
Symptoms
For many people, A-fib may have no symptoms. However, A-fib may cause a fast, pounding heartbeat (palpitations), shortness of breath or weakness. Episodes of atrial fibrillation may come and go, or they may be persistent.
Causes
ECG in atrial fibrillation The hallmark of atrial fibrillation is absence of P-waves and an irregularly irregular (i.e totally irregular) ventricular rate. The baseline (isoelectric line between QRS complexes) is characterized by either fibrillatory waves (f-waves) or just minute oscillations.
Prevention
In atrial fibrillation, electrical signals fire from many areas in the atria, causing the chambers to beat chaotically. Some or all of these chaotic signals enter the ventricles, causing a fast, irregular heartbeat. Atrial fibrillation (A-fib) is an irregular and often very rapid heart rhythm (arrhythmia) that can lead to blood clots in the heart.
Complications
What happens during AFib? Normally, your heart contracts and relaxes to a regular beat. In atrial fibrillation, the upper chambers of the heart (the atria) beat irregularly (quiver) instead of beating effectively to move blood into the ventricles.
What are the symptoms of atrial fibrillation?
What does ECG look like with atrial fibrillation?
What is the pathophysiology of atrial fibrillation?
What happens during AFIB?
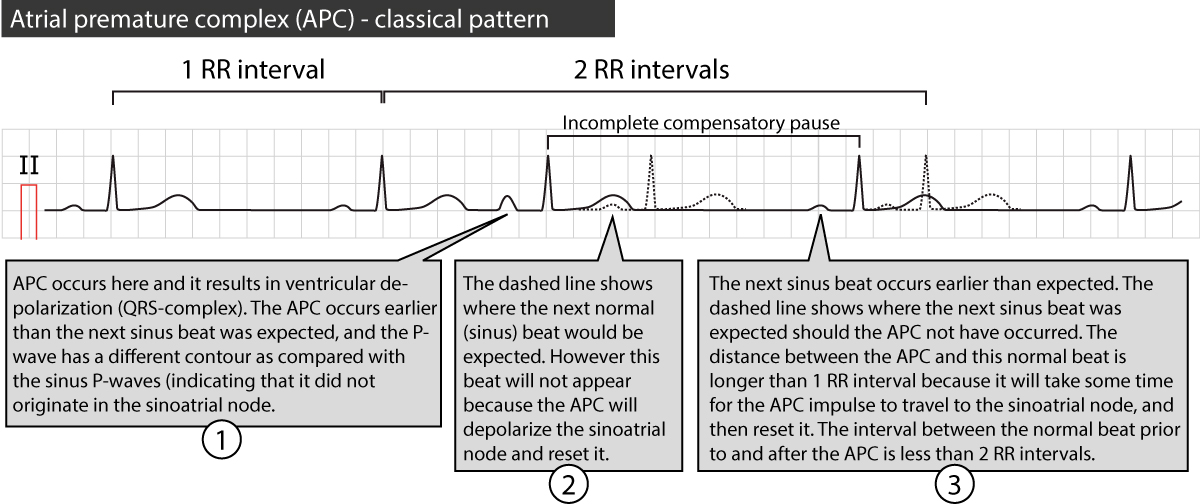
What characteristic is the hallmark of atrial flutter?
The ECG hallmark of typical atrial flutter is discordance in flutter wave "direction" between the inferior leads and lead V1. In counterclockwise circuits, flutter waves are directly negative in the inferior leads but are positive in lead V1. In clockwise circuits, the opposite is true.
How do you describe atrial fibrillation on ECG?
The diagnosis of atrial fibrillation is confirmed with a standard 12-lead ECG. P waves are absent, coarse “fibrillatory waves” can frequently be seen and sometimes no atrial activity can be identified. The QRS complexes are “irregularly irregular”, with varying R-R intervals.
What are the warning signs of atrial fibrillation?
Atrial fibrillation (Afib) is an irregular heart rhythm that begins in your heart's upper chambers (atria). Symptoms include fatigue, heart palpitations, trouble breathing and dizziness. Afib is one of the most common arrhythmias. Risk factors include high blood pressure, coronary artery disease and having obesity.
How do you detect atrial fibrillation?
Electrocardiogram (ECG or EKG). Wires connect the electrodes to a computer, which displays the test results. An ECG can show if the heart is beating too fast, too slow or not at all. An ECG is the main test for diagnosing atrial fibrillation.
