One of the major weaknesses of early versions of strain theory was that, following Merton's general lead, “success” was conceived and measured in largely economic terms; that is, the “success goal” was considered to be overwhelmingly related to the accumulation of money / wealth. Click to see full answer.
Full Answer
What is the strain theory according to Merton?
Strain theory is a sociology and criminology theory developed in 1938 by Robert K. Merton. The theory states that society puts pressure on individuals to achieve socially accepted goals (such as the American dream), though they lack the means. what is the most important cultural goal according to Merton?
What are the weaknesses of strain theory?
One of the major weaknesses of early versions of strain theory was that, following Merton's general lead, “success” was conceived and measured in largely economic terms; that is, the “success goal” was considered to be overwhelmingly related to the accumulation of money / wealth. Click to see full answer.
What is Merton’s theory of crime?
Merton developed his theory from a well-established observation from official statistics – that a higher proportion of acquisitive crime is committed by those from unskilled manual backgrounds (or ‘lower social classes’).
When did strain theory come into being?
April 16, 2016. Strain Theory was first developed by Robert Merton in the 1940s to explain the rising crime rates experienced in the USA at that time. Strain theory has become popular with Contemporary sociologists.

Which of the following is a critique of Merton's strain theory?
One critique of the strain theory is that it overemphasizes the role of social class in crime and deviance (Brym and Lie, 2007:197). Strain theory applies best to lower classes as they struggle most with the lack of resources to reconcile their goals.
What are the main assumptions of strain theory?
Strain theories are generally macrolevel theories, and they share several core assumptions: first, the idea that social order is the product of a generally cohesive set of norms; second, that those norms are widely shared by community members; and third, that deviance and community reactions to deviance are essential ...
What is the main idea of Merton's strain theory?
According to Merton's strain theory, societal structures can pressure individuals into committing crimes. Classic Strain Theory predicts that deviance is likely to happen when there is a misalignment between the “cultural goals” of a society (such as monetary wealth) and the opportunities people have to obtain them.
What is the most common adaptation in Robert Merton's strain theory of deviance?
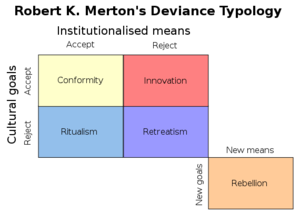
The conformist is the most common mode of adaptation. Such individuals accept both the goals as well as the prescribed means for achieving the goal. Conformists will accept, though not always achieve, the goals of society and the means approved for achieving them.
What are some criticisms of strain theory?
Strain theory has received several criticisms, such as: Strain theory best applies only to the lower class as they struggle with limited resources to obtain their goals. Strain theory fails to explain white collar crime, the perpetrator of whom have many opportunities to achieve through legal and legitimate means.
What would a strain theorist say is the main cause of crime?
Strain theories state that certain strains or stressors increase the likelihood of crime. These strains lead to negative emotions, such as frustration and anger. These emotions create pressure for corrective action, and crime is one possible response.
What was Robert K. Merton's theory of crime?
Social strain theory was developed by famed American sociologist Robert K. Merton. The theory states that social structures may pressure citizens to commit crimes. Strain may be structural, which refers to the processes at the societal level that filter down and affect how the individual perceives his or her needs.
What is Robert Agnew's general strain theory?
Agnew's general strain theory now acknowledges that events which are perceived to be especially negative by those who experience them are positively correlated with a greater likelihood of criminal behavior (Agnew & Froggio, 2007). Strain theory has been used to explain a variety of criminal phenomenon.
What is Robert K. Merton known for?
Robert King Merton (born Meyer Robert Schkolnick; July 4, 1910 – February 23, 2003) was an American sociologist who is considered a founding father of modern sociology, and a major contributor to the subfield of criminology. He served as the 47th President of the American Sociological Association.
Which of the following did Robert Merton advocate to cope with the problem of the inability to determine the question of functionality?
What did Merton advocate to cope with the problem of the inability to determine the question of functionality? Division of points of the system on the basis of need to fulfill identical functions (needs) over and over.
Which of the following was one of the major reasons for the widespread acceptance of strain theory?
A major reason for the widespread acceptance of strain theory was that its central thesis of blocked opportunity resonated with Americans' growing concern over equal opportunity, and with the fear that social injustice had deep cultural roots.
Which of the following is a criticism of social disorganization theory?
Which of the following are common criticisms of social disorganization theory? It fails to account for troubled neighborhoods that have strong, viable organizations.
What did Merton conclude about the American Dream?
Merton (1938) concluded that Americans were socialised into believing in the American Dream; that a consensus existed about what people's social goals should be: success and material wealth. However, equal access to those goals did not exist: there was a strain between the socially-encouraged goals of society and the socially-acceptable means ...
