
What major event occurs during interphase of the cell cycle?
- duplication of genetic information (i.e., DNA replication);
- division of genetic info into daughter cells (i.e., mitosis, meiosis, binary fission);
- division of the cytoplasm (although this doesn't necessarily occur in all species).
Which phases of the cell cycle does Interphase include?
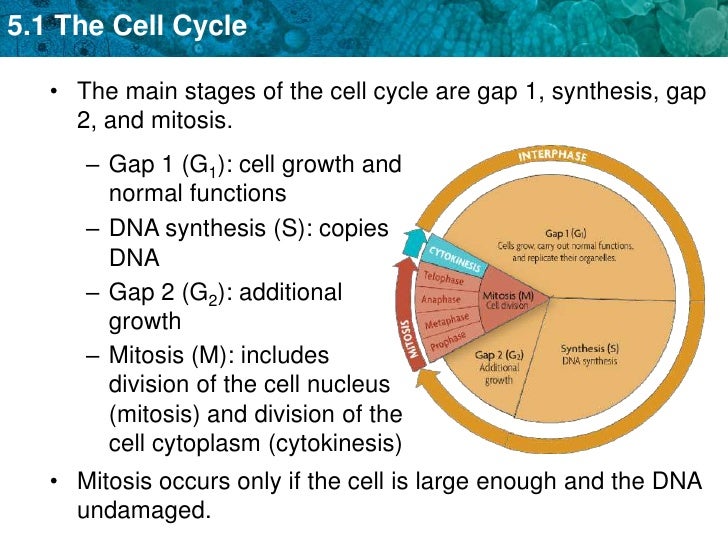
Interphase – This phase includes the G1 phase, S phase and the G2 phase. M phase – This is the mitotic phase and is divided into prophase, metaphase, anaphase and telophase. Cytokinesis – In this phase the cytoplasm of the cell divides.
What percent of the cell cycle does interphase take up?
Typically interphase lasts for at least 91% of the total time required for the cell cycle. Interphase proceeds in three stages, G 1, S, and G 2, followed by the cycle of mitosis and cytokinesis. What percent of the cell cycle is interphase?
What are the six stages of the cell cycle?
the period of the cell cycle at which the duplicated chromosomes are separated into identical nuclei; includes prophase, prometaphase, metaphase, anaphase, and telophase mitotic phase the period of the cell cycle when duplicated chromosomes are distributed into two nuclei and the cytoplasmic contents are divided; includes mitosis and cytokinesis

What are the 3 stages of interphase?
Interphase is composed of G1 phase (cell growth), followed by S phase (DNA synthesis), followed by G2 phase (cell growth).
What are the 4 steps of interphase in the cell cycle?
During this period, the cell is constantly synthesizing RNA, producing protein and growing in size. By studying molecular events in cells, scientists have determined that interphase can be divided into 4 steps: Gap 0 (G0), Gap 1 (G1), S (synthesis) phase, Gap 2 (G2).
What happens at interphase?
A cell spends most of its time in what is called interphase, and during this time it grows, replicates its chromosomes, and prepares for cell division. The cell then leaves interphase, undergoes mitosis, and completes its division.
Where does interphase occur?
Interphase is the longest part of the cell cycle. This is when the cell grows and copies its DNA before moving into mitosis. During mitosis, chromosomes will align, separate, and move into new daughter cells. The prefix inter- means between, so interphase takes place between one mitotic (M) phase and the next.
What are the 4 stages in mitosis?
These phases are prophase, prometaphase, metaphase, anaphase, and telophase.
What are the 4 phases of mitosis and what happens in each?
4:236:47What happens in the four stages of mitosis? - YouTubeYouTubeStart of suggested clipEnd of suggested clipLife. Anaphase is the shortest stage of mitosis. And accounts for roughly one percent of mitosis.MoreLife. Anaphase is the shortest stage of mitosis. And accounts for roughly one percent of mitosis.
How many phases are in the interphase stage of the cell cycle?