Why is there no P wave in atrial fibrillation?
A lack of visible P waves preceding QRS complexes suggests a lack of sinus beats; this may occur with sinus dysfunction or in the presence of fibrillation or flutter waves.
What is the main cause of atrial fibrillation?
The basic cause of AFib is disorganized signals that make your heart's two upper chambers (the atria) squeeze very fast and out of sync. They contract so quickly that the heart walls quiver, or fibrillate. Damage to your heart's electrical system can cause AFib.
What is the most common treatment for atrial fibrillation?
Heart rate medicines: The most common way to treat atrial fibrillation is with drugs that control your heartbeat....Potassium channel blockers, which slow the electrical signals that cause AFib:Amiodarone (Cordarone, Nexterone Pacerone),Dofetilide (Tikosyn)Sotalol (Betapace, Sorine, Sotylize)
What is the drug of choice for atrial fibrillation?
Beta blockers and calcium channel blockers are the drugs of choice because they provide rapid rate control. These drugs are effective in reducing the heart rate at rest and during exercise in patients with atrial fibrillation.
What medications can cause atrial fibrillation?
New-onset AF has been associated with cardiovascular drugs such as adenosine, dobutamine, and milrinone. In addition, medications such as corticosteroids, ondansetron, and antineoplastic agents such as paclitaxel, mitoxantrone, and anthracyclines have been reported to induce AF.
What is the heart rate in AFib?
The most obvious symptom of atrial fibrillation (AF) is palpitations caused by a fast and irregular heartbeat. A normal heart rate, when you are resting, should be between 60 and 100 beats a minute. In atrial fibrillation, it may be over 140 beats a minute.
Does AFib always have rapid heartbeat?
In atrial fibrillation, the heart rate is irregular and can sometimes be very fast. In some cases, it can be considerably higher than 100 beats a minute. This can cause problems including dizziness, shortness of breath and tiredness.
Can you tell AFib from pulse?
Although you may detect an abnormal heart rhythm by checking your pulse or listening to your heart, the only way to confirm an atrial fibrillation diagnosis is to get an electrocardiogram (EKG or ECG) from your healthcare provider.
What does heart flutter look like on ECG?
Atrial Fibrillation Causes and Complications Atrial flutter produces a distinctive "sawtooth" pattern on an electrocardiogram (EKG or ECG), a test used to monitor the heart and diagnose heart rhythm disorders. Like afib, atrial flutter develops from health conditions that affect the heart's internal electrical system.
Does atrial fibrillation have P waves?
In comparison with Sinus rhythm, AF has no P wave as the SA node is not functioning. However, the atria generate up to 600 stimuli/min and each stimuli is picked up by the ECG machine. So, instead of a P wave, what you see is a number of small waves of differing sizes known as fibrillatory "F" waves.
Does AFib have a QT interval?
In atrial fibrillation, as in sinus rhythm, the QT interval is a function of both the mean ventricular rate and the instantaneous ventricular rate, with the mean ventricular rate predominating; a simple correction of QT intervals for heart rate is therefore inadequate.
Does AFib show up on EKG?
Does AFib Show Up on an Electrocardiogram (EKG)? Yes. This simple, painless test is the most helpful to diagnose AFib. It records your heart's electrical activity.
What Is Atrial Fibrillation?
Atrial fibrillation (AF or AFib) is the most common irregular heart rhythm that starts in the atria. Instead of the SA node (sinus node) directing...
What Are The Dangers of Atrial Fibrillation?
Some people live for years with atrial fibrillation without problems. However, atrial fibrillation can lead to future problems: 1. Because the atri...
What Causes Atrial Fibrillation?
There is no one “cause” of atrial fibrillation, although it is associated with many conditions, including:
What Are The Symptoms of Atrial Fibrillation?
You may have atrial fibrillation without having any symptoms. If you have symptoms, they may include: 1. Heart palpitations - Sudden pounding, flut...
How to treat atrial fibrillation?
Treatment for atrial fibrillation may include medications, therapy to reset the heart rhythm and catheter procedures to block faulty heart signals.
What causes an increased risk of atrial fibrillation?
Heart disease. Anyone with heart disease — such as heart valve problems, congenital heart disease, congestive heart failure, coronary artery disease, or a history of heart attack or heart surgery — has an increased risk of atrial fibrillation.
