
What is the Hubble Distance from Earth?
The Hubble distance would be the distance between the Earth and the galaxies which are currently receding from us at the speed of light, as can be seen by substituting into the equation for Hubble's law, v = H0D . c H 0 − 1 . {\displaystyle cH_ {0}^ {-1}.}
What is the Hubble constant in km/s?
Their measurement of the Hubble constant is 73.3+5.3 −5.0 (km/s)/Mpc. Also in July 2019, astronomers reported another new method, using data from the Hubble Space Telescope and based on distances to red giant stars calculated using the tip of the red-giant branch (TRGB) distance indicator.
How do you calculate the Hubble length in light years?
(The numerical value of the Hubble length in light years is, by definition, equal to that of the Hubble time in years.) The Hubble distance would be the distance between the Earth and the galaxies which are currently receding from us at the speed of light, as can be seen by substituting into the equation for Hubble's law, v = H0D .
How do you find the distance of a galaxy using Hubble's law?
The simple formula to calculate the distance to the galaxy using Hubble's law is D = v/H o. Solve the equation after substituting the values to get the distance value. 3. What is Hubble's law formula?

How did Hubble measure distance?
The Hubble astronomers used trigonometric parallax to nail down the cluster's distance. This technique measures the tiny, apparent shift of an object's position due to a change in an observer's point of view. Hubble measured the apparent tiny wobble of the cluster stars due to Earth's motion around the Sun.
What is Hubble's time?
Noun. Hubble time (plural Hubble times) (astronomy, cosmology) A constant defined as , where is the Hubble constant. is equal to 4.55×1017 seconds or 14.4 billion years.
How is Hubble's Law calculated?
Hubble's Law - One of the most important formulas of the 20th century. It shows the expansion of the Universe by showing how distant galaxies are moving away from us. Formula: v = Ho d where: v = velocity of a galaxy, in km/s.
How fast is the universe expanding?
As reported in The Astrophysical Journal, researchers using the veteran space telescope have estimated that the expansion rate of the Universe is 73 kilometers per second per megaparsec plus or minus 1.
How many seconds old is the universe?
— 10,000 years: 315,569,520,000 (s) is very close to Notation 182 (330,491,912,986 seconds).
What is Hubble law in simple terms?
Hubble's law, which says simply that a galaxy's velocity (or as is sometimes plotted, its redshift) is directly proportional to its distance, also tells us something important about the state of the universe. If the universe is static and unchanging, there should be no correlation between distance and velocity.
Does the Milky Way have a halo?
The roughly spherical halo of the Milky Way is thought to have a radius of some 50,000 light-years (about 5 × 1017 kilometres), and its gas is a source of radio emission, particularly at the 21-centimetre wavelength (see 21-centimetre radiation).
Is universe expanding into something?
The universe is everything, so it isn't expanding into anything. It's just expanding. All of the galaxies in the universe are moving away from each other, and every region of space is being stretched, but there's no center they're expanding from and no outer edge to expand into anything else.
Is Hubble time the age of the universe?
has units of inverse time; the Hubble time tH is simply defined as the inverse of the Hubble constant, i.e. This is slightly different from the age of the universe which is approximately 13.8 billion years.
What is Hubble time quizlet?
The Hubble time is. an estimate of the age of the universe based on the Hubble constant. The cosmic background radiation comes from a time after the origin of the universe.
How long was Hubble supposed to last?
about 15 yearsWhen Hubble launched in 1990, it was expected to have a lifespan of about 15 years. Largely because of five successful astronaut servicing missions to the telescope, Hubble's technology was upgraded and improved, and the telescope remains scientifically productive to this day.
How long has Hubble been in space?
30 yearsThe telescope completed 30 years of operation in April 2020 and is predicted to last until 2030–2040.
1. What is Hubble's distance?
Hubble's distance is the distance to the galaxy or it is the distance of an object based on the Hubble flow.