During interphase, the cell undergoes normal growth processes while also preparing for cell division. In order for a cell to move from interphase into the mitotic phase, many internal and external conditions must be met. The three stages of interphase are called G1, S, and G2 .
What is the correct order of steps in the cell cycle?
The cell cycle is a four-stage process in which the cell increases in size (gap 1, or G1, stage), copies its DNA (synthesis, or S, stage), prepares to divide (gap 2, or G2, stage), and divides (mitosis, or M, stage).
How does DNA synthesis work?
During synthesis, the cell pauses its normal functioning. All resources are dedicated to replicating the DNA. This process starts with the two entwined stands of DNA being “unzipped” by various proteins. Other proteins, known as polymerase enzymes, start creating new strands to pair with each half of the DNA. This is done on each chromosome, which creates an identical copy of each, bound together as sister chromatids. If the cell is a somatic cell, it will enter mitosis after interphase and the sister chromatids will be separated, creating two identical copies of the genome in each cell. If the cell will give rise to a gamete it will enter meiosis after interphase. In meiosis, homologous chromosomes are separated in one division, then sister chromatid in the next, creating cells with only half of a full genome. These cells enter interphase, but synthesis stage cannot occur until fertilization occurs with another gamete. Either way, after synthesis, the cell must prepare for cell division.
How does meiosis separate cells?
The two divisions of meiosis are also separated by a special interphase, known as interkinesis in which the D NA does not replicate. This leads to a cell division that reduces the amount of DNA in each cell. However, a typical interphase in a cell will proceed as follows:
What is the term for the process of cell division in eukaryotes?
Related Biology Terms. Mitosis – A type of cell division in eukaryotes that creates identical daughter cells. Cytokinesis – The division of a cell membrane into two cells; the process that completes cell division. Resting Phase – A non-dividing stage of interphase that some cells can enter.
What happens after a cell divides its chromosomes?
During this stage, the cell performs its normal functions, and grows in size. The cell replicates organelles as necessary. As seen in the graphic above, cells can sometimes leave G ...
What is the purpose of interphase?
The purpose of interphase in all cell types is to prepare for cell division, which happens in a different stage of the cell cycle. Depending on which species of organism is dividing, the functions of the cell during interphase can vary widely. Some cell, like neurons, do not replicate their DNA during interphase, ...
What is the longest stage of the eukaryotic cell cycle?
Interphase is the longest stage in the eukaryote cell cycle. During interphase, the cell acquires nutrients, creates and uses proteins and other molecules, and starts the process of cell division by replicating the DNA. Interphase is divided into three distinct stages, Gap 1, Synthesis, and Gap 2, which are discussed below.
Why do plants need mitochondria?
In plants, both the mitochondria and the chloroplasts must be replicated to provide the daughter cells with organelles capable of producing energy.
What is Interphase?
The life of a cell involves a cycle of cell growth and cell division. Interphase is that phase of cell growth where multiple metabolic activities occur . It is the longest phase in the cell cycle and takes place in the cytoplasm and nucleus. Aside from undergoing metabolic reactions, the cell also replicates its DNA. The interphase prepares the cell for cell division, wherein mitosis or division of the nucleus takes place.
What is the term for the process during which a cell carries out various functions associated with its growth and survival?
Interphase refers to the ‘metabolic phase’ during which a cell carries out various functions associated with its growth and survival. A typical cell spends most of its life in the ‘metabolic phase’ or interphase. In this phase, the cell is living and preparing for later cell division. It also grows, replicates its DNA and prepares itself for mitosis (division of nucleus).
What is the life cycle of a cell?
Ans. The life of a cell involves a cycle of cell growth and cell division. Interphase is that phase of cell growth where multiple metabolic activities occur.
What is the role of interphase in the cell cycle?
The cell cycle comprises cell growth and cell division. Interphase plays an important role in a cell cycle by preparing the cell for cell division.
What is the checkpoint in Gap 1?
