When to use an independent t test?
There are three main types of t-test:
- An Independent Samples t-test compares the means for two groups.
- A Paired sample t-test compares means from the same group at different times (say, one year apart).
- A One sample t-test tests the mean of a single group against a known mean.
What is an example of a single sample t test?
One-sample t-test example Imagine we have collected a random sample of 31 energy bars from a number of different stores to represent the population of energy bars available to the general consumer. The labels on the bars claim that each bar contains 20 grams of protein.
What is t test for dependent samples?
UNDERSTANDING THE DEPENDENT-SAMPLES tTEST A dependent-samples ttest (a.k.a. matched or paired-samples, matched-pairs, samples, or subjects, simple repeated-measures or within-groups, or correlated groups) assesses whether the mean difference between paired/matched observations is significantly different from zero.
How to perform a two sample t test?
t-Test
- First, perform an F-Test to determine if the variances of the two populations are equal. This is not the case.
- On the Data tab, in the Analysis group, click Data Analysis. Note: can't find the Data Analysis button? ...
- Select t-Test: Two-Sample Assuming Unequal Variances and click OK.
- Click in the Variable 1 Range box and select the range A2:A7.
When should you use an independent samples t-test?
Use an independent samples t test when you want to compare the means of precisely two groups—no more and no less! Typically, you perform this test to determine whether two population means are different.
What are the independent samples?
Independent samples are samples that are selected randomly so that its observations do not depend on the values other observations. Many statistical analyses are based on the assumption that samples are independent. Others are designed to assess samples that are not independent.
What is independent and dependent t-test?
If your data are independent, for example, a t-test for independent samples is calculated or an analysis of variance without repeated measures. If your data are dependent, for example, a t-test for dependent samples or an ANOVA with measurement repetitions is calculated.
What does independent test mean?
Independent sample t-test is a statistical technique that is used to analyze the mean comparison of two independent groups. In independent samples t-test, when we take two samples from the same population, then the mean of the two samples may be identical.
How do you identify an independent sample?
Therefore, it's important to know whether your samples are dependent or independent: If the values in one sample affect the values in the other sample, then the samples are dependent. If the values in one sample reveal no information about those of the other sample, then the samples are independent.
How do you report independent samples t-test?
The basic format for reporting the result of a t-test is the same in each case (the color red means you substitute in the appropriate value from your study): t(degress of freedom) = the t statistic, p = p value. It's the context you provide when reporting the result that tells the reader which type of t-test was used.
What is the difference between independent and dependent samples?
Two (or more) samples are called independent if the members chosen for one sample do not determine which individuals are chosen for a second sample. Two (or more) samples are called dependent if the members chosen for one sample automatically determine which members are to be included in the second sample.
What is the importance of using an independent t-test?
The independent sample t-test is a useful statistical method of hypothesis testing when an organization wants to determine whether there is a statistical difference between two categories, groups, or items and, furthermore, if there is a statistical difference, whether that difference is significant.
What is the difference between a one sample t-test and an independent t-test?
The one-sample t-test compares the mean of a single sample to a predetermined value to determine if the sample mean is significantly greater or less than that value. The independent sample t-test compares the mean of one distinct group to the mean of another group.
What is the primary focus of the independent t-test?
As with all hypothesis tests, the general purpose of the independent-measures t test is to determine whether the sample mean difference obtained in a research study indicates a real mean difference between the two populations (or treatments) or whether the obtained difference is simply the result of sampling error.
What is t-test used for?
The t-test, also known as t-statistic or sometimes t-distribution, is a popular statistical tool used to test differences between the means (averages) of two groups, or the difference between one group's mean and a standard value.
What are two independent samples?
The independent samples mean that the two samples cannot be from the same group of people and they cannot be related in any way. However, two-sample T-test can also be used for pairwise comparisons when the “two” samples represent the same items tested in different scenarios.
What are independent and dependent samples?
Two (or more) samples are called independent if the members chosen for one sample do not determine which individuals are chosen for a second sample. Two (or more) samples are called dependent if the members chosen for one sample automatically determine which members are to be included in the second sample.
What is an example of two independent samples?
For example to compare heights of males and females, we could take a random sample of 100 females and another random sample of 100 males. The result would be two samples which are independent of each other.
