Full Answer
Which statement best describes an electron?
The statement, which describe an electron is this: IT HAS A NEGATIVE CHARGE AND IT IS LOCATED IN ORBITALS AROUND THE NUCLEUS. Each atom is made up of three sub particles, which are electron, proton and neutron.
Is electron considered as matter?
Matter is made of atoms and electrons are part of atoms, thus the answer is yes. Originally Answered: is an electron matter? Most definitely YES. Just like everything else that we touch, feel and see around us, even down to photons of light. Originally Answered: is an electron matter?
What is the job of an electron?
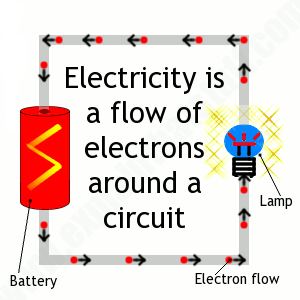
Electrons play an essential role in numerous physical phenomena, such as electricity, magnetism, chemistry and thermal conductivity, and they also participate in gravitational, electromagnetic and weak interactions.
Does an electron determine what element it is?
Electron configurations provide insight into the chemical behaviour of elements by helping determine the valence electrons of an atom. It also helps classify elements into different blocks (such as the s-block elements, the p-block elements, the d-block elements, and the f-block elements).
See more

What is the definition of electrons in science?
An electron is a negatively charged subatomic particle that can be either bound to an atom or free (not bound). An electron that is bound to an atom is one of the three primary types of particles within the atom -- the other two are protons and neutrons. Together, electrons, protons and neutrons form an atom's nucleus.
What is meant by electron with example?
Electrons are the smallest of the particles that make up an atom, and they carry a negative charge. The number of protons and electrons is equal in a neutral atom. The hydrogen atom, for example, has just one electron and one proton. The uranium atom, on the other hand, has 92 protons, and therefore, 92 electrons.
What is the meaning of one electron?
an elementary particle that is a fundamental constituent of matter, having a negative charge of 1.602 × 10−19 coulombs, a mass of 9.108 × 10−31 kilograms, and spin of ½, and existing independently or as the component outside the nucleus of an atom.
What are the example of electron?
The definition of an electron is the lightest basic electrically-charged particle. An example of an electron is what orbits the nucleus of an atom.
What are electrons made of?
The Atom Builder Guide to Elementary Particles Atoms are constructed of two types of elementary particles: electrons and quarks. Electrons occupy a space that surrounds an atom's nucleus. Each electron has an electrical charge of -1. Quarks make up protons and neutrons, which, in turn, make up an atom's nucleus.
Where do electrons come from?
Electrons can be created through beta decay of radioactive isotopes and in high-energy collisions, for instance when cosmic rays enter the atmosphere. The antiparticle of the electron is called the positron; it is identical to the electron except that it carries electrical charge of the opposite sign.
What are electrons and protons?
Electrons are a type of subatomic particle with a negative charge. Protons are a type of subatomic particle with a positive charge. Protons are bound together in an atom's nucleus as a result of the strong nuclear force. Neutrons are a type of subatomic particle with no charge (they are neutral).
How many electrons exist?
The current estimate is that there are 100000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000 (that's 1 followed by 80 zeros!)
Do electrons have size?
Mass of electron is 9x10^-31. But it has no size . Because, in the vision of quantum mechanics, electron is considered as a point particle with no volume and its size is also unclear.
Where are the electrons?
outer shellThe protons and neutrons are found in the middle of the atom in the nucleus. Meanwhile, the electrons are found on the outer shell of the atom.
Is electrons negative or positive?
negative chargeProtons and Electrons A proton carries a positive charge (+) and an electron carries a negative charge (-), so the atoms of elements are neutral, all the positive charges canceling out all the negative charges.
What is the electron symbol?
e-Fundamental Subatomic ParticlesParticleSymbolChargeelectrone--1protonp++1neutronno0
What is an electron for class 9th?