When Gap 1 is completed, a checkpoint known as G1/S scrutinises the cell in order to verify if it is fit to go for DNA replication. At this step, damages or errors in the DNA are checked to ensure that cell replication thrives.
What happens to DNA during mitosis?
During mitosis, the nuclear DNA of the cell is broken down into visible chromosomes and is separated by the mitotic spindle.
What happens when a cell is damaged?
If certain cells are found to be damaged or erroneous, they undergo apoptosis or programmed cell death.
Why Is The Cell Cycle Necessary?
The cells of an animal must undergo the cell cycle for various reasons. The cell cycle helps cellular systems grow and produce more cells, capable of creating larger, more complex structures. The cell cycle is also responsible for the replacement of cells. When a cell is damaged or wears out from use, it must be replaced by another cell that can carry out the same function.
What happens to sister chromatids in mitosis?
Most cells are somatic cells, and during mitosis, the sister chromatids will be separated, ensuring that there are two copies of the DNA in each cell. Meanwhile, gametes (sex cells) will enter the meiosis phase instead of mitosis after interphase completes.
What is the G1 in a cell?
Gap 1, or G1, begins immediately after one cell has divided into two. The parent cell has already finished dividing chromosomes and the process of cytokinesis has created two new cells. G1 represents a return to normal function, the cell begins carrying out its regular tasks, growing in size while it does so and replicating any organelles it needs. It also begins to synthesize the molecular compounds it needs for later steps in the cell cycle.
What happens during the cell phase of mitosis?
The actual replication and division of a single cell into two different cells happens during mitosis and cytokinesis. The rest of the cell phase consists of interphase, and the cell grows and replicates DNA during this time. Interphase: Makes up the time between one mitotic phase and the next. The cell grows and copies DNA.
Why is interphase important in plants?
— Lewis Thomas. Interphase is an important and necessary part of the cell cycle. It enables the cell to reset itself after division ...
What happens during interphase?
During interphase of a cell cycle, the cell copies DNA, grows, and carries out its normal functions. The cell cycle refers to the cycle that has cells reproduce and divide. The cell cycle is divided into two or three main phases: interphase, mitosis, and cytokinesis. What exactly happens in the interphase of a cell cycle?
How many haploid cells are there?
The homologous chromosomes are separated in the first round of division, then the sister chromatids separate in the next. This is what leads to four haploid cells, which only have half of the entire genome. After the end of synthesis, the cell starts to prepare for cell division once more. G2.
What is the name of the process where cells replicate and make two new cells?
Cell cycle is the name we give the process through which cells replicate and make two new cells. Cell cycle has different stages called G1, S, G2, and M. G1 is the stage where the cell is preparing to divide. To do this, it then moves into the S phase where the cell copies all the DNA. So, S stands for DNA synthesis. After the DNA is copied and there's a complete extra set of all the genetic material, the cell moves into the G2 stage, where it organizes and condenses the genetic material, or starts to condense the genetic material, and prepares to divide. The next stage is M. M stands for mitosis. This is where the cell actually partitions the two copies of the genetic material into the two daughter cells. After M phase completes, cell division occurs and two cells are left, and the cell cycle can begin again.
What happens to the daughter cells in the cell cycle?
The resulting cells, known as daughter cells, each enter their own interphase and begin a new round of the cell cycle.
What does S stand for in biology?
So, S stands for DNA synthesis. After the DNA is copied and there's a complete extra set of all the genetic material, the cell moves into the G2 stage, where it organizes and condenses the genetic material, or starts to condense the genetic material, and prepares to divide. The next stage is M. M stands for mitosis.
What is the term for the process of a cell growing and dividing?
Cell Cycle. Cell Cycle. =. A cell cycle is a series of events that takes place in a cell as it grows and divides. A cell spends most of its time in what is called interphase, and during this time it grows, replicates its chromosomes, and prepares for cell division.
What is the mitotic spindle?