What are paired and independent samples?
Paired-samples t tests compare scores on two different variables but for the same group of cases; independent-samples t tests compare scores on the same variable but for two different groups of cases.
What is the measure of variability?
Variance, and the closely related standard deviation, are measures of variability. Each group in your analysis has its own variance . The independent samples t test has two methods. One method assumes that the two groups have equal variances while the other does not assume they are equal. The form that does not assume equal variances is known as Welch’s t-test.
Why is it important to draw a random sample?
Drawing a random sample from the population you are studying helps ensure that your data represent the population. Representative samples are vital when you want to make inferences about the population. If your data do not represent the population, your analysis results will not be valid for that population.
What is null hypothesis?
Null hypothesis: The means for the two populations are equal.
What is continuous data in a T test?
T tests require continuous data. Continuous variables can take on any numeric value, and the scale can be meaningfully divided into smaller increments, including fractional and decimal values. There are an infinite number of possible values between any two values. Typically, you measure continuous variables on a scale. For example, when you measure temperature, weight, and height, you have continuous data.
When to use independent samples t test?
Use an independent samples t test when you want to compare the means of precisely two groups— no more and no less! Typically, you perform this test to determine whether two population means are different. This procedure is an inferential statistical hypothesis test, meaning it uses samples to draw conclusions about populations. The independent samples t test is also known as the two sample t test.
When is a t-test valid?
For the independent samples t test, when each group is larger than 15, your data can be skewed and the test results will still be valid. However, if your sample size is less than 15 per group, graph your data and determine whether the two distributions are skewed or has outliers. Either condition can cause the test results to be invalid. In this case, you might need to use a nonparametric test.
Why is the confidence interval negative?
The negative values reflect the fact that Method A has a lower mean than Method B (i.e., Method A – Method B < 0). Because the confidence interval excludes zero (no difference), we can conclude that the population means are different.
What is the independent sample t test?
The Independent Samples t Test is a parametric test.
What is the difference between the independent samples t test statistic and the pooled variance?
The difference between these two rows of output lies in the way the independent samples t test statistic is calculated. When equal variances are assumed , the calculation uses pooled variances; when equal variances cannot be assumed, the calculation utilizes un-pooled variances and a correction to the degrees of freedom.
What is the test statistic for independent samples?
The test statistic for an Independent Samples t Test is denoted t. There are actually two forms of the test statistic for this test, depending on whether or not equal variances are assumed. SPSS produces both forms of the test, so both forms of the test are described here. Note that the null and alternative hypotheses are identical for both forms of the test statistic.
What happens if you reject the null hypothesis of Levene's test?
This implies that if we reject the null hypothesis of Levene's Test, it suggests that the variances of the two groups are not equal; i.e., that the homogeneity of variances assumption is violated .
How to compare two groups of categories in SPSS?
If your categories are numerically coded, you will enter the numeric codes. If your group variable is string, you will enter the exact text strings representing the two categories. If your grouping variable has more than two categories (e.g., takes on values of 1, 2, 3, 4), you can specify two of the categories to be compared (SPSS will disregard the other categories in this case).
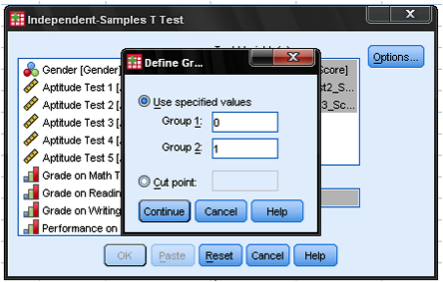
How to use C grouping in t test?
C Define Groups: Click Define Groups to define the category indicators (groups) to use in the t test. If the button is not active, make sure that you have already moved your independent variable to the right in the Grouping Variable field. You must define the categories of your grouping variable before you can run the Independent Samples t Test procedure.
How to move variables in independent sample?
Move variables to the right by selecting them in the list and clicking the blue arrow buttons. You can move a variable (s) to either of two areas: Grouping Variable or Test Variable (s).
What is the outcome variable that has equal standard deviations?
Homogeneity: the outcome variable has equal standard deviations in our 2 (sub)populations. This is not needed if the sample sizes are roughly equal. Levene's test is sometimes used for testing this assumption.
