The main objectives of primary treatment of wastewater are:
- To reduce the strength of sewage to the extent 30% to 50%.
- To remove settleable solids by 80% to 90%.
- To reduce BOD by 30% to 35%.
- To make the sewage fit for further treatment process.
Why water treatment is so important to your health?
- flushing out waste from your body
- regulating body temperature
- helping your brain function
Why do we need to treat wastewater?
- tainted drinking water
- water scarcity and water shortages
- foul lakes and rivers
- lower numbers of aquatic species
- dangers to livestock
- reduced waterfront property values
Why are sewage systems important?
- Volume of sewage generated with peak flow collection criterea.
- Input sewage parameters of BOD, COD, TSS etc.
- Desired output treated sewage water parameters of BOD COD, TSS , PH etc depending upon the intended consumption of treated water.
- Sludge disposal criteria, may be gas generation for electricity production.
- Land availability
Why is water important 3 reasons?
Why Is Water So Important to Life on Earth?
- Oxygen. Plants deserve appreciation for producing breathable air and for what they are able to do with water.
- Weather. Global patterns of weather and precipitation are dictated by the movement, quantity and temperature of water, both in the ocean and in the atmosphere.
- Agriculture. ...
- Fisheries. ...
- Sustainability. ...

What is the importance benefits of wastewater treatment?
Wastewater treatment systems eliminate disease-causing bacteria and kills harmful organisms. It filters out such contaminants before the wastewater leaves the tank and enters the ground. This filtering process prevents diseases from entering water sources or reaching plants and farm animals.
What is the most important part of wastewater treatment?
Wastewater treatment is usually broken down into two sections: primary treatment, which removes grease, dirt, gravel, and floatable waste, and secondary treatment, which removes even more suspended solids and pollutants by using biological processes.
What are the three main purposes of water treatment?
Water treatment is a process involving different types of operations (physical, chemical, physicochemical and biological), the aim of which is to eliminate and/or reduce contamination or non-desirable characteristics of water.
What is the process of wastewater treatment?
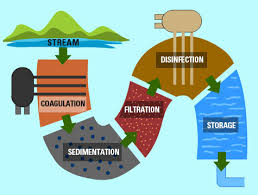
Treatment StepsStep 1: Screening and Pumping. ... Step 2: Grit Removal. ... Step 3: Primary Settling. ... Step 4: Aeration / Activated Sludge. ... Step 5: Secondary Settling. ... Step 6: Filtration. ... Step 7: Disinfection. ... Step 8: Oxygen Uptake.
Why Treat Wastewater?
It's a matter of caring for our environment and for our own health. There are a lot of good reasons why keeping our water clean is an important priority:
Wastewater treatment
The major aim of wastewater treatment is to remove as much of the suspended solids as possible before the remaining water, called effluent, is discharged back to the environment. As solid material decays, it uses up oxygen, which is needed by the plants and animals living in the water.
What is wastewater treatment?
Wastewater treatment is done to purify wastewater to minimize its solids, organisms and chemicals.
What is the primary goal of advanced treatment of raw sewage?
In advanced treatment, the main goal is to remove nutrients, especially nitrogen and phosphorus, various toxic substances (such as heavy metals and orher synthetic hazardous wastes).
What is phase separation?
Phase separation transfers impurities into a non-aqueous phase. Phase separation may occur at intermediate points in a treatment sequence to remove solids generated during oxidation or polishing. Grease and oil may be recovered for fuel or saponification. Solids often require dewatering of sludge in a wastewater treatment plant. Disposal options for dried solids vary with the type and concentration of impurities removed from water.
What is industrial wastewater treatment?
Industrial wastewater treatment describes the processes used for treating wastewater that is produced by industries as an undesirable by-product. After treatment, the treated industrial wastewater (or effluent) may be reused or released to a sanitary sewer or to a surface water in the environment. Some industrial facilities generate wastewater that can be treated in sewage treatment plants. Most industrial processes, such as petroleum refineries, chemical and petrochemical plants have their own specialized facilities to treat their wastewaters so that the pollutant concentrations in the treated wastewater comply with the regulations regarding disposal of wastewaters into sewers or into rivers, lakes or oceans. : 1412 This applies to industries that generate wastewater with high concentrations of organic matter (e.g. oil and grease), toxic pollutants (e.g. heavy metals, volatile organic compounds) or nutrients such as ammonia. : 180 Some industries install a pre-treatment system to remove some pollutants (e.g., toxic compounds), and then discharge the partially treated wastewater to the municipal sewer system. : 60
What is a clarifier used for?
Clarifiers are widely used for wastewater treatment. Phase separation transfers impurities into a non-aqueous phase. Phase separation may occur at intermediate points in a treatment sequence to remove solids generated during oxidation or polishing. Grease and oil may be recovered for fuel or saponification.
How is grit removed from wastewater?
Solids such as stones, grit, and sand may be removed from wastewater by gravity when density differences are sufficient to overcome dispersion by turbulence. This is typically achieved using a grit channel designed to produce an optimum flow rate that allows grit to settle and other less-dense solids to be carried forward to the next treatment stage. Gravity separation of solids is the primary treatment of sewage, where the unit process is called "primary settling tanks" or "primary sedimentation tanks." It is also widely used for the treatment of other types of wastewater. Solids that are denser than water will accumulate at the bottom of quiescent settling basins. More complex clarifiers also have skimmers to simultaneously remove floating grease such as soap scum and solids such as feathers, wood chips, or condoms. Containers like the API oil-water separator are specifically designed to separate non-polar liquids.