During metaphases, the mitotic spindle facilitates the movement of chromosomes such that they align along the centre of the cell, at the metaphase plate. At this point, sister chromatids are still attached to one another. Following metaphase, there is an important checkpoint called the spindle checkpoint.
What is the process of mitosis?
The mitotic phase describes a series of processes during which the replicated DNA condenses into visible chromosomes, which are aligned, separated, and passed on to two new daughter cells. The movement of chromosomes is orchestrated by specialised structures called microtubules. Mitosis can be further subdivided into four main phases: prophase, prometaphase, metaphase, anaphase and telophase ( PPMAT ). Sometimes, prometaphase is not considered a separate phase. These phases result in the division of the cell nucleus (also called karyokinesis ), and then the separation of the cytoplasm to form two new daughter cells (also called cytokinesis ).
What is the name of the phase of mitosis?
Mitosis encompasses prophase, prometaphase, metaphase, anaphase telophase. During these phases, the nuclear envelope disappears, the mitotic spindle forms, chromosomes condense and are lined up at the metaphase plate, and separated by being pulled to each side of the cell
What happens to the chromosomes during prophase?
During prophase, the chromosomes start to condense the nuclear envelope breaks down, and the associated organelles break up and move towards the edge of the cell. A structure called the mitotic spindle also starts to form here.
What are the two main stages of the cell cycle?
The cell cycle is made up of two main stages: interphase and mitosis
When the chromosomes are properly aligned, anaphase can proceed?
Anaphase is the process during which the sister chromatids separate at the centromere and are pulled to the edge of the cell. These chromatids are now referred to as chromosomes.
What happens during the S phase?
During the S phase, all the genetic information in the cell is copied by the process of DNA replication. This process of replication generates sister chromatids, which are identical pairs of chromosomes. These sister chromatids are attached to each other by a centromere. A centromere is a specialised sequence of DNA that links ...
How long does the cell cycle take?
A typical human cell might take about 24 hours to divide, but fast-cycling mammalian cells, like the ones that line the intestine, can complete a cycle every 9-10 hours when they're grown in culture.
What does the prefix "inter" mean?
The prefix inter - means between, reflecting that interphase takes place between one mitotic (M) phase and the next. Image of the cell cycle. Interphase is composed of G1 phase (cell growth), followed by S phase (DNA synthesis), followed by G2 phase (cell growth). At the end of interphase comes the mitotic phase, ...
How many stages of mitosis are there?
Mitosis takes place in four stages: prophase (sometimes divided into early prophase and prometaphase), metaphase, anaphase, and telophase. You can learn more about these stages in the video on mitosis. In cytokinesis, the cytoplasm of the cell is split in two, making two new cells.
How many steps does mitosis go through?
The cell goes through 4 steps (prophase, metaphase, anaphase, and telophase.) The cells at the end of the process also have the same amount of chromosomes as the parent cell. At the end, 2 cells are produced. Mitosis is used to make body cells, and occurs in the body.
How do different types of cells split their time?
Different types of cells also split their time between cell cycle phases in different ways. In early frog embryos, for example, cells spend almost no time in G and G and instead rapidly cycle between S and M phases—resulting in the division of one big cell, the zygote, into many smaller cells.
Where does cytokinesis take place?
Importantly, cytokinesis takes place differently in animal and plant cells. Cytokinesis in animal and plant cells. In an animal cell, a contractile ring of cytoskeletal fibers forms at the middle of the cell and contracts inward, producing an indentation called the cleavage furrow. Eventually, the contractile ring pinches the mother cell in two, ...
What is the name of the structure that separates DNA in the cell during the S phase?
S phase. In S phase, the cell synthesizes a complete copy of the DNA in its nucleus. It also duplicates a microtubule-organizing structure called the centrosome. The centrosomes help separate DNA during M phase.
What is Cell Cycle?
It is a series of stages a cell passes through, to divide and produce new cells.
What is the interphase of a cell?