2. How to calculate distance using Hubble's law?
The simple formula to calculate the distance to the galaxy using Hubble's law is D = v/Ho. Solve the equation after substituting the values to get...
3. What is Hubble's law formula?
Hubble's law states that the velocity of the galaxy that is known as the redshift is directly proportional to the distance. It's formula is v = Hod.
4. How to use the Hubble law distance calculator?
Just you need to provide the wither speed or distance details in Hubble's law distance calculator to get the result.
5. What is the Hubble constant?
Hubble constant is used to describe the expansion of the universe. Its value is H = 70.4 km/s per million-light-years.
How is the Hubble constant measured?
Currently, there are three main ways to measure the Hubble constant: by using astronomical measurements to look at objects nearby and see how fast they are moving; by using gravitational waves from collisions of black holes or neutron stars; or by measuring the light left over from the Big Bang, known as the cosmic microwave background.
How to measure the Hubble constant?
To measure the Hubble constant by observing the universe, astronomers need to be able to measure two things: 1 The distance to astronomical objects 2 The “recession velocity” of each object (i.e., how fast it is moving away from the observer)
Where did the Hubble constant get its name?
It gets its name from UChicago alum Edwin Hubble, who was first to calculate the constant from his measurements of stars in 1929. Despite nearly a hundred years of astronomical measurements and calculations, scientists still can’t agree on the exact value of the Hubble constant. The true number could reveal missing pieces in our understanding ...
Why do stars always have the same wavelengths?
These always occur at the same wavelengths because they are created by the elements in stars’ atmospheres. When redshift changes the wavelength of all the light and absorption lines coming from a distant star, astronomers can measure how much it has shifted to calculate how fast the star is travelling away from us.
What did Einstein predict about the universe?
In the early 1920s, mathematicians used Einstein’s equations for general relativity to predict that the universe should be expanding, but scientists had not yet proven this through observations. At the time, astronomers didn’t even have the observations to settle the Great Debate about the size of the universe; some even argued that the universe did not extend beyond the Milky Way.
Where did Hubble work?
While working at California’s Mount Wilson Observatory, Hubble used his extensive telescope experience to make measurements of Cepheid variable stars. Hubble used the work of fellow astronomer Henrietta Leavitt to predict the brightness of these stars, which enabled him to calculate their distances from Earth.
How does the expansion of the universe happen?
The expansion of the universe is driven by all the mass, radiation and energy contained within it. The Friedmann equation, derived from Einstein’s famous equations for general relativity, can be used to predict how quickly the universe is expanding mathematically. These equations state that a denser universe expands more quickly, so expansion was fastest when all of the particles in the universe were packed closely together after the Big Bang. Over the past 14 billion years, these particles—and their accompanying energy and radiation—have spread out to vast distances.
Step by Step Process to Calculate Hubble Distance
The following are the steps to calulate the distance between earth and the galaxy with the help of Hubble's law.
What is Hubble's Law?
Astronomers first saw that galaxies are moving away from us. One astronomer named Edwin Hubble and George Lemaitre says that the speed they are moving is directly proportional to the distance between them.
How far is the Hubble telescope from Earth?
It was launched into orbit by space shuttle Discovery on April 24, 1990. Hubble orbits about 547 kilometers (340 miles) above Earth. It is the length of a large school bus and weighs as much as two adult elephants.
How many observations does Hubble have?
Hubble is solar-powered. Hubble takes sharp pictures of objects in the sky such as planets, stars and galaxies. Hubble has made more than one million observations. These include detailed pictures of the birth and death of stars, galaxies billions of light years away, and comet pieces crashing into Jupiter's atmosphere.
What is the purpose of the fine guidance sensor on the Hubble telescope?
As Hubble orbits Earth, the Fine Guidance Sensors lock onto stars. The Fine Guidance Sensors are part of the Pointing Control System and aim Hubble in the right direction. The telescope can lock onto a target that is one mile away without moving more than the width of a human hair.
What telescope took this picture of the Tadpole Galaxy and its tail of large, bright blue star clusters?