Electrons are subatomic particles that hold an elementary charge of magnitude -1. The charge of an electron is equal in magnitude to the charge held by a proton (but has an opposite sign). Therefore, electrically neutral atoms/molecules must have an equal number of electrons and protons.
What is proton with example?
The definition of a proton is a particle with a positive charge that is in the nucleus of an atom. An example of a proton is the single proton in the nucleus of a hydrogen atom.
What is protons and electrons?
Summary. Electrons are a type of subatomic particle with a negative charge. Protons are a type of subatomic particle with a positive charge. Protons are bound together in an atom's nucleus as a result of the strong nuclear force. Neutrons are a type of subatomic particle with no charge (they are neutral).
What is the electron symbol?
e-Fundamental Subatomic ParticlesParticleSymbolChargeelectrone--1protonp++1neutronno0
Are electrons positive or negative?
Because a proton has a positive charge (+) and an electron has a negative charge (-), element atoms are neutral, with all positive charges cancelli...
Who named Electron?
G. Johnstone Stoney invented the term “electron” in 1891 to describe the unit of charge discovered in tests that conveyed electric current through...
Do protons and electrons have the same mass?
Electrons are a sort of negative-charged subatomic particle. Protons and neutrons have about the same mass as electrons, yet they are both signific...
Are protons and electrons equal?
Protons and electrons are in equal proportions in an atom. Because protons and electrons have equal and opposing charges, atoms are generally neutral.
Why do electrons repel each other?
A free electron will flow in the opposite direction of the force lines since it has the opposite charge qualities as a positive charge. As a result...
What are Electrons?
Electrons are subatomic particles that hold an elementary charge of magnitude -1. The charge of an electron is equal in magnitude to the charge held by a proton (but has an opposite sign). Therefore, electrically neutral atoms/molecules must have an equal number of electrons and protons. Although the magnitude of the charges held by protons and electrons are the same, the size and mass of an electron are much smaller than that of a proton (the mass of an electron is roughly 1/1836 the mass of a proton).
Who invented the term "electron"?
G. Johnstone Stoney invented the term “electron” in 1891 to describe the unit of charge discovered in tests that conveyed electric current through chemicals. J.J. Thomson’s Cambridge classmate Joseph Larmor used the phrase in this context.
Why are protons and electrons in equal proportions?
Protons and electrons are in equal proportions in an atom. Because protons and electrons have equal and opposing charges, atoms are generally neutral.
Why are element atoms neutral?
Because a proton has a positive charge (+) and an electron has a negative charge (-), element atoms are neutral, with all positive charges cancelling out all negative charges. The number of protons, neutrons, and electrons in an atom varies from one to the next.
What is the nucleus of an atom?
The nucleus contains the protons and the neutrons. Considering the solar system, it has been observed that the sun is at its centre, and the planets revolve around it. Similarly, in an atom, the nucleus is at the centre, and the electrons revolve around the nucleus. Electron structure.
Which subatomic particle has the same mass as an electron?
Electrons are a sort of negative-charged subatomic particle. Protons and neutrons have about the same mass as electrons, yet they are both significantly more massive (approximately 2,000 times as massive as an electron). A proton’s positive charge is the same magnitude as an electron’s negative charge.
Why is the mass of an electron negligible?
This is because matter behaves differently at the quantum scale. For example, the uncertainty associated ...
What is the mass of an electron?
: an elementary particle consisting of a charge of negative electricity equal to about 1.602 × 10−19 coulomb and having a mass when at rest of about 9.109 × 10−31 kilogram or about ¹/₁₈₃₆ that of a proton.
How many electron volts does a neutrinos have in 2021?
— Anna Blaustein, Scientific American, 28 June 2021 For instance, the neutrinos investigated by the MINOS experiment average about six billion electron volts of energy.
What is the structure of electrons in an atom called?
The detailed structural arrangement of electrons within an atom is referred to as the electronic configuration of the atom.
What is the mass of an electron?