G1 phase (Gap 1) – G1 phase is the phase of the cell between mitosis and initiation of replication of the genetic material of the cell. During this phase, the cell is metabolically active and continues to grow without replicating its DNA.
What is the term for the series of events that results in the duplication of the cell alongwith the DNA?
Cell cycle refers to the series of events that results in the duplication of the cell alongwith the DNA.
What is the mitotic phase?
This is the mitotic phase or the phase of the equational division as the cell undergoes a complete reorganization to give birth to a progeny that has the same number of chromosomes as the parent cell.
What phase does centriole divide?
The centriole also divides into two centriole pairs in the cells which contain centriole. G2 phase (Gap 2) –During this phase, the RNA, proteins, other macromolecules required for multiplication of cell organelles, spindle formation, and cell growth are produced as the cell prepares to go into the mitotic phase.
What is the process of separating chromosomes and DNA?
Mitosis. The process by which a eukaryotic cell separates the nuclear DNA and chromosomes and divides into two different but similar sets of nuclei is known as mitosis. The chromosomes are pulled apart by a mitotic spindle, which is a specialized structure consisting of microtubules.
How long does it take for a cell to divide?
Human cells exhibit typical eukaryotic cell cycle and take around 24 hours to complete one cycle of growth and division. The duration of the cycle, however, varies from organism to organism and cell to cell.
Interphase Definition
Stages of Interphase
- Gap 1
After cells have finished dividing their chromosomes, and cytokinesis has divided the cell membrane, the two new cells enter the first stage of interphase, Gap 1 or G1. During this stage, the cell performs its normal functions, and grows in size. The cell replicates organelles as neces… - Synthesis
During synthesis, the cell pauses its normal functioning. All resources are dedicated to replicating the DNA. This process starts with the two entwined stands of DNA being “unzipped” by various proteins. Other proteins, known as polymerase enzymes, start creating new strands to pair with …
Related Biology Terms
- Mitosis– A type of cell division in eukaryotes that creates identical daughter cells.
- Cytokinesis– The division of a cell membrane into two cells; the process that completes cell division.
- Resting Phase– A non-dividing stage of interphase that some cells can enter.
- Meiosis– Two consecutive cell divisions between which no DNA replication takes place.
Quiz
- 1. A cell just finished dividing. It starts gathering nutrients and growing. It stops growing, and does not start DNA replication. What stage is the cell in? A. G0 B. G1 C. G2 2. A cell has grown a little, and replicated its DNA. What comes next? A. Sythesis B. Gap 2 C.Mitosis 3. Why is there no interphase in bacteria? A. Bacterial cell cycles are much simpler B. Bacteria are always in interph…
What Is interphase?
- While cells live, they continually undergo cell division. It is a process in which daughter cells arise which mature and produce more daughters and the cycle goes on. The life of a cell involves a cycle of cell growth and cell division. Interphase is that phase of cell growth where multiple metabolic activities occur. It is the longest phase in the...
Stages of Interphase
- Gap 1
1. During this stage, the cell synthesizes high levels of protein and carries out normal functions related to cell growth. 2. The cell expands its size and volume due to production of cell organelles. 3. The cell needs to produce a large quantity of ribosomes to prepare itself for the later stages. … - S Phase
1. The cell performs replication of its DNA in the S phase. 2. Semiconservative replication occurs during this phase, in that the number of chromosomes remains constant during DNA doubling. 3. Along with DNA duplication, the cell also duplicates a microtubule-organizing structure called th…
Controlling The Interphase
- When Gap 1 is completed, a checkpoint known as G1/S scrutinises the cell in order to verify if it is fit to go for DNA replication. At this step, damages or errors in the DNA are checked to ensure...
- A mechanism called molecular switching takes place during which multiple proteins interact with DNA. This process continues to take place throughout the entire duration of the S phase.
- When Gap 1 is completed, a checkpoint known as G1/S scrutinises the cell in order to verify if it is fit to go for DNA replication. At this step, damages or errors in the DNA are checked to ensure...