Credits: Universe by Freedman and Kaufmann. The Hubble Space Telescope took this picture of the Tadpole Galaxy and its tail of large, bright blue star clusters. Credits: NASA. The "Hubble Ultra Deep Field" shows many galaxies far from Earth. Credits: NASA.
What are the instruments that Hubble uses?
Hubble has five scientific instruments which include cameras and spectrographs. A spectrograph is an instrument that splits light into its individual wavelengths. The Wide Field Camera 3 is Hubble’s main camera. It studies everything from the formation of distant galaxies to the planets in the solar system.
Why do Hubble pictures have colors?
Hubble pictures start out as shades of black and white. The Space Telescope Science Institute adds colors to the pictures for different reasons. Sometimes colors are chosen to show how an object might look to the human eye. Other times colors are used to highlight an important detail.
What did Hubble study?
Hubble has also studied the atmospheres of planets revolving around stars similar to Earth’s sun.
What is the Hubble telescope?
NASA’s Hubble Space Telescope is the first astronomical observatory placed into orbit around Earth with the ability to record images in wavelengths of light spanning from ultraviolet to near-infrared. Hubble continues to operate high above the blurring effects of Earth’s atmosphere.
When was the Hubble spacecraft launched?
Hubble continues to operate high above the blurring effects of Earth’s atmosphere. Hubble was launched on April 24, 1990, in the cargo bay of Space Shuttle Discovery and deployed the following day. Hubble continues to provide images of unprecedented resolution from which many new and exciting discoveries have been made.
How has the Hubble telescope impacted the universe?
The telescope has had a major impact on every area of astronomy, from the solar system to objects at the edge of the universe. Scientists have used Hubble to observe the most distant stars and galaxies as well as the planets in our solar system.
How many observations has the Hubble telescope made?
Including that trip, there were five astronaut servicing missions to Hubble. Since its fifth and final repair mission in 2009, the telescope has made over 1.4 million observations, located distant swirling galaxies and plotted pockets of dark matter.
Why did Hubble win the Nobel Prize?
Analysis of Hubble’s images even helped earned scientists the Nobel Prize in 2011 for discovering that the rate that our universe is rapidly accelerating. In short, when Earth has questions, Hubble answers.
How many technical papers are there on the orbiting telescope?
Data and from the orbiting telescope are the backbone of more than 15,000 technical papers. It also, of course, continues to dazzle us with stunning pictures of stars, galaxies and planets.
Does Hubble need repair?
Hubble has operated far beyond its planned lifetime, but it has needed some repair work.
How much data does Hubble generate?
Hubble generates about 10 terabytes of new data per year. The total archive is currently over 150 TB in size.
How many observations has Hubble made?
Hubble has made more than 1.3 million observations since its mission began in 1990. Astronomers using Hubble data have published more than 15,000 scientific papers, making it one of the most productive scientific instruments ever built. Those papers have been cited in other papers 738,000 times.
Why is the Hubble telescope named?
The Hubble Space Telescope is named in honor of astronomer Edwin Hubble. More on Dr. Hubble. In the centuries that followed, telescopes grew in size and complexity and, of course, power. They were placed far from city lights and as far above the haze of the atmosphere as possible. Edwin Hubble, for whom the Hubble Telescope is named, ...
What is Hubble used for?
Scientists have used Hubble to observe the most distant stars and galaxies as well as the planets in our solar system. Hubble's launch and deployment in April 1990 marked the most significant advance in astronomy since Galileo's telescope. Thanks to five servicing missions and more than 25 years of operation, our view of ...
How accurate is the Hubble telescope?
In order to take images of distant, faint objects, Hubble must be extremely steady and accurate. The telescope is able to lock on to a target without deviating more than 7/1000th of an arcsecond, or about the width of a human hair seen at a distance of 1 mile.
How big is Hubble's mirror?
