
The precise sample of a syllogism is that the first, important premise stocks some thing with a second, minor premise, which in flip ends in a end, like this:
- I am creeped out, however additionally fascinated, through all spiders.
- That extensive tarantula is a spider.
- I am creeped out, however additionally fascinated, through that extensive tarantula.
What are some examples for the law of syllogism?
Law of Syllogism Examples. The law of syllogism is present in all areas of life. For example, politicians use it to get your vote. They say: “If you vote for me for a second term, I will make decisions as I did in my first term.” “If I make decisions as I did in my first term, then I will help the homeless.”
What are the rules of syllogism and an example?
What are the rules of syllogism?
- Rule One: There must be three terms: the major premise, the minor premise, and the conclusion – no more, no less.
- Rule Two: The minor premise must be distributed in at least one other premise.
- Rule Three: Any terms distributed in the conclusion must be distributed in the relevant premise.
Which is an example of a good syllogism?
Types of Syllogism
- Categorical Syllogism Examples. As we know, our first example about roses was a categorical syllogism. ...
- Conditional Syllogism Examples. Conditional syllogisms follow an, "If A is true, then B is true" pattern of logic. ...
- Disjunctive Syllogism Examples. ...
- Enthymemes Examples. ...
- Syllogistic Fallacy Examples. ...
Which statement represents the law of syllogism?
There are also three parts involved in the law of syllogism, and each of these parts is called a conditional statement. A conditional statement has a hypothesis, which follows after the word if, and it has a conclusion, which follows after the word then. A letter is used to represent each phrase of the conditional statement.
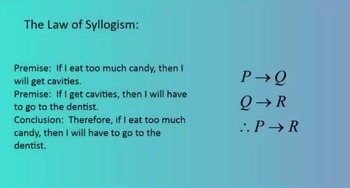
What is an example of syllogism?
An example of a syllogism is "All mammals are animals. All elephants are mammals. Therefore, all elephants are animals." In a syllogism, the more general premise is called the major premise ("All mammals are animals"). The more specific premise is called the minor premise ("All elephants are mammals").
What is an example of the Law of detachment?
For example, if it is raining, then the tree will be wet. The hypothesis is attached to the "if" and the conclusion is attached to the "then." So, what is the law of detachment in geometry? In geometry, the law of detachment states that if P leads to Q and P is true, then Q must be true.
How do you determine the Law of syllogism?
In mathematical logic, the Law of Syllogism says that if the following two statements are true:(1) If p , then q .(2) If q , then r .(3) If p , then r .
Which statement is the Law of syllogism?
The Law of Syllogism If p equals q and if q equals r, then p equals r.
What's the difference between Law of detachment and syllogism?
0:327:43Law of Detachment and Syllogism - YouTubeYouTubeStart of suggested clipEnd of suggested clipWell with law of syllogism you'll notice that there's three or more quantities involved whereas lawMoreWell with law of syllogism you'll notice that there's three or more quantities involved whereas law of detachment. There's just two quantities the hypothesis.
What is the meaning of the Law of syllogism in geometry?
Syllogism refers to drawing inferences from given prepositions or sentences. The Law of Syllogism is actually a part of deductive reasoning where we arrive at conclusions by logical reasoning. It is similar to the transitive property: if a = b and b= c, then a=c. It is like a chain rule.
What is the purpose of syllogism?
Syllogisms are the most common way of arranging premises into a good argument. A syllogism is a form of deductive argument where the conclusion follows from the truth of two (or more) premises.
How do you structure a syllogism?
Basic structure A syllogism consists of three parts—a major premise, a minor premise, and a conclusion. Each of the premises has one term in common with the conclusion.
Who invented the Law of syllogism?
In its earliest form (defined by Aristotle in his 350 BCE book Prior Analytics), a syllogism arises when two true premises (propositions or statements) validly imply a conclusion, or the main point that the argument aims to get across.
What is categorical syllogism examples?
Here is an example of a valid categorical syllogism: Major premise: All mammals are warm-blooded. Minor premise: All black dogs are mammals. Conclusion: Therefore, all black dogs are warm-blooded.
What is the pattern of a syllogism?
A syllogism is a method of reasoning by drawing a conclusion from two premises. The particular pattern of a syllogism is that the first, major premise shares something with a second, minor premise, which in turn leads to a conclusion, like this: I am creeped out, but also fascinated, by all spiders.
How do you say the word syllogism?
0:210:26How to Pronounce Syllogism - YouTubeYouTubeStart of suggested clipEnd of suggested clipSyllogism syllogism.MoreSyllogism syllogism.
What is the Law of Detachment?
The Law of Detachment says that we must detach ourselves from the result or outcome in order to allow what we desire to materialize in the physical universe. When we have done our part, we must learn to let go of the outcome for things to materialize. And once we do let go, it's when things materialize.
What is the rule of detachment?
A rule of detachment is construed as a rule that permits the acceptance of a statement h representing a factual inductive conclusion, given that certain criteria are satisfied.
What is the Law of detachment in relationships?
