The general price level is a hypothetical measure of overall prices for some set of goods and services (the consumer basket ), in an economy or monetary union during a given interval (generally one day), normalized relative to some base set.
What is general price level in economics?
General price level. An index that measures the change in price of goods in an economy over time and hence the purchasing power of the currency of the country. For instance, in the U.S. it is represented by the CPI (Consumer Price Index) maintained by the U.S. Department of Labor.
What is the advantage of general price level accounting?
This can provide a more accurate picture of a company's value. It is used to supplement a company's ordinary financial statements. It is less commonly called general price level accounting.
What is the definition of price in economics?
As in the case of the definition of price in the economy, demand for a security increases when its price drops. This forms the support line. When the price increases, a sell-off occurs, cutting off demand. This is where the resistance zone lies. In economics, price level refers to the buying power of money or inflation.
What is the importance of price level?
Price levels provide a snapshot of prices at a given time, making it possible to review changes in the broad price level over time. As prices rise (inflation) or fall (deflation), consumer demand for goods is also affected. This leads to broad production measures such as gross domestic product (GDP) higher or lower.
What happens when the general price level?
When the general price level rises, (i.e., when there is inflation in the economy), the value of money, i.e., the purchasing power of each rupee falls. This simply means that more money is now required to buy a fixed basket of goods and services.
What determines the general price level?
The most common price level index is the consumer price index (CPI). The price level is analyzed through a basket of goods approach, in which a collection of consumer-based goods and services is examined in aggregate. Changes in the aggregate price over time push the index measuring the basket of goods higher.
What does general price level means?
The general price level is a hypothetical measure of overall prices for some set of goods and services (the consumer basket), in an economy or monetary union during a given interval (generally one day), normalized relative to some base set.
What is an example of price level?
We can think of this price level for a basket of goods as a general price index that is comprised of various goods and services in the country. For example, the consumer price index (CPI) in the United States is a representative price level for a basket of goods.
Is a rise in the general level of prices?
Inflation is defined as a rise in the general price level. In other words, prices of many goods and services such as housing, apparel, food, transportation, and fuel must be increasing in order for inflation to occur in the overall economy.
How many types of price levels are there?
The three major price level indicators that economists and policymakers often refer to are, the Consumer Price Index (CPI), GDP deflator, and the Producer Price Index (PPI). These indicators are used by central banks to monitor inflation levels in their respective economies.
Why general price level is studied in macroeconomics?
It studies the aggregate variables. General Price level is the sum aggregate of prices of all the goods and services produced within an economy. Any increase or decrease in the general price level signifies the corresponding change in the prices of all the goods.
Is general price level under microeconomics?
General price level is related to the prices of most of the commodity in a nation at a certain period of time. Therefore, it is not a micro variable.
What is general price index in accounting?
What are Price Indices? A price index (PI) is a measure of how prices change over a period of time, or in other words, it is a way to measure inflation. There are multiple methods on how to calculate inflation (or deflation).
What determines the level of prices in a market quizlet?
What determines the level of prices in a market? For the purposes of this course, the answer is demand and supply.
Is general price level under microeconomics?
General price level is related to the prices of most of the commodity in a nation at a certain period of time. Therefore, it is not a micro variable.
Is general price level micro or macro?
General price level is studied in Macroeconomics.
Why general price level is studied in macroeconomics?
It studies the aggregate variables. General Price level is the sum aggregate of prices of all the goods and services produced within an economy. Any increase or decrease in the general price level signifies the corresponding change in the prices of all the goods.
What does alteration in the general price level mean?
An alteration in the general price level accordingly means a change in the relation between goods on the one hand and money on the other. On the origin and evolution of the word 'inflation.'. A rapid increase in the procurement prices obviously will be translated into higher food prices and thus increase the general price level.
What will happen if procurement prices increase?
A rapid increase in the procurement prices obviously will be translated into higher food prices and thus increase the general price level.
What is the CPI?
For instance, in the U.S. it is represented by the CPI ( Consumer Price Index) maintained by the U.S. Department of Labor.
What was the CPI in the second quarter of 2016?
In the second quarter of 2016 the general price level(measured by the Consumer Price Index - CPI) contracted at about the same rate (2%) as in the first quarter.
What Does Price Level Mean?
What is the definition of price level? The price level has a significant impact on the purchase of goods and services but also on the purchasing power of money. For instance, if P is the amount of money required to buy a specified quantity of goods and services, then one dollar can buy 1/P.
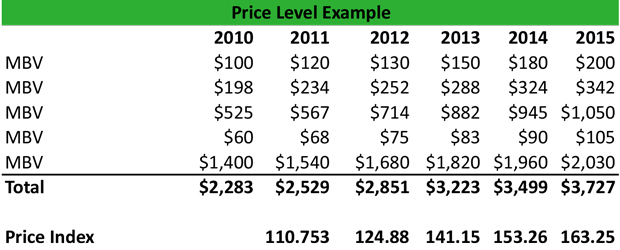
Example
Alex is an economist at the IMF, and he prepares a basket of goods from 2010 to 2015, consisting of five basic items, with the following prices and quantities for the relevant years:
Summary Definition
Define Price Level: Price level means the average cost of all goods on the market or in a category or the economy.
What is the price level of an economy?
An economy’s price level is the weighted average price of goods and services produced in an economy.
How does the price level increase?
The price level also increases when the money supply is increased and too much money is chasing too few goods and services. This is expressed in the equation M x V = P x Y, where M is the money supply, V is the velocity of money, P equals the price level, and Y is the output. Assuming V and Y are held constant, any increase in the money supply must increase the price level. In this case, more money is being used to buy a certain fixed number of goods. The price level would remain constant when the economy is growing and the money supply increase matches the increase in output.
What is cost push inflation?
Cost-push inflation increases the price level following a decrease in the economy’s short-run aggregate supply. Normally this is caused by a supply shock which reverberates throughout the economy. An increase in the price of a commonly used commodity can trigger a supply shock.
How does aggregate supply and demand work?
Economists use the aggregate supply and demand model to show anticipated movements in an economy’s price level. The aggregate supply is the total goods and services that producers are willing to supply (produce) at a given price level. The aggregate demand is the total goods and services that consumers are willing to purchase at a given price level. Like the microeconomic supply and demand model, the resulting price level and output (real gross domestic product) is determined by their intersection. On the graph below, the short-run equilibrium is met where the aggregate demand (AD) and short-run aggregate supply (SRAS) intersect. PL is the resulting price level and RGDP is the economy’s equilibrium real gross domestic product.
General price level accounting
Restating conventional financial statements (which are stated in nominal currency) in units of general purchasing power to adjust for inflation .
Inflation Accounting
A method of accounting that includes inflation. In inflation accounting, one records price changes that affect the purchasing power of current assets and the value of the company's long-term assets and liabilities. This can provide a more accurate picture of a company's value. It is used to supplement a company's ordinary financial statements.