What is the null hypothesis for independent samples t-test?
The null hypothesis for an independent samples t-test is (usually) that the 2 population means are equal. If this is really true, then we may easily find slightly different means in our samples. So precisely what difference can we expect? An intuitive way for finding out is a simple simulation.
What is independent sample t-test?
An independent samples t-test evaluates if 2 populations have equal means on some variable. If the population means are really equal, then the sample means will probably differ a little bit but not too much. Very different sample means are highly unlikely if the population means are equal. This sample outcome thus suggest ...
Why are the samples independent?
This sample outcome thus suggest that the population means weren't equal after all. The samples are independent because they don't overlap; none of the observations belongs to both samples simultaneously. A textbook example is male versus female respondents.
Is Cohen's D in SPSS?
Cohen’s D is painfully absent from SPSS except for SPSS 27. However, you can easily obtain it from Cohens-d.xlsx. Just fill in 2 sample sizes, means and standard deviations and its formulas will compute everything you need to know.
What does a nalyze C ompare mean?
First off, let's navigate to A nalyze C ompare Means Independen t Samples T Test as shown below.
What is the effect size of ANOVA?
the effect size for ANOVA is (partial) eta squared rather than Cohen’s D.
What is the most common effect size measure for t-tests?
The most common effect size measure for t-tests is Cohen’s D , which we find under “point estimate” in the effect sizes table (only available for SPSS version 27 onwards).
What is independent observation?
independent observations. This often holds if each row of data represents a different person.
How many lines of results does each dependent variable have?
As previously discussed, each dependent variable has 2 lines of results. Which line to report depends on Levene’s test because our sample sizes are not (roughly) equal:
What is the null hypothesis for independent samples t-test?
The null hypothesis for an independent samples t-test is that two populations have equal means on some metric variable. For example, do men spend the same amount of money on clothing as women? We can't reasonably ask the entire population of men and women how much they spend. So we'll draw a sample of men and women.
When to use Levene's test?
If sample sizes are not roughly equal, then Levene's test may be used to test if homogeneity is met. If that's not the case, then you should report adjusted results. These are shown in the SPSS t-test output under “ equal variances not assumed ”.
Independent T Test – SPSS
Many students have issues reporting their Independent T Test results in APA format. Generally, APA Results can be reported as follow:
Assumptions
When you choose to analyse your data using an independent t-test, part of the process involves checking to make sure that the data you want to analyse can actually be analysed using an independent t-test.
Example of Independent T Test
The concentration of cholesterol (a type of fat) in the blood is associated with the risk of developing heart disease, such that higher concentrations of cholesterol indicate a higher level of risk, and lower concentrations indicate a lower level of risk.
Output of the independent t-test in SPSS
SPSS generates two main tables of output for the independent t-test.
Reporting the output
Based on the results above, we could report the results of the study as follows (N.B., this does not include the results from your assumptions tests or effect size calculations):
What is the significance value of the homogeneity of variance test?
This test for homogeneity of variance provides an F -statistic and a significance value ( p -value). We are primarily concerned with the significance value – if it is greater than 0.05 (i.e., p > .05), our group variances can be treated as equal. However, if p < 0.05, we have unequal variances and we have violated the assumption of homogeneity of variances.
How to correct for the Levene's test for equality of variances?
If the Levene's Test for Equality of Variances is statistically significant, which indicates that the group variances are unequal in the population, you can correct for this violation by not using the pooled estimate for the error term for the t -statistic, but instead using an adjustment to the degrees of freedom using the Welch-Satterthwaite method. In all reality, you will probably never have heard of these adjustments because SPSS Statistics hides this information and simply labels the two options as "Equal variances assumed" and "Equal variances not assumed" without explicitly stating the underlying tests used. However, you can see the evidence of these tests as below:
What is the null hypothesis in independent t-test?
The null hypothesis for the independent t-test is that the population means from the two unrelated groups are equal: In most cases, we are looking to see if we can show that we can reject the null hypothesis and accept the alternative hypothesis, which is that the population means are not equal: To do this, we need to set a significance level (also ...
What is the independent t test?