What is the anomie theory?
While Durkheim's concept of anomie was rather vague, Merton explains the idea in quite a detailed way: as the product of a strain between socially-accepted goals and the socially-accepted means to achieve them. While Merton's theory was based on 20 th century America, it is transferable to any contemporary, western, developed capitalist society.
Why did people believe that to achieve the American dream they had to work hard and they would succeed?
People were socialised into believing that to achieve the American Dream they had to work hard and they would succeed because the society was a meritocracy. Individuals made various adaptations in response to this strain, some of which were likely to lead to crime.
Does Merton believe in social goals?
Merton does not consider the source of social goals, nor in whose interests society is socialised into believing. Marxists would argue that the former is bourgeois ideology; that the latter is in the interests of capitalism.
Do people conform to Merton's theory?
As previously mentioned, most people conform most of the time, but those who don't often socialise together (e.g. gangs). Merton does not address this, but it is taken up by functionalist subcultural theorists who have developed Merton's theory.
What is the relationship between Durkheim and Merton?
The Relationship between Merton and Durkheim. Durkheim’s writings reflect on the social conditions of France. Merton on the social and economic conditions of America. Durkheim developed the theory of anomie, a state where there is an absence of norms regulating human behaviour. Arguing deviance and crime arose from this state.
What was the worst economic disaster America had ever seen?
The worst economic disaster America had ever seen. This situation would provide the contexts for work and crime which Merton would theorise on in his work ‘ Social Structure and Anomie ‘ in 1938. Brought on by Black Friday, on October 24th, 1929, when the stock market crashed.
What was the role of Merton in sociology?
Merton was key to sociology and his role shouldn’t be primarily reduced to Strain Theory. He also coined the terms ‘role model’ and ‘self-fulfilling prophecy’ when he wrote on the concept of serendipity.
What is the strain theory?
The Theory. Merton’s Strain Theory quickly became one of the more popular Crime and Deviance positions. Merton’s Strain theory argued deviation from social norms is a result of the strain a person feels when they’re unable to achieve legitimately (legally). People only engage in deviant behaviour because they are unable to achieve social goals ...
How to see Merton's strain theory?
The best way to see Merton’s Strain Theory in practice is to examine The American Dream. The American dream presupposes that through hard work an individual can experience upwards social mobility for themselves, and their offspring. This can happen regardless of age, sex, ethnicity, or any other factor. As long as you work hard, money and success should come your way. It doesn’t factor in structural elements which may prevent this dream from becoming a reality e.g. discriminatory employment practices, or unequal access to opportunities. Structural factors to one side there are still individual and cultural factors at play that may prevent an individual from attaining The American Dream.
Why does Merton's strain theory lead to crime?
Highlights that society is still inherently unequal, and that some people do have it easier to progress than others . Cons.
Why do people engage in deviant behaviour?
People only engage in deviant behaviour because they are unable to achieve social goals and standards through legitimate (legal) means. A strain an individual may experience may be, lack of education, lack of experience, lack of contacts, lack of funds. These strains push individuals towards Crime and Deviance.
What is the term for an imbalance between cultural goals and institutionalised means?
Merton developed the concept of ‘anomie’ to describe this imbalance between cultural goals and institutionalised means. He argued that such an imbalanced society produces anomie – there is a strain or tension between the goals and means which produce unsatisfied aspirations. Merton argued that when individuals are faced with a gap between their ...
What is Merton's theory?
Merton developed his theory from a well-established observation from official statistics – that a higher proportion of acquisitive crime is committed by those from unskilled manual backgrounds (or ‘lower social classes’).
Why was Merton's strain theory important?
Merton’s strain theory is an important contribution to the study of crime and deviance – in the 1940s it helped to explain why crime continued to exist in countries , such as America, which were experiencing increasing economic growth and wealth.
What is the strain theory of deviance?
Argues that crime is a result of people being socialised into expecting success but not achieving this success due to limited opportunities. Strain Theory argues that crime occurs when there aren’t enough legitimate opportunities for people to achieve the normal success goals of a society.
What did Merton argue about the dream?
HOWEVER, Merton argued that for those from lower social classes, this ‘dream’ had become an ideology, masking the fact that the legitimate opportunities are not available to all, and worse, those who failed to achieve success via legitimate means were condemned for their apparent lack of effort.
What did Merton argue about the illegitimate crime?
In short, Merton argued that America was a highly unequal and divided society which promoted goals that only some of its population could realistically hope to achieve.
What was the American dream?
The ‘American Dream’ encouraged individuals to pursue a goal of success which was largely measured in terms of the acquisition of wealth and material possessions. People were expected to pursue this goal through legitimate means such as education and work.
