What do the ventricles do in the brain?
Jul 23, 2021 · The key function of the ventricular system is the production and recycling of Cerebrospinal Fluid (CSF) throughout the central nervous system including the brain and the spinal cord. In terms of ...
What is the function of the ventricular system?
Apr 04, 2022 · The ventricles of the brain are a communicating network of cavities filled with cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) and located within the brain parenchyma. The ventricular system is composed of 2 lateral ventricles, the third ventricle, the cerebral aqueduct, and the fourth ventricle (see the images below). The Ventricles of the Brain. The ventricles are structures that produce …
How many ventricles are in the human brain?
Mar 15, 2022 · Each brain ventricle’s main function is to produce, secrete, and convey CSF. Lateral ventricles The first and the second ventricles are known as the lateral ventricles. Each of the lateral ventricles are located in each hemisphere of the cerebral cortex, one in the left hemisphere, one in the right.
What causes swollen ventricles in the brain?
What is the main function of the ventricles in the brain? The Ventricles of the Brain. The ventricles are structures that produce cerebrospinal fluid, and transport it around the cranial cavity. They are lined by ependymal cells, which form a structure called the choroid plexus. It is within the choroid plexus that CSF is produced.

What is the function of the ventricles?
The ventricles are interconnected with each other, and also with the central canal of the spinal cord and with the subarachnoid space (space between two of the linings that separate the brain from the skull). CSF is produced by the lining of the ventricles.
Why is the ventricular system important?
The ventricular system is critically important to the normal functioning of the central nervous system . It protects the brain by allowing it to “float” in a fluid bath and provides a shock absorber against head trauma. The CSF itself also helps to provide nutrients to the brain and to keep the brain in chemical balance.
How many lateral ventricles are there?
There are two lateral ventricles—one on each side of the cerebral cortex. The lateral ventricles are continuous with the third ventricle, which is lower in the brain. The third ventricle is continuous with the fourth ventricle, which runs along the brainstem. Dorling Kindersley RF/Getty Images.
What causes hydrocephalus in the ventricular system?
A blockage to the flow of CSF causes the pressure to rise within the ventricular system and can produce hydrocephalus. Infection (such as meningitis) or bleeding can change the characteristics of the CSF.
What is a lumbar puncture?
The lumbar puncture (LP), also called the spinal tap, can be used to measure the pressure within in the spinal canal, and to test the CSF for signs of infection, inflammation, or hemorrhage. The LP is often quite important for diagnosing diseases of the central nervous system.
What is the function of the ventricles?
The ventricles function to produce, circulate, and reabsorb CSF throughout the brain and spinal cord of the central nervous system.
What is the ventricular system?
The ventricular system is a network of communicating cavities within the brain, called ventricles, that function to produce, transport, and reabsorb cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) throughout the central nervous system. The main structures that make up the ventricular system include:
How many ventricles are there in the ventricular system?
The ventricular system comprises two lateral ventricles, one third ventricle, and one fourth ventricle that communicate with each other through the interventricular foramina and cerebral aqueduct. We will use labeled diagrams and lateral views of the brain to learn the anatomy, boundaries, and locations of each ventricle.
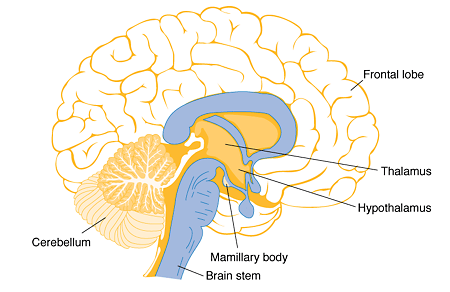
Where is the third ventricle located?
The third ventricle is located in the midline of the brain, in the diencephalon, below the lateral ventricles. Each lateral ventricle connects to the third ventricle through an interventricular foramen (drawn in to help visualize).
What is the role of CSF in the brain?
CSF has several important roles such as providing buoyancy, protection, chemical stability, and waste elimination to the brain. Buoyancy - The CSF-filled ventricles and surrounding CSF in the subarachnoid space allow the brain to “float” and become buoyant thereby reducing the weight of the brain in the cranium.
What is the function of CSF?
Chemical Stability - The CSF maintains a stable environment for the brain. Filtration System - The CSF provides nutrients and removes metabolic waste from the central nervous system as it gets reabsorbed into the vasculature. We will discuss how CSF is produced and the flow of CSF through the ventricular system.
What are lateral ventricles?
The lateral ventricles are cavities created by surrounding structures that form the walls of the ventricle. The lateral ventricles have a medial wall, roof, and a floor/lateral wall. The structures that form these walls vary depending on which segment of the ventricle is being viewed.
What is the ventricular system?
Ventricles are a communicating network of chambers filled with cerebrospinal fluid (CSF). The ventricular system is the pathway for the CSF and is critical to the central nervous system ’s overall functioning. Developmental anomalies that impact the ventricular system include hydrocephalus and neural tube defects.
Where are the lateral ventricles located?
The pair of lateral ventricles are the largest of the four ventricles in the brain. They are located in the largest part of the brain, the cerebrum. The third ventricle is in the diencephalon, located in the center of the brain. The fourth ventricle is located in the hindbrain.
Where does CSF go in the brain?
The CSF moves from the lateral ventricles to the third ventricle and finally to the fourth ventricle, where it exits and bathes the brain and spinal cord. The CSF is then absorbed back into the bloodstream. The ventricular system helps the central nervous system function properly. The fluid it produces protects the brain and provides ...