The Law of Detachment states that in order to manifest our desires, we must release attachment to the outcome itself as well as the path we might take to get there.
What is detachment in spirituality?
Every spiritual tradition includes some form of offering (and some form of God), but for detachment practice, the two most powerful ways to offer are to dedicate your actions and to turn over your fears, desires, doubts, and obstructions to the one Consciousness.
What is the law of syllogism?
The law of syllogism states that it is possible to cut out middle steps in deductive reasoning. That is, if a first thing implies a second thing and that thing implies a third thing, then it is possible to say the first implies the third.
How many events can a syllogism be?
The law of syllogism can be employed with just two statements with three events, or it can be used for strings of hundreds of statements. It just requires that all intermediate conditional statements be true in order for the abridged statement to be true.
What is the antecedent of a conditional statement?
Recall that an antecedent is the part of a conditional statement that follows the word “if.” The consequence is the part that follows the word “that.” In a syllogism, the consequence of one statement is the antecedent of another.
How many events can a transitive property of equality be used with?
This law is very similar to the transitive property of equality. It can be used with more than three events and is important for making logical arguments make sense in any branch of mathematics.
Is the law of syllogism present in all areas of life?
The law of syllogism is present in all areas of life.
What Is Syllogism?
A simple syllogism definition is that it's a form of deductive reasoning where you arrive at a specific conclusion by examining premises or ideas.
How many rules are there for syllogism?
There are six known rules of syllogism. However, they mainly apply to categorical syllogism, since that is the only category that requires three components: major premise, minor premise, conclusion. Here are six rules that will ensure you're making a strong and accurate argument.
What is a syllogism in Shakespeare?
Syllogisms make for colorful literary devices. They explain situations indirectly, affording readers the opportunity to practice reasoning and deduction skills. Shakespeare was a master of many things, including syllogism. Here is an example of a syllogism fallacy in The Merchant of Venice:
What is the premise of the syllogism "I'm holding a flower"?
I'm holding a flower. Many syllogisms contain three components. Major premise - All roses are flowers. Minor premise - This is a rose. Conclusion - I'm holding a flower. However, there are different types of syllogisms. Take a look at each type of syllogism, along with examples.
Why do we need syllogisms in an essay?
They create a formula for you to abide by, in order to ensure your main point is flawless. Syllogisms also allow you to test your theories according to syllogistic fallacies. When examining your main argument or point for discussion, be sure you haven't made any presumptions that your audience might disagree with.
What is syllogism in the Merchant of Venice?
The Merchant of Venice by William Shakespeare. Syllogisms make for colorful literary devices. They explain situations indirectly , affording readers the opportunity to practice reasoning and deduction skills. William Shakespeare was a master of many things, including syllogism.
What are the three components of a categorical syllogism?
However, they mainly apply to categorical syllogism, since that is the only category that requires three components: the major premise, minor premise and conclusion. Learn the six rules that ensure you're making a strong and accurate argument.
What is a syllogism?
Within logic, various types of arguments, premises, and conclusions can be formed. A syllogism is a method of reasoning by drawing a conclusion from two premises. The particular pattern of a syllogism is that the first, major premise shares something with a second, minor premise, which in turn leads to a conclusion, like this:
What is the conclusion of a syllogism?
The conclusion connects the universal truth of the major premise to the immediate example of the minor premise: "Then this three-sided polygon is a triangle.". Conclusions often begin with "Then.". The law of syllogism is also known as reasoning by transitivity.
What is the structure of a syllogism?
The Structure of a Syllogism. In a syllogism, the major premise is broad and wide, like saying, "All triangles have three sides and three interior angles.". The major premise is often a conditional statement, beginning with "If.".
What is Euclid's parallel postulate?
Euclid's Parallel Postulate tells us that for every line and a point not on that line, only one line can contain that point and be parallel to the line. The law of syllogism can help you to apply that postulate:
What are the premises of an argument?
Statements 1 and 2 are called the premises of the argument. If they are true, then statement 3 must be a valid conclusion.
What is logic in geometry?
Logic in Geometry. Logic is a learned skill; it is as much a branch of mathematics as it is a kind of philosophy, or reasoning. Logic in geometry allows you to see connections and patterns, to make leaps of understanding from the single event to universal truths.
What is a three sided polygon?
Then this three-sided polygon is a triangle.
What is the law of syllogism?
The Law of Syllogism is actually a part of deductive reasoning where we arrive at conclusions by logical reasoning.
How many conditional arguments are there in the rule of syllogism?
In the rule of syllogism, there are three conditional arguments.
What is conditional syllogism?
Conditional Syllogism: If A is true, then B is true (If A, then B).
How many parts are there in a syllogism?
In the rule of syllogism, there are three parts involved.
What is the negation and inversion of the original statement which conveys the same meaning called?
The negation and inversion of the original statement which conveys the same meaning is called the contrapositive.
What is a syllogism?
Here’s a quick and simple definition: A syllogism is a three-part logical argument, based on deductive reasoning, in which two premises are combined to arrive at a conclusion. So long as the premises of the syllogism are true and the syllogism is correctly structured, the conclusion will be true. An example of a syllogism is "All mammals are ...