How does oxidation affect wastewater?
Oxidation reduces the biochemical oxygen demand of wastewater, and may reduce the toxicity of some impurities . Secondary treatment converts organic compounds into carbon dioxide, water, and biosolids through oxidation and reduction reactions. Chemical oxidation is widely used for disinfection.
What are the processes used in wastewater treatment plants?
Processes commonly used include phase separation (such as sedimentation), biological and chemical processes (such as oxidation) or polishing. The main by-product from wastewater treatment plants is a type of sludge which is usually treated in the same or another wastewater treatment plant.
How much of the world's wastewater is treated?
At the global level, an estimated 52% of municipal wastewater is treated. However, wastewater treatment rates are highly unequal for different countries around the world. For example, while high-income countries treat approximately 74% of their municipal wastewater, developing countries treat an average of just 4.2%.
What is the purpose of wastewater treatment facilities?
Summary. The main goal of wastewater treatment facilities is to protect humans and the ecosystem from harmful and toxic elements found in wastewater. Water treatment facilities were designed to speed up the natural process of purifying water because the natural process is overloaded.
Why do we need water treatment facilities?
Water treatment facilities are designed to speed up the natural process of purifying water. With billions of people and even more wastewater, the natural process is overloaded. Without wastewater treatment, the amount of wastewater would cause devastation, as it still does today in developing countries. Globally, over 80 percent of all wastewater is discharged without treatment. 1 In the countries that do have water treatment facilities, they use various methods to treat water with one common goal: purify water as much as possible and send it back into the environment to keep humans and the Earth safe and thriving.
Why is wastewater important for the ecosystem?
Wastewater treatment also protects the ecosystem. Fish and aquatic life require fresh water. When their water environment is laden with wastewater, they cannot survive. If chemicals, such as nitrogen and phosphates, enter streams, rivers or large bodies of water in excessive amounts, it causes excessive plant growth which release toxins into ...
How much of the world's wastewater is discharged without treatment?
Globally, over 80 percent of all wastewater is discharged without treatment. 1 In the countries that do have water treatment facilities, they use various methods to treat water with one common goal: purify water as much as possible and send it back into the environment to keep humans and the Earth safe and thriving.
What are the health risks of wastewater treatment?
Unclean water poses significant health risks, accounting for 1.7 million deaths annually, of which over 90 percent are in developing countries. 2 Several water-related diseases, including cholera and schistosomiasis, remain widespread across many developing countries, where only a very small fraction (in some cases less than 5 percent) of domestic and urban wastewater is treated prior to its release into the environment 3.
Why is natural water treatment overloaded?
While Mother Nature does her best to naturally process wastewater, there is too much for her to handle. Because the global population is so large and growing, so is wastewater. Nature can’t keep up with naturally processing the excessive amounts of wastewater.
What is the purpose of wastewater treatment?
If wastewater is not properly treated, then the environment and human health can be negatively impacted, reported the United States Geological Survey (USGS). Among the impacts are harm to fish and wildlife populations, oxygen depletion, beach closures and other restrictions on recreational water use.
How is wastewater formed?
Wastewater is formed by a number of activities such as bathing, washing, using the toilet, and rainwater runoff. Wastewater is essentially used water that has been affected by domestic, industrial and commercial use.
What happens to wastewater after grit is removed?
Once the screening process is complete and grit has been removed, the wastewater still contains organic and inorganic matter along with other suspended solids.
What is activated sludge?
People tend to use the activated sludge process instead of trickling filters, since the activated sludge process speeds up the work of the bacteria. After the sewage leaves the settling tank in the primary stage, it is pumped into an aeration tank.
How does wastewater go through a plant?
As wastewater enters a plant for treatment, it flows through a screen. This removes large floating objects, such as rags and sticks, which clog pipes or damage equipment. Once the wastewater has been screened, it passes into a grit chamber, where cinders, sand, and small stones settle to the bottom.
What is the process of removing chlorine from sedimentation tanks?
Many states now also require the removal of excess chlorine before discharge to surface waters by a process called dechlorination, according to the EPA.
What is primary treatment?
Primary Treatment. Primary treatment removes material that will either float or readily settle out by gravity. This treatment includes the physical processes of screening, comminution—the act of reducing a material to minute particles or fragments—grit removal and sedimentation. As wastewater enters a plant for treatment, it flows through a screen.
What is the purpose of Sewage Treatment Plants?
Sewage is made up of wastewater from homes and businesses, as well as perhaps pre-treated industrial waste. There are numerous sewage treatment processes from which to choose.
Advantages & Disadvantage of a Sewage Treatment Plant
A sewage treatment plant has numerous advantages. Let’s have a look at a few of them:
Effects of wastewater pollutants
If wastewater is not adequately treated, it can have a severe influence on the environment and human health. Fish and wildlife populations may be harmed, oxygen levels may be depleted, beach closures and other limits on recreational water usage, restrictions on fish and shellfish harvesting, and drinking water contamination may occur.
How does the Sewage Treatment Plant protect our environment?
Untreated sewage water pollutes our ecosystem and rivers in the thousands of gallons range. A liter of wastewater pollutes 8 liters of clean water, according to researchers and scientists. You can see how dangerous it is for the river now.