Why is my head so large?
The condition is marked by a disproportionally large head size due to the buildup of excess CSF in the ventricles. Pressure from the extra fluid can damage the brain and impair brain function. Hydrocephalus can also occur in children and adults due to trauma, infection, stroke, and tumors.
What is the shape of the lateral ventricle?
Each lateral ventricle, one on each side of the brain, sits in a “C” shape. Each side connects to the third ventricle by the interventricular foramina. The fourth ventricle is diamond shaped and sits below the third ventricle. The cerebral aqueduct connects the third ventricle to the fourth.
How to diagnose congenital hydrocephalus?
Congenital hydrocephalus may be diagnosed by fetal ultrasound. Most of the time, the condition is suspected during a physical exam following birth. In infants, children, and adults, a diagnosis may be confirmed with computed tomography ( CT scan ), magnetic resonance imaging ( MRI ), or an ultrasound.
Who is Kathi Valeii?
The Pathway for Cerebrospinal Fluid in the Brain. Kathi Valeii is a freelance writer covering the intersections of health, parenting, and social justice. Nicholas R. Metrus, MD, is a board-certified neurologist and neuro-oncologist. He currently serves at the Glasser Brain Tumor Center in Summit, New Jersey.
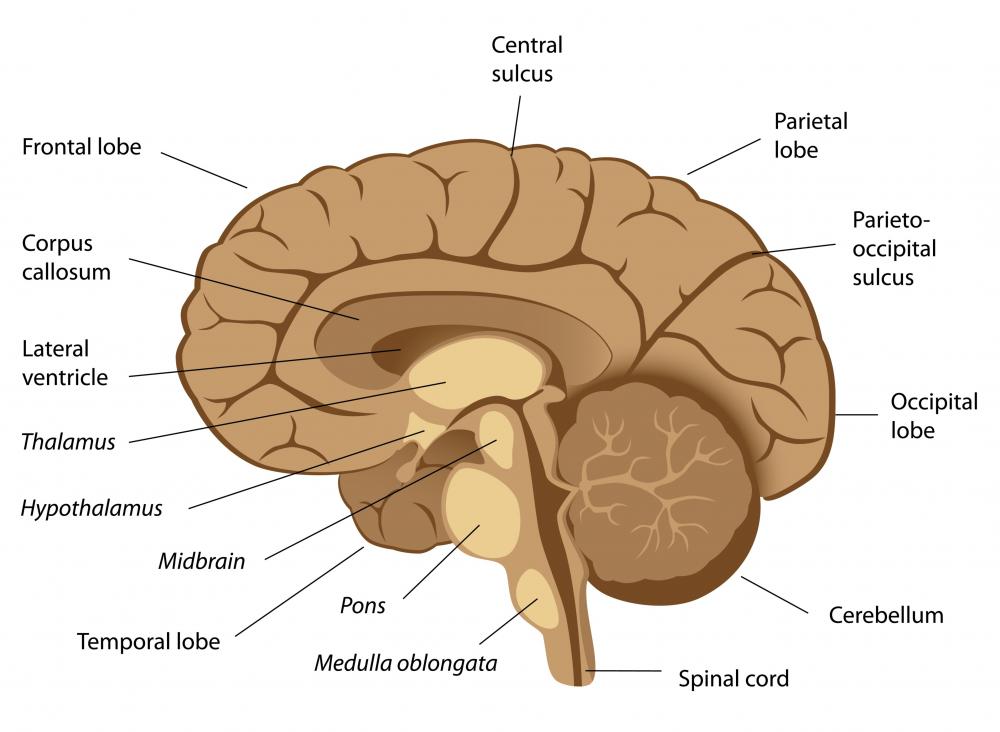
Anatomy
Function
- Aside from cerebrospinal fluid, your brain ventricles are hollow. Their sole function is to produce and secrete cerebrospinal fluid to protect and maintain your central nervous system. CSF is constantly bathing the brain and spinal column, clearing out toxins and waste products released by nerve cells. One such waste product—the amyloid A-b peptide...
Associated Conditions
- Infection, head trauma, and bleeding in the braincan cause inflammation in the ventricles and subarachnoid space. That inflammation blocks the flow of cerebrospinal fluid, causing the ventricles to swell in size and placing pressure on the brain. The following ventricle-related conditions are life threatening. If you are experiencing any of the symptoms described below, cal…
Tests
- Hydrocephalus, meningitis, ventriculitis, and brain hemorrhage are diagnosed using one or more of the following: 1. Lumbar puncture(LP) 2. Computed tomography(CT) scan 3. Magnetic resonance imaging(MRI) Lumbar puncture (LP), also called a spinal tap, can be used to measure pressure within the spinal canal. It is also used to test cerebrospinal fluid for signs of infection, i…
Summary
- Cerebrospinal fluid is produced in the lining of your brain's ventricles. After it drains from these four chambers, CFS circulates in the canals that surround your brain and spinal cord, ensuring your central nervous system is nourished and protected. Traumatic brain injury, bacterial meningitis, and brain hemorrhage can cause inflammation in and around your ventricles. As a re…
A Word from Verywell
- If you or a loved one has survived one of these conditions, consider joining a support group online or in your community. Support groups can be invaluable for many survivors, as they offer a safe place to share personal stories and ask for advice from people who understand what you're going through.