What is the other name of thymosin?
Thymosin (also known as thymus peptide, thymus hormone, thymosin).Thymosin is a protein secreted by the thymus. It is a group of peptides and protein hormones.
What is the function of thymosin beta 4?
Thymosin is a 5-Da polypeptide hormone secreted by the thymus gland. Thymosin α1 stimulates the development of precursor T cells in the thymus to mature T cells. Of the thymosin peptide family, thymosin β4, is the most abundant member and is also expressed in many cell types.
What does thymus mean in medical terms?
Any of a group of small proteins, originally isolated from the thymus, that are involved in a variety of functions including angiogenesis, cell migration, regulation of actin polymerization, and the immune response. The American Heritage® Medical Dictionary Copyright © 2007, 2004 by Houghton Mifflin Company.
What is Thymosin Fraction 5?
The supposition that the role of the thymus might involve a hormone -like mechanism led to the isolation from thymus tissue of a biologically active preparation. Known as "Thymosin Fraction 5", this was able to restore some aspects of immune function in animals lacking thymus gland.

What is the function of thymosin?
Thymosin is a hormone secreted from the thymus. Its primary function is to stimulate the production of T cells, which are an important part of the immune system. Thymosin also assists in the development of B cells to plasma cells to produce antibodies.
What is the other name of thymosin?
Thymosins are a group of small peptides with molecular weights of 1000–15,000Da, originally isolated from the thymus gland (Goldstein, 2007; Goldstein et al., 2005), although it is now known that the major thymosins [thymosin-α1, thymosin-β4 (Tβ4), thymosin-β10, thymosin-β15] are present in a variety of mammalian ...
Is thymosin a hormone?
Thymosin is a 5-Da polypeptide hormone secreted by the thymus gland. Thymosin α1 stimulates the development of precursor T cells in the thymus to mature T cells.
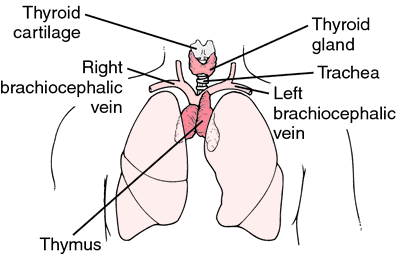
Where is thymosin located?
The thymus gland, located behind your sternum and between your lungs, is only active until puberty. After puberty, the thymus starts to slowly shrink and become replaced by fat. Thymosin is the hormone of the thymus, and it stimulates the development of disease-fighting T cells.
What type of hormone is thymosin?
polypeptide hormoneThymosin is a 5-Da polypeptide hormone secreted by the thymus gland. Thymosin α1 stimulates the development of precursor T cells in the thymus to mature T cells.
Which gland produces thymosin?
Your thymus produces and releases several hormones including: Thymopoietin: fuels the production of T-cells and tells the pituitary gland to release hormones. Thymosin and thymulin: help make specialized types of T-cells. Thymic humoral factor: keeps your immune system working properly.
Who discovered thymosin?
Professor Allan GoldsteinFour decades ago, Professor Allan Goldstein discovered the thymosins, a family of hormone-like molecules that have powerful effects on the human immune system. In a laboratory at the Albert Einstein College of Medicine of Yeshiva University in New York, Dr.
What is the target organ for thymosin?
Major Hormones: Origin, Target, FunctionHORMONEGLAND ORIGINTARGET TISSUEThyroid hormoneThyroid glandThroughout bodyParathyroid hormoneParathyroid glandsBones, intestines, and kidneysThymosinThymusWhite blood cellsAldosteroneAdrenal glandKidneys20 more rows
Discovery
The discovery of thymosins in the mid 1960s emerged from investigations of the role of the thymus in development of the vertebrate immune system. Begun by Allan L.
Function and application
Thymosin produces GM-CSF (white blood cell stimulating factor) by stimulating keratinocytes in the epidermis.