Hubble's primary mirror is 2.4 meters (7 feet, 10.5 inches) across. It was so finely polished that if you scaled it to be the diameter of the Earth, you would not find a bump more than 6 inches tall. Hubble is 13.3 meters (43.5 feet) long — the length of a large school bus. For Hubble achievements, please see: https://www.nasa.gov/hubble-highlights.
How does Hubble change angles?
To change angles, it uses Newton’s third law by spinning its wheels in the opposite direction. It turns at about the speed of a minute hand on a clock, taking 15 minutes to turn 90 degrees.
How fast does the Hubble telescope travel?
The Hubble Space Telescope orbits just above Earth’s atmosphere at an altitude of approximately 340 miles (547 km). Hubble orbits at a speed of 17,000 miles per hour (27,000 kph) and completes one orbit approximately every 95 minutes. Hubble gets clear images because it’s above Earth’s atmosphere, not because it travels or flies closer to cosmic objects.
How does the Hubble Space Telescope work?
The Hubble Space Telescope is equipped with cameras that take images over a broad range of wavelengths. Hubble’s images are recorded in grayscale, but scientists can create a composite color image by taking exposures using different color filters on the telescope, assigning a color to each filter that corresponds to the wavelength of that filter, and combining the images. Sometimes, parts of images are assigned colors to visually show what isn’t visible to the human eye (for example, infrared wavelengths that your eye cannot detect), or to highlight the presence of certain elements.
What is the name of the space telescope science institute?
The Space Telescope Science Institute (STScI) is located in Baltimore, Maryland and oversees Hubble’s science operations. STScI manages the selection process of proposals to use Hubble, schedules the resulting observations, processes the data, and so forth.
What is the step effect on Hubble?
Three of the camera’s four light detectors imaged “wide fields,” while the fourth detector (PC for planetary camera) had higher resolution but covered a smaller portion of the sky. With all four combined, the “step” effect resulted, meaning there are areas where Hubble observations were not taken.
When will the James Webb Space Telescope launch?
The James Webb Space Telescope is scheduled to launch in late 2021.
Is Hubble a scarce resource?
Time with Hubble is a scarce resource and highly competitive . Approximately 150 scientists from around the world evaluate and rank proposals as part of the Time Allocation Committee. The proposals are evaluated based on their scientific merit, and the committee’s recommended selection is then forwarded to the STScI director for final approval. Ten percent of Hubble’s observation time is also set aside for discretionary purposes as decided by the director. Observations such as the Hubble deep fields and the Hubble Frontier Fields have come from the director’s discretionary time.
Where did Hubble find the universe?
Utilizing the 100-inch telescope at California's Mount Wilson Observatory (at the time the world's largest telescope) Hubble obtained spectra and measurements of the distance to a few dozen galaxies, leading to the discovery that the Universe is expanding.
What did Hubble find when he plotted the redshift vs. the distance of the galaxie?
When Hubble plotted the redshift vs. the distance of the galaxies, he found a surprising relation: more distant galaxies are moving faster away from us. Hubble concluded that the fainter and smaller the galaxy, the more distant it is, and the faster it is moving away from us, or that the recessional velocity of a galaxy is proportional to its distance from us:
What did Hubble find about the redshift of a galaxy?
In 1929 Hubble published his findings, detailing revealed that the fainter and smaller a galaxy appeared, the higher was its redshift.
How to determine the value of Ho?
In order to precisely determine the value of Ho, we must determine the velocities and distances to many galaxies. Hubble's law has been confirmed by subsequent research and provides the cornerstone of modern relativistic cosmological theories of our expanding universe. In 1963 astronomers discovered cosmic objects known as quasars that exhibit larger redshifts than any of the remotest galaxies previously observed. The extremely large redshifts of various quasars suggest that they are moving away from the Earth at tremendous velocities (i.e., approximately 90 percent the speed of light) and thereby constitute some of the most distant objects in the universe.
What is the name of the hazy patches of light that are then known as spiral nebulae?