The rest mass of the electron is 9.1093837015 × 10 −31 kg, which is only 1/1,836 the mass of a proton. An electron is therefore considered nearly massless in comparison with a proton or a neutron, and the electron mass is not included in calculating the mass number of an atom.
How do electrons move around an atom?
Within any given atom, electrons move about the nucleus in an orderly arrangement of orbitals, the attraction between electrons and nucleus overcoming repulsion among the electrons that would otherwise cause them to fly apart. These orbitals are organized in concentric shells proceeding outward from the nucleus with an increasing number of subshells. The electrons in orbitals closest to the nucleus are held most tightly; those in the outermost orbitals are shielded by intervening electrons and are the most loosely held by the nucleus. As the electrons move about within this structure, they form a diffuse cloud of negative charge that occupies nearly the entire volume of the atom. The detailed structural arrangement of electrons within an atom is referred to as the electronic configuration of the atom. The electronic configuration determines not only the size of an individual atom but also the chemical nature of the atom. The classification of elements within groups of similar elements in the periodic table, for example, is based on the similarity in their electron structures.
How are electrons held in orbitals?
These orbitals are organized in concentric shells proceeding outward from the nucleus with an increasing number of subshells. The electrons in orbitals closest to the nucleus are held most tightly; those in the outermost orbitals are shielded by intervening electrons and are the most loosely held by the nucleus.
How are electrons bound to the nucleus?
Under ordinary conditions electrons are bound to the positively charged nuclei of atoms by the attraction between opposite electric charges. In a neutral atom the number of electrons is identical to the number of positive charges on the nucleus.
When were electrons discovered?
The electron was discovered in 1897 by the English physicist J.J. Thomson during investigations of cathode rays. His discovery of electrons, which he initially called corpuscles, played a pivotal role in revolutionizing knowledge of atomic structure. Under ordinary conditions electrons are bound to the positively charged nuclei of atoms by the attraction between opposite electric charges. In a neutral atom the number of electrons is identical to the number of positive charges on the nucleus. Any atom, however, may have more or fewer electrons than positive charges and thus be negatively or positively charged as a whole; these charged atoms are known as ions. Not all electrons are associated with atoms; some occur in a free state with ions in the form of matter known as plasma.
What is a lepton?
A lepton is a subatomic particle that reacts only by the electromagnetic, weak, and gravitational forces; it does not respond to the short-range strong force that acts between quarks and binds protons and neutrons in the atomic nucleus. Get a Britannica Premium subscription and gain access to exclusive content.
How do electrons help us observe?
In fact, we use electrons to observe atoms. This method of observation works by using a beam of accelerated electrons as a source of illumination – allowing us to observe objects a million times smaller than a human hair (~ 0.1 nm) which is just enough to “view” individual atoms.
When was the electron discovered?
So, if we can’t see the electron how did we discover it? The electron was discovered in 1879 by J. J. Thompson when he was investigating the bright glow observed on a phosphorescent screen when a high voltage is applied across two electrodes in a partially evacuated tube – a cathode ray tube.
What is the electron cloud?
Unlike the Bohr model the electrons don’t exist in precisely-defined orbits and instead all that is known about these point particles is their probable distribution around the atom – generally referred to as an electron cloud.
What is the energy of a spherical system?
In this model, which expands on the work of physicists David Bohm, Jacob Bekenstein, Stephen Hawking and Gerard ’t Hooft, the energy – or information – of any spherical system is proportional to the number of Planck Spherical Units (PSUs) or voxels within the spherical volume (volume entropy) and the number of voxels available on the spherical surface horizon (surface entropy). This holographic relationship between the interior and the exterior defines the mass-energy density of the system while the inverse defines the mass expressed by the system at any given moment – or as described by David Bohm, the unfolded and the enfolded, respectively.
How are discrete emission lines observed in Bohr's model?