The independent t-test, also called the two sample t-test, independent-samples t-test or student's t-test, is an inferential statistical test that determines whether there is a statistically significant difference between the means in two unrelated groups.
What is the format of a t-statistic?
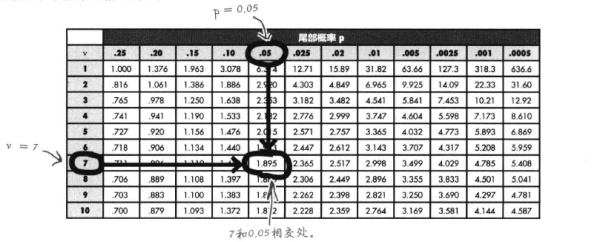
The format of the test result is: t (df) = t -statistic, p = significance value. Therefore, for the example above, you could report the result as t (7.001) = 2.233, p = 0.061.
What is an unrelated group?
Unrelated groups, also called unpaired groups or independent groups, are groups in which the cases (e.g., participants) in each group are different. Often we are investigating differences in individuals, which means that when comparing two groups, an individual in one group cannot also be a member of the other group and vice versa.
Do residuals need to be distributed?
Note: Technically, it is the residuals that need to be normally distributed, but for an independent t-test, both will give you the same result.
What is side by side boxplot?
Side-by-side boxplots are provided by the GLM procedure. This can help visually identify major outliers and help visually show if variances might be unequal. The boxplot below seems to indicate one minor outlier but subjectively, not enough evidence to suggest we move to a different analysis method.
What is the purpose of the Proc TTEST?
PROC TTEST includes QQ plots for each treatment group along with a folded F-test to help identify unequal variances. While this information can aid in validating assumptions, the Shapiro-Wilk Normality Test, in addition to QQ plots, should be used to help evaluate normality. Furthermore, Levene’s Test for Equality of Variances is generally preferred when evaluating whether variances between groups are equal. Thus, SAS code has been provided to demonstrate both the Shapiro-Wilk and Levene’s tests.
When is a pooled t-test appropriate?
Variance -An independent samples pooled t-test is appropriate when variances are assumed equal. An independent samples Satterthwaite t-test is appropriate when variances are considered unequal. The appropriate row to evaluate will be based on the results of the Levene’s Test for Homogeneity of Variances above. In our example, the “Satterthwaite” test is appropriate since variances are considered unequal between the 4 and 8 cylinder treatment groups.
What is a Cyl column?
cyl – This column identifies the levels of the treatment variable of interested along with the mean differences between the levels.
What does DF mean in math?
DF – The degrees of freedom associated with each variable and overall error.
Is the data for each cylinder group normally distributed?
So far, we have determined that the data for each cylinder group is normally distributed, variances are unequal, and we do not have major influential outliers. Our next step is to officially perform an independent samples t-test to determine whether 4 and 8 cylinder cars show significant differences between their average mpg expenditure.
What does the 4 and 8 mean in a QQ plot?
The ‘4’ and ‘8’ in the top left corner of each plot indicates which group each QQ plot corresponds too. The vast majority of points should follow each line.
How to identify outliers in R?
Outliers can be easily identified using boxplot methods, implemented in the R function identify_outliers () [rstatix package].
What is homogeneity of variance?
Homogeneity of variances. the variance of the outcome variable should be equal in each group. Recall that, the Welch t-test does not make this assumptions.
Why is a QQ plot preferred?
Note that, if your sample size is greater than 50, the normal QQ plot is preferred because at larger sample sizes the Shapiro-Wilk test becomes very sensitive even to a minor deviation from normality.
How many people are in the genderweight datarium?
Demo dataset: genderweight [in datarium package] containing the weight of 40 individuals (20 women and 20 men).
What is the independence of the observations?
Independence of the observations. Each subject should belong to only one group. There is no relationship between the observations in each group. No significant outliers in the two groups. Normality. the data for each group should be approximately normally distributed.
What does it mean when the p-values are greater than the significance level?
From the output, the two p-values are greater than the significance level 0.05 indicating that the distribution of the data are not significantly different from the normal distribution. In other words, we can assume the normality.
Which test is used when data are not normally distributed?
Note that, in the situation where the data are not normally distributed, it’s recommended to use the non parametric two-samples Wilcoxon test.