- A mechanism called molecular switching takes place during which multiple proteins interact with DNA. This process continues to take place throughout the entire duration of the S phase.
- If certain cells are found to be damaged or erroneous, they undergo apoptosis or programmed cell death.
- A second checkpoint is present at the G2 phase, after the synthesis of DNA in the S phase, during which kinase enzymes are used to control various processes in cell division cycles.
M Phase
- During the mitotic (M Phase), the cell divides its duplicated DNA and cytoplasm to make two new daughter cells.
- M Phase involves two division-related processes: mitosis and cytokinesis
- During mitosis, the nuclear DNA of the cell is broken down into visible chromosomes and is separated by the mitotic spindle.
- During the mitotic (M Phase), the cell divides its duplicated DNA and cytoplasm to make two new daughter cells.
- M Phase involves two division-related processes: mitosis and cytokinesis
- During mitosis, the nuclear DNA of the cell is broken down into visible chromosomes and is separated by the mitotic spindle.
- During cytokinesis, the cytoplasm of the cell divides to create two new daughter cells.
Interphase and The Cell Cycle
- The cell cycle comprises cell growth and cell division. Interphase plays an important role in a cell cycle by preparing the cell for cell division.
- Interphase facilitates the growth of a cell, helps in the synthesis of important proteins and organelles and the replication of DNA.
- Several external and internal conditions need to be met by the cell prior to mitosis.
- The cell cycle comprises cell growth and cell division. Interphase plays an important role in a cell cycle by preparing the cell for cell division.
- Interphase facilitates the growth of a cell, helps in the synthesis of important proteins and organelles and the replication of DNA.
- Several external and internal conditions need to be met by the cell prior to mitosis.
- There also exists a unique stage called G0 which some cells undergo, which does not allow cell division.
Interphase in Different Cells
- Different cells have different kinds of interphase mechanisms.
- For example, a eukaryotic cell undergoes all the stages of interphase (Gap 1, Synthesis Phase and Gap 2).
- Cells that undergo cell division spend around 95% of their time in the interphase.
- Certain cells which do not undergo cell division remain permanently in the interphase, where…
- Different cells have different kinds of interphase mechanisms.
- For example, a eukaryotic cell undergoes all the stages of interphase (Gap 1, Synthesis Phase and Gap 2).
- Cells that undergo cell division spend around 95% of their time in the interphase.
- Certain cells which do not undergo cell division remain permanently in the interphase, whereas more active cells like the skin cells must enter the interphase in order to synthesise all the necessa...
Things to Remember
- Interphase in a cell is that part of a cell growth where several metabolic reactions take place.
- It comprises three stages: G1,S Phase and G2.
- Additionally, there is also a G0 phase for cells that do not undergo cell division.
- In the G1 phase, the cell grows and synthesizes ribosomes to prepare for the later stages.
Why Is The Cell Cycle Necessary?
The Cell Cycle
- The cell cycle is what creates new cells. The actual replication and division of a single cell into two different cells happens during mitosis and cytokinesis. The rest of the cell phase consists of interphase, and the cell grows and replicates DNA during this time. 1. Interphase: Makes up the time between one mitotic phase and the next. The cell grows and copies DNA. 2. Mitotic phase: …
Interphase of The Cell Cycle8*
- The interphase of a cellcan itself be subdivided into three separate chunks: 1. Gap 1 2. Synthesis 3. Gap 2 G1 Gap 1, or G1, begins immediately after one cell has divided into two. The parent cell has already finished dividing chromosomes and the process of cytokinesis has created two new cells. G1 represents a return to normal function, the cell b...
What Happens in mitosis?
- Mitosis is itself divided into phases: 1. prophase 2. prometaphase 3. metaphase 4. anaphase 5. telophase During prophase the chromosomes condense around each other, while the nuclear envelope surrounding the nucleolus disappears, letting the contents of the nucleolus out into the cytoplasm. Prometaphase sees the chromosomes keep condensing while a structure called the …