What is the electrical connection between the atria and the ventricles?
In atrial fibrillation, the signals in the upper chambers of your heart are chaotic. As a result, they quiver. The AV node — the electrical connection between the atria and the ventricles — is bombarded with impulses trying to get through to the ventricles.
What is the signal that sends blood out of the heart?
In a typical heart rhythm, a tiny cluster of cells at the sinus node sends out an electrical signal (sinus node impulse). The signal follows a specific path through the upper chambers (atria) and into the lower chambers (ventricles), causing them to squeeze and pump out blood. In atrial fibrillation, electrical signals fire from many areas in the atria, causing the chambers to beat chaotically. Some or all of these chaotic signals enter the ventricles, causing a fast, irregular heartbeat.
What is the heart made of?
Your heart is made up of four chambers — two upper chambers (atria) and two lower chambers (ventricles). Within the upper right chamber of your heart (right atrium) is a group of cells called the sinus node. This is your heart's natural pacemaker. The sinus node produces the signal that normally starts each heartbeat.
Is atrial fibrillation life threatening?
Although atrial fibrillation itself usually isn't life-threatening, it is a serious medical condition that sometimes requires emergency treatment. A major concern with atrial fibrillation is the potential to develop blood clots within the upper chambers of the heart.
What is the normal heart rate?
The normal range for a heart rate is 60 to 100 beats a minute. Your heart is made up of four chambers — two upper chambers (atria) and two lower chambers (ventricles). Within the upper right chamber of your heart (right atrium) is a group of cells called the sinus node. This is your heart's natural pacemaker.
Where does atrial fibrillation occur?
Because atrial fibrillation usually begins in the pulmonary veins or at their attachment to the left atrium, energy is applied around the connections of the pulmonary veins to the left atrium during the pulmonary vein ablation procedure.
What is the most common test for atrial fibrillation?
The most commonly used tests to diagnose atrial fibrillation include: Electrocardiogram (ECG or EKG): The ECG draws a picture on graph paper of the electrical impulses traveling through the heart muscle. An EKG provides an electrical “snapshot” of the heart.
What is electrical cardioversion?
Electrical Cardioversion: A cardioversion electrically “resets” the heart. Medications alone are not always effective in converting atrial fibrillation to a more normal rhythm. Sometimes cardioversion is used to restore a normal heart rhythm and allow the medication to successfully maintain the normal rhythm.
What is the most common irregular heart rhythm that starts in the atria?
Atrial fibrillation ( AF or AFib) is the most common irregular heart rhythm that starts in the atria. Instead of the SA node (sinus node) directing the electrical rhythm, many different impulses rapidly fire at once, causing a very fast, chaotic rhythm in the atria.
What is the rate of impulses in the atria?
The ventricles contract irregularly, leading to a rapid and irregular heartbeat. The rate of impulses in the atria can range from 300 to 600 beats per minute. There are two types of atrial fibrillation. Paroxysmal is intermittent, meaning it comes and goes and continuous is persistent.
What is an ECG recording of atrial fibrillation?
An ECG recording of atrial fibrillation. Instead of the impulse traveling in an orderly fashion through the heart, many impulses begin at the same time and spread through the atria, competing for a chance to travel through the AV node.
Why is AV node ablation used?
Because the patient will continue to have atrial fibrillation, an anticoagulant medication is prescribed to reduce the risk of stroke. Important note: Due to better treatment alternatives, AV node ablation is rarely used to treat atrial fibrillation.
Why is AFIB so complex?
However, AFib can be complex because individuals experience symptoms so differently. It can have multiple causes. For instance, thyroid abnormalities can cause AFib. It is also associated with congestive heart failure, structural heart disease, and heart valve problems.
What Causes AFib?
Following this pattern, the heart beats top-to-bottom, top-to-bottom. In atrial fibrillation, the upper chambers go into a sustained chaotic rhythm causing three things to happen:
What is the most common arrhythmia?
Atrial Fibrillation (AFib) is the most commonly diagnosed arrhythmia (heart rhythm problem), affecting millions of Americans. It is characterized by fast and irregular heart rhythms caused by electrical abnormalities located in the pulmonary veins of the left atrium. Left untreated, AFib can lead to congestive heart failure and stroke.
