Element Properties
| atomic number | 8 |
| atomic weight | 15.9994 |
| melting point | −218.4 °C (−361.1 °F) |
| boiling point | −183.0 °C (−297.4 °F) |
| density (1 atm, 0 °C) | 1.429 g/litre |
Full Answer
What are the functions of urea?
What Are the Functions of Urea?
- History. Urea was first discovered in 1773 by Hillaire Rouelle of France. ...
- Function. Urea is used most popularly as a fertilizer due to its high levels of nitrogen. ...
- Features. Urea is not very combustible, so it can easily be stored. ...
- Uses. ...
- Production. ...
What are the different uses of urea?
Urea Uses - What Is Urea Used For?
- It is mainly used as a nitrogen release fertilizer to make the product water-soluble.
- Urea is used as a stabilizer in most of the nitrocellulose explosive products.
- It is used in manufacturing high explosive materials like urea nitrate (CH5N3O4)
- It is used as an important reagent in lanthanide chemistry.
What is urea and how is it produced?
Urea [CO(NH 2)2] is a soluble organic compound containing 46% nitrogen. It occurs naturally in urine and some moulds and fungi. Urea is manufactured synthetically by reacting natural gas, atmospheric nitrogen and water together at high temperature and pressure to produce ammonia and carbon dioxide. These gases
What is a substitute for urea?
- Urea: 9.3 grams/L (In contrast, DEF requires 32.5% urea)
- Chloride: 1.87 grams/L
- Sodium: 1.17 grams/L
- Potassium: 0.750 grams/L
- Creatinine: 0.670 grams/L
- Other dissolved ions, inorganic and organic compounds

What is urea explain?
Urea, also known as carbamide, is a safe, useful compound with a significant history. It is a naturally occurring molecule that is produced by protein metabolism and found abundantly in mammalian urine.
Why is urea found in urine?
Your body creates ammonia when it breaks down protein from foods. Ammonia contains nitrogen, which mixes with other elements in your body, including carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen, to form urea. Urea is a waste product that is excreted by the kidneys when you urinate.
What is urea in human body in English?
Urea: A nitrogen-containing substance normally cleared from the blood by the kidney into the urine. Diseases that compromise the function of the kidney often lead to increased blood levels of urea, as measured by the blood urea nitrogen (BUN) test. Urea is of major historical significance.
What is the function of urea in the human body?
Urea is the major constituent of the urine and the principal means for disposal of nitrogen derived from amino acid metabolism. Specialized phloretin-inhibitable urea transporters are expressed in kidney medulla and play a central role in urea excretion and water balance.
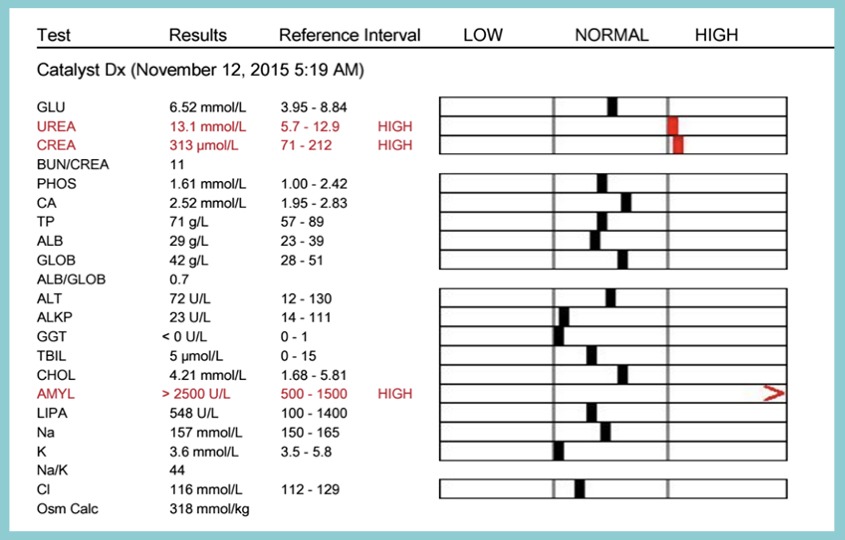
What is normal urea level?
In general, around 6 to 24 mg/dL (2.1 to 8.5 mmol/L ) is considered normal. But normal ranges may vary, depending on the reference range used by the lab and your age.
What happens if urea is high?
Uremia can lead to kidney failure when left untreated. Someone with uremia may have seizures, loss of consciousness, heart attacks, and other life-threatening symptoms. Some will need a kidney transplant. Kidney failure may also damage other organs, so untreated uremia can result in liver or heart failure.
How can we remove urea from urine?