During the 1920's, Edwin Powell Hubble demonstrated that the small hazy patches of light which were then known as "spiral nebulae" are actually entire galaxies containing hundreds of billions of stars.
What is the absorption line of hydrogen?
Absorption lines of hydrogen, normally measured to be at 4861Å and 6563Å, are measured in the spectrum of a particular galaxy to be at 4923Å and 6647Å .
Who was responsible for determining the distance to a galaxy?
Historical Note: It is not common for any other astronomers to be mentioned along with Edwin Hubble as being responsible for figuring out how the distance to a galaxy is related to its recession velocity. However, Hubble did not work alone and many other astronomers deserve credit for establishing the distance--redshift relationship.
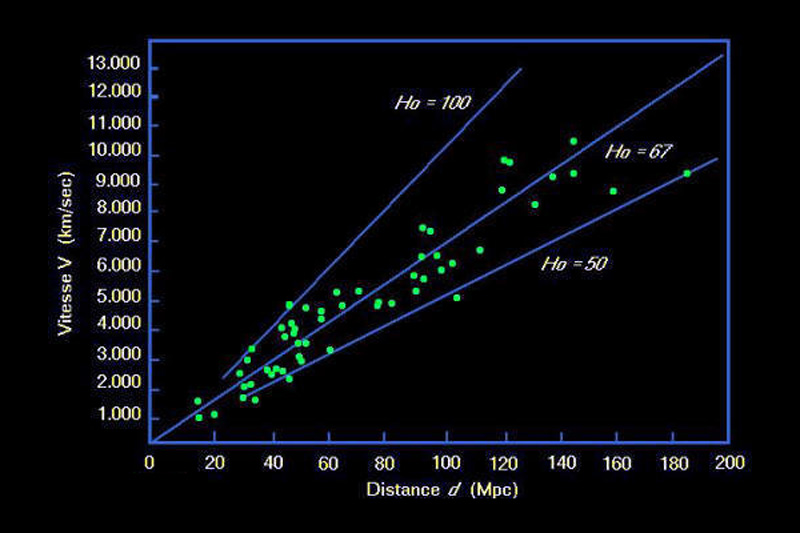
Overview
Units derived from the Hubble constant
The Hubble constant has units of inverse time; the Hubble time tH is simply defined as the inverse of the Hubble constant, i.e.
This is slightly different from the age of the universe which is approximately 13.8 billion years. The Hubble time is the age it would have had if the expansion had been linear, and it is different from the real age of the universe because the expansion is not linear; they are related by a dime…
Discovery
A decade before Hubble made his observations, a number of physicists and mathematicians had established a consistent theory of an expanding universe by using Einstein's field equations of general relativity. Applying the most general principles to the nature of the universe yielded a dynamic solution that conflicted with the then-prevalent notion of a static universe.
Interpretation
The discovery of the linear relationship between redshift and distance, coupled with a supposed linear relation between recessional velocity and redshift, yields a straightforward mathematical expression for Hubble's law as follows:
where
• is the recessional velocity, typically expressed in km/s.
Derivation of the Hubble parameter
Start with the Friedmann equation:
where is the Hubble parameter, is the scale factor, G is the gravitational constant, is the normalised spatial curvature of the universe and equal to −1, 0, or 1, and is the cosmological constant.
If the universe is matter-dominated, then the mass density of the universe can just be taken to include matter so
Determining the Hubble constant
The value of the Hubble constant is estimated by measuring the redshift of distant galaxies and then determining the distances to them by some other method than Hubble's law. This approach forms part of the cosmic distance ladder for measuring distances to extragalactic objects. Uncertainties in the physical assumptions used to determine these distances have caused varying …
See also
• Accelerating expansion of the universe
• Cosmology
• Dark matter
• Tests of general relativity
External links
• NASA's WMAP - Big Bang Expansion: the Hubble Constant
• The Hubble Key Project
• The Hubble Diagram Project
• Coming to terms with different Hubble Constants (Forbes; 3 May 2019)