What is the hallmark of atrial fibrillation?
The hallmark of atrial fibrillation is absence of P-waves and an irregularly irregular (i.e totally irregular) ventricular rate . The baseline (isoelectric line between QRS complexes) is characterized by either fibrillatory waves (f-waves) or just minute oscillations. Fibrillatory waves are small with varying morphology and high frequency (300 to 600 waves per minute). The amplitude of f-waves may vary from small to large. Large f-waves must not be mistaken for flutter waves (F-waves) which are seen in atrial flutter. It is, luckily, easy to distinguish these two because f-waves always show varying morphology whereas flutter waves are more or less identical (f-waves also have higher frequency than flutter waves). Figures 1 and 2 shows ECG examples of atrial fibrillation.
Why is atrial fibrillation often discovered first?
Unfortunately, atrial fibrillation is too often discovered first at hospital admission due to its complications (stroke, thromboembolism, heart failure, dyspnea). Most individuals, however, do experience symptoms and they do so before developing complications.
How long does a paroxysmal atrial fibrillation last?
Paroxysmal atrial fibrillation: Paroxysmal atrial fibrillation has a duration of less than 7 days.
What is the Holter ECG used for?
Holter ECG may be used to assess the number of arrhythmia episodes and occurrences or asymptomatic episodes. If the patient may have coronary heart disease, exercise stress test (exercise ECG) should be considered.
How fast is ventricular rate?
The ventricular rate is completely irregular, typically in the range of 100 to 180 beats per minute . The patients age, active medications and concomitant AV-blocks modify the ventricular rate. Atrial fibrillation with very rapid ventricular rate may appear as a regular rhythm (which is yet another reason to switch from 25 mm/s to 50 mm/s paper speed), which is why it is important to carefully measure the regularity of the rhythm. Refer to ECG in Figure 3. When in doubt, it is generally safe to apply carotid massage, which increases vagal activity to the atrioventricular node and thus increases blocking in the atrioventricular node; this lower ventricular rate and makes the irregularity more clear.
What is the role of the autonomic nervous system in a paroxysmal atrial fibrillation?
One third of all individuals with paroxysmal atrial fibrillation experience their episodes in situations with high vagal activity (during sleep, at rest or high sympathetic activity (during exercise, stress etc). The autonomic nervous system modifies the action potentials in atrial myocardium, particularly around the pulmonary veins. However, the autonomic innervation of the atria is not homogenous (the spread of autonomic fibers in the atria varies) which means that the effect on the action potentials is also not homogenous and this promotes atrial fibrillation.
How effective is anticoagulation for atrial fibrillation?
Fortunately, the treatment of atrial fibrillation has come a long way. Treatment with anticoagulation is highly effective in reducing stroke risk. Wrfarin and novel oral anticoagulants can reduce the risk of stroke by 70%, as compared with placebo.
What happens during AFib?
In atrial fibrillation, the upper chambers of the heart (the atria) beat irregularly (quiver) instead of beating effectively to move blood into the ventricles.
What is the name of the heart condition that can lead to blood clots?
What is Atrial Fibrillation (AFib or AF)? Atrial fibrillation (also called AFib or AF) is a quivering or irregular heartbeat (arrhythmia) that can lead to blood clots, stroke, heart failure and other heart-related complications. At least 2.7 million Americans are living with AFib.
Is AFIB a serious condition?
Even though untreated atrial fibrillation doubles the risk of heart-related deaths and is associated with a 5-fold increased risk for stroke, many patients are unaware that AFib is a serious condition. Watch an animation of atrial fibrillation. Less than half of AF patients believe they have an increased risk for stroke or heart-related ...
Is atrial fibrillation a serious condition?
Only 33% of AF patients think atrial fibrillation is a serious condition. Less than half of AF patients believe they have an increased risk for stroke or heart-related hospitalizations or death.

Overview
Symptoms
Causes
Risk Factors
Complications
Prevention
- Some people with atrial fibrillation (A-fib) don't notice any symptoms. Those who do have atrial fibrillation symptoms may have signs and symptoms such as: 1. Sensations of a fast, fluttering or pounding heartbeat (palpitations) 2. Chest pain 3. Dizziness 4. Fatigue 5. Lightheadedness 6. Reduced ability to exercise 7. Shortness of breath 8. Weakness Atrial fibrillation may be: 1. Occa…