3:2715:09Extracting urea from my own pee - YouTubeYouTubeStart of suggested clipEnd of suggested clipProcess it to do this I transfer it all to a beaker. And start adding concentrated nitric acid thisMoreProcess it to do this I transfer it all to a beaker. And start adding concentrated nitric acid this reaction produces a lot of heat. And it can easily get out of control.
Why is blood urea low?
Abnormally low levels of BUN can be a sign of malnutrition, lack of protein in the diet, and liver disease. Therefore, other tests included in a panel test like the comprehensive metabolic panel may provide helpful information for understanding the significance of low blood urea nitrogen.
What is normal range of urea and creatinine?
We defined the normal range as range within the single SD-line of the remainder. The estimated normal range of BUN was 14-23 mg/dl both in male and female elderly subjects, and that of Cr was 0.9-1.3 mg/dl in male and was 0.7-1.1 mg/dl in female.
Is urea good for health?
Urea is used to treat dry/rough skin conditions (such as eczema, psoriasis, corns, callus) and some nail problems (such as ingrown nails). It may also be used to help remove dead tissue in some wounds to help wound healing. Urea is known as a keratolytic.
Which food reduce blood urea?
Alkaline vegetables including Chinese cabbage, carrot and potato help to alkalize urine and reduce the effects of high blood urea levels. Several other foods are known to reduce urea and creatinine levels such as cucumber, lemon, red bell pepper, cinnamon and turmeric.
What is urea?
Urea is the chief nitrogenous end product of the metabolic breakdown of proteins in all mammals and some fishes. It occurs not only in the urine of...
What is the chemical name of urea?
The chemical name of urea is carbamide, the diamide of carbonic acid. Its formula is H2NCONH2.
Who first synthesized urea?
German chemist Friedrich Wöhler first synthesized urea from ammonium cyanate in 1828. It was the first generally accepted laboratory synthesis of a...
What is urea used for?
Urea is used as a fertilizer and feed supplement, as well as a starting material for the manufacture of plastics and drugs.
Overview
Urea, also known as carbamide, is an organic compound with chemical formula CO(NH2)2. This amide has two –NH2 groups joined by a carbonyl (C=O) functional group.
Urea serves an important role in the metabolism of nitrogen-containing compounds by animals and is the main nitrogen-containing substance in the urine of mammals. It is a colorless, odorless solid, highly soluble in water, and practically non-toxic (LD50 is 15 g/kg for rats). Dissolved in water, it i…
Uses
More than 90% of world industrial production of urea is destined for use as a nitrogen-release fertilizer. Urea has the highest nitrogen content of all solid nitrogenous fertilizers in common use. Therefore, it has a low transportation cost per unit of nitrogen nutrient. The most common impurity of synthetic urea is biuret, which impairs plant growth. Urea breaks down in the soil to give ammo…
Adverse effects
Urea can be irritating to skin, eyes, and the respiratory tract. Repeated or prolonged contact with urea in fertilizer form on the skin may cause dermatitis.
High concentrations in the blood can be damaging. Ingestion of low concentrations of urea, such as are found in typical human urine, are not dangerous with additional water ingestion within a reasonable time-frame. Many animals (e.g. dogs) have a much more concentrated urine and it c…
Physiology
Amino acids from ingested food that are used for the synthesis of proteins and other biological substances — or produced from catabolism of muscle protein — are oxidized by the body as an alternative source of energy, yielding urea and carbon dioxide. The oxidation pathway starts with the removal of the amino group by a transaminase; the amino group is then fed into the urea cycle. The first step in the conversion of amino acids from protein into metabolic waste in the liver is re…
Analysis
Urea is readily quantified by a number of different methods, such as the diacetyl monoxime colorimetric method, and the Berthelot reaction (after initial conversion of urea to ammonia via urease). These methods are amenable to high throughput instrumentation, such as automated flow injection analyzers and 96-well micro-plate spectrophotometers.
Related compounds
Ureas describes a class of chemical compounds that share the same functional group, a carbonyl group attached to two organic amine residues: RR'N–C(O)–NRR'. Examples include carbamide peroxide, allantoin, and hydantoin. Ureas are closely related to biurets and related in structure to amides, carbamates, carbodiimides, and thiocarbamides.
History
Urea was first discovered in urine in 1727 by the Dutch scientist Herman Boerhaave, although this discovery is often attributed to the French chemist Hilaire Rouelle as well as William Cruickshank.
Boerhaave used the following steps to isolate urea:
1. Boiled off water, resulting in a substance similar to fresh cream
2. Used filter paper to squeeze out remaining liquid
Production
Urea is produced on an industrial scale: In 2012, worldwide production capacity was approximately 184 million tonnes.
For use in industry, urea is produced from synthetic ammonia and carbon dioxide. As large quantities of carbon dioxide are produced during the ammonia manufacturing process as a byproduct from hydrocarbons (predominantly natu…