Why Do Writers Use Syllogisms?
Writers use syllogisms because they're a useful tool for making an argument more convincing in persuasive writing and rhetoric. More specifically, writers might choose to use syllogism because:
How many parts does a syllogism have?
Sometimes the word syllogism is used to refer generally to any argument that uses deductive reasoning. Although syllogisms can have more than three parts (and use more than two premises), it's much more common for them to have three parts (two premises and a conclusion). This entry only focuses on syllogisms with three parts.
What is a fallacy in logic?
A "fallacy" is the name for a mistake in logic. Syllogisms often seem like very simple statements, but you may be surprised how often people make logical mistakes when trying to put together simple syllogisms. For example, it may seem logical to make a statement like "Some A are B, and some C are A, therefore some C are B," such as:
What is the syllogism in "To His Coy Mistress"?
Syllogism in "To His Coy Mistress" by Andrew Marvell. If you look closely, you can see that this poem by Andre Marvell contains a subtle syllogism, scattered throughout the poem. Embedded in the beginning, middle, and end of the poem are the major premise, the minor premise, and the conclusion.
Why are universal syllogisms called universal?
Universal syllogisms are called "universal" because they use words that apply completely and totally, such as "no" and "none" or "all" and "only.". The two most common forms of universal syllogisms are: "All A are B, and all C are A, so all C are B.". (This is the most common type of syllogism.) All mammals are animals.
What are the three lines of a syllogism?
Syllogisms can be represented using the following three-line structure, in which A, B, and C stand for the different terms: All A are B. All C are A. Therefore, all C are B. Another way of saying the same thing is as follows: If A = B. and C = A. then C = B.
What are the laws of logic?
There are two laws of logic involved in deductive reasoning: 1 Law of Detachment 2 Law of Syllogism
How many laws of logic are involved in deductive reasoning?
There are two laws of logic involved in deductive reasoning:
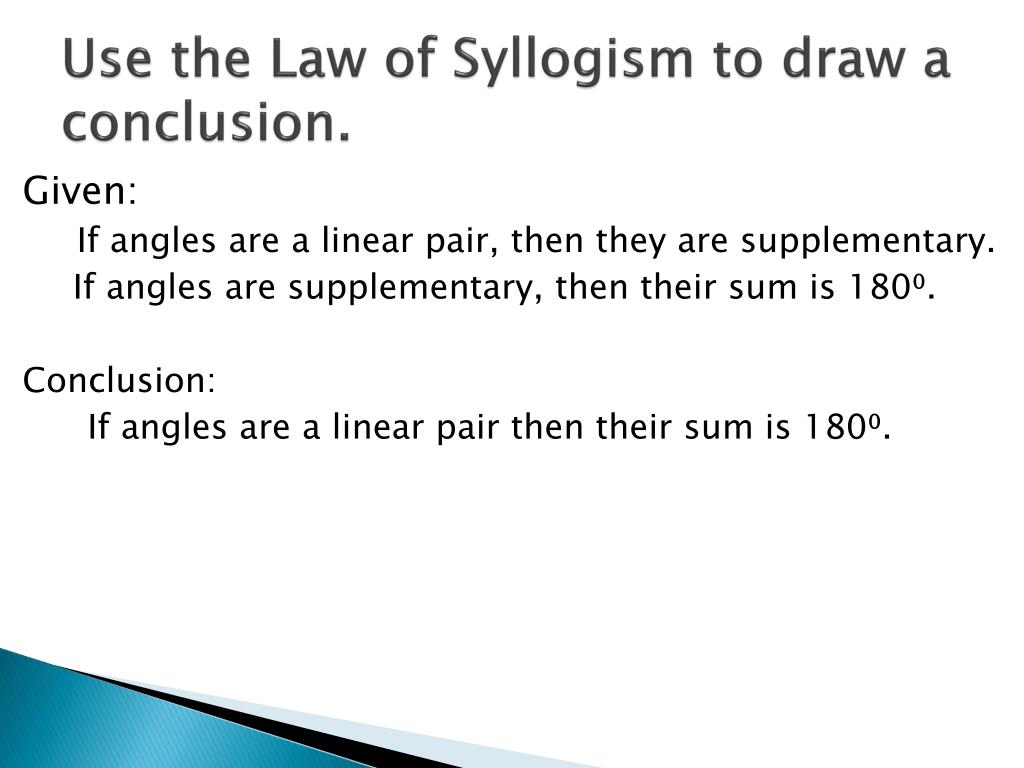
Table of Contents
Logic in Geometry
Syllogism Definition
Syllogism Examples
The Structure of A Syllogism
Syllogism in Geometry Examples
- The power of logic is seen over and over in geometric proofs. When you substitute terms, for example, you are following the law of syllogism: 1. If ∠A is supplementary to ∠B 2. and if ∠B = 115° 3. then ∠A = 65° Perhaps without even noticing, you solve many steps in geometric proofs using the law of syllogism. The law of syllogism directs you to use...
Lesson Summary