What is Strain Theory?
Strain theory was proposed by Robert Merton, an American sociologist who is also well-known for his works on the functionalist theory. It is an aspect of functionalism, which in itself is a constructivist theory. Strain theory attempts to explain conflict or deviance via the four functions of deviance.
The Strain Theory Overview
Merton offered four definitions in his works on strain theory, which can be summarized as follows:
Why is Strain Theory Important?
It gives an insight into the source of crime. Strain theory suggests that when people cannot achieve their goals, they feel strained—this strain leads them to commit crimes to reduce that strain.
The Weak Strain Theory
The weak form of strain theory suggests that people who are blocked from legitimate means to achieve goals will simply accept their situation and not commit crimes.
Strong Strain Theory
Robert K. Merton (1957) outlined a strong strain theory. The theory proposes that an individual will exhibit criminal behavior if they suffer from blocked opportunities and cannot achieve legitimate goals through legitimate means.
The Strain Theory Expansion
In a 1972 article, Merton expanded on strain theory. He stated that the deviant act is an adaptation to certain kinds of strain. Our society places a great emphasis on success as we are often told that we will be more satisfied if we are rich, successful, and powerful.
Take Away
The strain theory is a framework for understanding how people react to the challenges and pressures of everyday life. With this knowledge, you can better understand why your customers behave in certain ways—responding or not responding as expected.
What is the relationship between functionalist and strain theory?
The functionalist and strain theories both show some relationship between deviance and social structure. While the functionalist theory seeks to explain the functions of deviance and crime in society, the strain theory helps to deepen our understanding by connecting these ideas to the antagonistic relationship between cultural goals ...
What is the feminist theory of crime?
The feminist theory proposes to examine deviance and crime from the angle of gender, borrowing ideas from gender roles and differences to explain deviance and crime in society. This is one drawback of the strain and functionalist theories – the inability to explain the gender inequality. Today, deviance and crime has taken a new spin – ...
What is deviance function?
Functionalists believe deviance functions as a tool for society to define (or redefine) morality (Brym and Lie, 2007:195). Strain theory is closely entwined - of the adaptations, rebellion and innovation have the highest entrenchment in criminal activity, while ritualism and retreatism are more likely considered as social diversions ...
What is the motivation behind white collar crime?
Functionalist and strain theory assume people’s inherent goodness; people are driven by social factors to crime and deviance. However this is not always true. The control theory balances this by providing an opposing perspective.
What is the conflict theory?
The conflict theory originating from Marx, speaks of the struggle between the powerful (bourgeoisie) trying to remain lord of the powerless (referring to the working class; proletariat) who fight to have a better life.
What is the drawback of labeling theory?
However, the drawback of labeling theory is how it acts as a self-fulfilling prophecy. When judges and policemen operate, they are now primed to label certain stereotypes of individuals as deviants and criminals. This stigmatization has a direct and often unfair impact on the individuals labeled as deviant.
Is strain theory inadequate for street crimes?
However, if we examine the wide spectrum of deviant and criminal acts, strain theory account inadequately for crimes beyond the narrow scope of street crimes; crimes considered as white-collar crimes are more rampant among the middle and upper-classes who suffice materially.

Contexts
The Theory
The American Dream
A Culture of Winning
The Relationship Between Merton and Durkheim
How Does Strain Affect people?
Evaluation of Strain Theory
Other Social Theorists
- Since Merton created Strain Theory, other theorists have developed on the theory. Robert Agnew developed General Strain Theory believing Merton’s theory was too vague. It argues individuals may commit crime due to emotion and not financial gain. Violence in these circumstances may be a way to cope. Robert Agnew argued that strain theory could still...
Conclusion
References
Strain Theory: The Basics
Five Adaptations to Strain
Explaining The Higher Rates of Offending Among Lower Social Classes
Criticisms of Strain Theory
- Firstly, not all working class individuals turn to crime, and so we need something else to explain why some of them do and some of them do not. Subcultural theorists argued that the role of workin...
- Secondly, Merton’s reliance on official statistics means he over-estimates the extent of working class crime and underestimates the extent of middle class, or white collar crime.
- Firstly, not all working class individuals turn to crime, and so we need something else to explain why some of them do and some of them do not. Subcultural theorists argued that the role of workin...
- Secondly, Merton’s reliance on official statistics means he over-estimates the extent of working class crime and underestimates the extent of middle class, or white collar crime.
- Thirdly, Strain theory only really explains economic crime, it doesn’t really explain violent crime.
- Marxists point out that lack of equality of opportunity is at the heart of the Capitalist system. (Elites make the system work for them, which disadvantages the lower classes).
The Continuing Relevance of Strain Theory
Sources
Crime and Deviance Revision Bundle For Sale