So, when a spectral analysis of hydrogen was made – that is when the light emitted from a hydrogen gas passes through and is refracted by a prism – discrete emission lines are observed. In the Bohr model, these emission lines are explained by the transition of electrons between orbitals – so when light energy is absorbed by the electron it transitions to a higher energy level – this higher energy level is excited and is therefore not as stable so when it relaxes back to a stable state it emits a photon as it drops down to a lower energy level – and it is this emitted photon that is observed.
What is the smallest particle in the universe?
From all these experiments Thomson concluded that the electron was a particle that made up all matter and ended the idea that the atom was the smallest particle. Instead the atom was made up of these subatomic particles which he called corpuscles and are now referred to as the electron.
What is important to note when we make such a measurement of the energy?
What is important to note is that when we make such a measurement of the energy, we are in fact making a measurement of a single ion (i.e. an electron surrounding a central nucleus) – not a single electron.
Where did the term "electron" come from?
Term first suggested in 1891 by Irish physicist G. J. Stoney (1826–1911); electr (ic) + -on (from the names of charged particles, as ion, cation, anion) with perhaps accidental allusion to Greek ḗlektron amber (see electric)
What is the charge of an electron?
Also called negatron. Physics, Chemistry. an elementary particle that is a fundamental constituent of matter, having a negative charge of 1.602 × 10 −19 coulombs, a mass of 9.108 × 10 −31 kilograms, and spin of ½, and existing independently or as the component outside the nucleus of an atom.
What is the root of the word "electricity"?
The Greek name for amber , ηλεκτρον ( electron ), is the root from which our word electricity is derived.
What is the movement of large numbers of electrons through conductors?
The movement of large numbers of electrons through conductors constitutes an electric current.
What is the mass of a lepton?
a stable elementary particle present in all atoms, orbiting the nucleus in numbers equal to the atomic number of the element in the neutral atom; a lepton with a negative charge of 1.602 176 462 × 10 –19 coulomb, a rest mass of 9.109 381 88 × 10 –31 kilogram, a radius of 2.817 940 285 × 10 –15 metre, and a spin of 1/2.
What is the unit of charge equal to the charge on one electron?
Electricity. a unit of charge equal to the charge on one electron.
Where are electrons found?
electron. [ (i- lek-tron) ] An elementary particle with a negative charge and a very small mass. Electrons are normally found in orbits around the nucleus of an atom. The chemical reactions that an atom undergoes depend primarily on the electrons in the outermost orbits (the valence electrons ).
What is oxidation in chemistry?
Key Takeaways: Oxidation in Chemistry 1 Oxidation occurs when an atom, molecule, or ion loses one or more electrons in a chemical reaction. 2 When oxidation occurs, the oxidation state of the chemical species increases. 3 Oxidation doesn't necessarily involve oxygen! Originally, the term was used when oxygen caused electron loss in a reaction. The modern definition is more general.
Why is ethanol oxidized?
For example, according to this definition, when ethanol is oxidized into ethanal: CH 3 CH 2 OH → CH 3 CHO. Ethanol is considered oxidized because it loses hydrogen. Reversing the equation, ethanal can be reduced by adding hydrogen to it to form ethanol.
What is the opposite of oxidation?
Oxidation occurs when the oxidation state of a molecule, atom or ion is increased. The opposite process is called reduction, which occurs when there is a gain of electrons or the oxidation state of an atom, molecule, or ion decreases. An example of a reaction is that between hydrogen and fluorine gas to form hydrofluoric acid :
What type of chemical reaction is oxidation and reduction?
A type of chemical reaction in which oxidation and reduction occurs is called a redox reaction, which stands for reduction-oxidation.
Does oxygen cause electron loss?
Oxidation doesn't necessarily involve oxygen! Originally, the term was used when oxygen caused electron loss in a reaction. The modern definition is more general.
Is oxygen oxidation or reduction?
This definition is the opposite of the oxygen definition, so it may cause confusion. Still, it's good to be aware. According to this definition, oxidation is the loss of hydrogen, while reduction is the gain of hydrogen.