golgi cisternae, which gradually mature and progressively move through the Golgi in the cisto transdirection.
How are lysosomes targeted?
Targeting of lysosomal proteins by phosphorylation of mannose residues. Proteins destined for incorporation into lysosomes are specifically recognized and modified by the addition of phosphate groups to the 6 position of mannose residues. In the first (more...)
What are the four regions of the Golgi?
Although the number of such compartments has not been established, the Golgi is most commonly viewed as consisting of four functionally distinct regions: the cisGolgi network, the Golgi stack(which is divided into the medialand transsubcompartments), and the transGolgi network(Figure 9.23) . Proteins from the ERare transported to the ER-Golgi intermediate compartment and then enter the Golgi apparatusat the cisGolgi network. They then progress to the medialand transcompartments of the Golgi stack, within which most metabolic activities of the Golgi apparatus take place. The modified proteins, lipids, and polysaccharides then move to the transGolgi network, which acts as a sorting and distribution center, directing molecular traffic to lysosomes, the plasma membrane, or the cell exterior.
What is the process of protein glycosylation?
Protein Glycosylation within the Golgi. Protein processing within the Golgi involves the modification and synthesis of the carbohydrateportions of glycoproteins. One of the major aspects of this processing is the modification of the N-linked oligosaccharides that were added to proteinsin the ER.
What is the first modification of proteinsdestined for secretion or for the plasma membrane?
The first modification of proteinsdestined for secretion or for the plasma membraneis the removal of three additional mannose residues. This is followed by the sequential addition of an N-acetylglucosamine, the removal of two more mannoses, and the addition of a fucose and two more N-acetylglucosamines.
Which polysaccharides are synthesized in the Golgi apparatus?
The other cell wall polysaccharides (hemicelluloses and pectins), however, are complex, branched chain molecules that are synthesized in the Golgi apparatus and then transported in vesicles to the cell surface.
What is the Golgi apparatus?
Golgi apparatus is the site for the synthesis of various glycolipids, sphingomyelin, etc. In the plant cells, complex polysaccharides of the cell wall are synthesised in the Golgi apparatus. To learn more about Golgi Apparatus and other cells organelles, visit BYJU’S. Test your Knowledge on Golgi Apparatus. Q 5.
What is the function of Golgi bodies?
Golgi Bodies Functions. Its main function is the packaging and secretion of proteins. It receives proteins from Endoplasmic Reticulum. It packages it into membrane-bound vesicles, which are then transported to various destinations, such as lysosomes, plasma membrane or secretion.
How many Golgi stacks are there in an animal cell?
Animal cells generally contain around 10 to 20 Golgi stacks per cell, which are connected by tubular connections. Golgi complex is mostly found near the nucleus. Creation, or evolution, whichever one, you hold a belief in has worked in wondrous ways to evolve or design the various living beings in this world in the most optimum ways.
Where is the Golgi apparatus found?
The name is given on the name of the scientist, who discovered the organelle, i.e. Camillo Golgi. It is found in all the eukaryotic cells , plants as well as animals. They are membrane-bound organelle present in the cytosol of the cell.
How many cisternae are in a Golgi?
Cisternae is a flattened, disk-shaped, stacked pouches that make up the Golgi apparatus. A Golgi stack mostly contains 4 to 8 cisternae.
What is the Golgi apparatus?
In plant cells, the Golgi Apparatus is the site of synthesis for complex polysaccharides that form a part of the cell wall of plants. The Golgi Apparatus forms the transportation network for movement of molecules and proteins to and from other organelles of the cell.
What is the function of the Golgi complex?
Also known as the Golgi complex, its primary function is to receive, process and sort proteins coming from and to the ER. Functionally, The Golgi Apparatus has four distinct regions: The cis Golgi network, The Golgi Stack which is further divided into medial and trans sub-regions, and the trans-Golgi network.
What is the process of glycoproteins in the Golgi apparatus?
Protein processing events for glycoproteins within the Golgi apparatus comprises of a series of events that terminates in modification or glycosylation of the carbohydrate moieties of the protein structures. In the ER, the proteins undergo post-translational modifications.
How are proteins transported to the Golgi apparatus?
Proteins, lipids, and other molecules are transported from and to the Golgi apparatus using the secretory pathway.
Where does the processing of carbohydrate occur?
Processing of these carbohydrate moieties occurs in the Golgi Apparatus . The very first step in the modification of these proteins in the Golgi Apparatus is the removal of mannose residues. Following this, N-acetylglucosamine is added, and two more mannose residues are removed.
Which polysaccharides are synthesized in the Golgi apparatus?
Complex branched-chain polysaccharides such as hemicellulose and pectin are synthesized in the Golgi Apparatus.
Which apparatus is involved in the secretory pathway that allows movement of materials into the cell?
In a similar fashion, the Golgi apparatus is also involved in a secretory pathway that allows movement of materials into the cell, from its Cis-face.
.PNG)
Definition
Operation
- Regardless of the product, the vesicles containing the product move from the endoplasmic reticulum and into the cis face of the Golgi apparatus. In laymans terms, this is the side facing the endoplasmic reticulum. The side furthest from the endoplasmic reticulum is known as the trans face of the Golgi apparatus, and this is where products are headed. After having any modificatio…
Products
- There are many products that are produced by eukaryotes, from proteins that can carry out chemical reactions to lipid molecules that can build new cell membranes. Some products are meant for the endoplasmic reticulum or the Golgi apparatus itself and travel in the opposite direction of most vesicles. While the endoplasmic reticulum produces most of the products and …
Causes
- In secretory cells, or cells which produce large amounts of a substance that your body needs, the Golgi apparatus will be very large. Consider the cells in your stomach that secrete acid. The acid is produced by reactions in the endoplasmic reticulum and is modified as is goes through the Golgi apparatus. Once to the trans side of the Golgi apparatus, the acid is packaged in a vesicle and s…
Structure
- The image below shows the structure of the Golgi apparatus. The cis face of the organelle is closest to the endoplasmic reticulum. The trans face is the side furthest from the nucleus, which secretes vesicles to various parts of the cell. Further, there are a number of lumens and cisternae through which products flow. These appear as a series of flattened sacs stack on each other, m…
Formation
- The most prevalent theory of how the Golgi apparatus forms is the cisternal maturation model. This model suggests that the sacs themselves tend to move from the cis face to the trans face of the Golgi apparatus over time. New sacs are formed closest to the endoplasmic reticulum. These sacs age as they move towards the trans face of the Golgi apparatus and their product become…
Development
- Although it may seem like there could never be enough lipids to produce the continual flow of cell membrane needed to continually make transport vesicles between the endoplasmic reticulum and the Golgi apparatus, there are constantly segments of cell membrane being produced and recycled by the endoplasmic reticulum, Golgi apparatus, lysosomes, and other organelles in the …
Function
- The Golgi also creates lysosomes. These sacs contain digestive materials. The sacs are pinched off from the Golgi apparatus, and they are used to process materials which have been phagocytized or to digest organelles which no longer function. The lysosome delivers raw ingredients to the endoplasmic reticulum. While this article primarily discusses the operation of …