
Pramlintide is a synthetic form of amylin
Amylin
Amylin, or islet amyloid polypeptide, is a 37-residue peptide hormone. It is cosecreted with insulin from the pancreatic β-cells in the ratio of approximately 100:1. Amylin plays a role in glycemic regulation by slowing gastric emptying and promoting satiety, thereby preventing post-p…
How does pramlintide reduce postprandial glucose levels?
Clinical evaluations of pramlintide have shown reductions in postprandial glucose concentrations through at least three distinct mechanisms of action, including slowing of gastric emptying, prevention of the postprandial rise in plasma glucagon, and increased satiety, leading to decreased caloric intake and potential weight loss. 12 – 17
What is pramlintide?
Pramlintide is a man-made form of a hormone that occurs naturally in the body. Pramlintide lowers blood sugar in three ways. It slows the rate that food moves from your stomach to your intestines, which keeps your blood sugar from rising too fast.
What is the mechanism of action of the Amylin analog of pramlintide?
Pramlintide is an Amylin Analog. The mechanism of action of pramlintide is as an Amylin Agonist.
Does pramlintide cause liver damage?
Pramlintide is a recombinant DNA produced polypeptide analogue of human amylin that is used in combination with insulin in the therapy of diabetes. Pramlintide has not been associated with serum enzyme elevations during therapy or with instances of clinically apparent liver injury.
How does pramlintide lower blood sugar?
By slowing digestion, limiting food intake, and keeping the body from raising blood glucose levels on its own during the period immediately following meals, Symlin minimizes the blood glucose rise that occurs after meals in most people with diabetes.
Is pramlintide a GLP-1 agonist?
Both have translated into hormone-based therapies for diabetes in the forms of GLP-1 receptor (GLP-1R) agonists (e.g. exenatide) and the amylin agonist, pramlintide.
What is the drug pramlintide used for?
Pramlintide injection is used to treat high blood sugar in patients with type 1 and type 2 diabetes who are also using mealtime insulin and have failed to control blood sugar levels. This medicine is available only with your doctor's prescription.
Is pramlintide a GLP-1?
Pramlintide (Symlin) and exenatide (Byetta), injectable drugs that utilize the alternative hormones amylin and glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1), respectively, have been approved for the management of diabetes.
Which GLP-1 agonist is best for weight loss?
Evidence supports both GLP-1 agonists liraglutide and semaglutide as effective agents for weight loss in patients with obesity without diabetes, with semaglutide data providing a more significant weight loss in clinical trials.
How does amylin regulate blood glucose?
Amylin affects glucose control through several mechanisms, including slowed gastric emptying, regulation of postprandial glucagon, and reduction of food intake (table 1). Glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1) exhibits similar properties as amylin, with the exception of insulin secretory effects.
What class of drugs is pramlintide?
Pramlintide is in a class of medications called antihyperglycemics. It works by slowing the movement of food through the stomach. This prevents blood sugar from rising too high after a meal, and may decrease appetite and cause weight loss.
When do you administer pramlintide?
SYMLIN should be administered subcutaneously immediately prior to each major meal (≥250 kcal or containing ≥30 grams of carbohydrate). SYMLIN should be at room temperature before injecting to reduce potential injection site reactions.
What are the contraindications of pramlintide?
SYMLIN is contraindicated in patients with any of the following: serious hypersensitivity reaction to SYMLIN or to any of its product components. hypoglycemia unawareness. confirmed gastroparesis.
Is pramlintide an incretin?
Exenatide belongs to a class of drugs called incretin mimetics, so called because they imitate natural hormones called incretins. Pramlintide is a synthetic amylin analog, meaning it is chemically identical to a hormone produced by the pancreas called amylin.
What drugs are amylin analogs?
Amylin AnaloguesACTOS.Amaryl.Avandia.Bydureon.Byetta.Corticosteroids.Eylea.Forxiga.More items...
What is the mode of action of sitagliptin?
Sitagliptin increases insulin production and decreases hepatic glucose overproduction. Sitagliptin prolongs the action of GLP-1 and GIP. By enhancing active incretin levels, sitagliptin increases insulin production and lowers glucagon secretion from alpha cells, which decreases hepatic glucose overproduction.
Where do you inject pramlintide?
This medicine is given as a shot under the skin of your stomach or upper thigh. Inject pramlintide at a site that is more than 2 inches away from your insulin injection.
What is the brand name for pramlintide?
Pramlintide (trade name Symlin) is an injectable amylin analogue drug for diabetes (both type 1 and 2), developed by Amylin Pharmaceuticals (now a wholly owned subsidiary of AstraZeneca).
Does pramlintide cause weight gain?
Conclusions: Based on preliminary evidence, pramlintide facilitates modest weight loss in obese or overweight patients with and without diabetes.
Does pramlintide cause hypoglycemia?
Pramlintide does not cause hypoglycemia, but when used with insulin, it can cause insulin-induced hypoglycemia. Nausea and hypoglycemia are the most common side effects of pramlintide therapy. The nausea has been described as mild to moderate in studies and has typically dissipated after 4–8 weeks.
Before Taking This Medicine
You should not use this medicine if you are allergic to pramlintide or metacresol, or: 1. if you have a digestive condition called "delayed gastric...
How Should I Use Pramlintide?
Follow all directions on your prescription label. Your doctor may occasionally change your dose to make sure you get the best results. When you fir...
What Happens If I Miss A Dose?
Take the missed dose as soon as you remember, but only if you are getting ready to eat a meal. Skip the missed dose if it is almost time for your n...
What Happens If I Overdose?
Seek emergency medical attention or call the Poison Help line at 1-800-222-1222. Overdose may cause diarrhea, vomiting, dizziness, cold sweats, war...
What Should I Avoid While Using Pramlintide?
Severe hypoglycemia may impair your thinking or reactions, and may result in an injury if you have an accident. Be careful if you drive, operate ma...
Pramlintide Dosing Information
Usual Adult Dose for Diabetes Type 1:15 mcg subcutaneously, injecting immediately prior to each major mealComments:-Mealtime insulin doses (includi...
What Other Drugs Will Affect Pramlintide?
Other drugs may interact with pramlintide, including prescription and over-the-counter medicines, vitamins, and herbal products. Tell each of your...
Amylin the Hormone
Amylin is a 37–amino acid peptide neuroendocrine hormone, which is co-secreted, along with insulin, by the pancreatic β-cells. Physiologically, amylin and insulin concentrations increase several-fold in response to nutrient intake. Together, insulin and amylin create a diurnal profile that can be described as synergistic.
Patient Profile
Pramlintide is approved for use in the United States and is indicated for patients with type 1 or type 2 diabetes who take mealtime insulin. 8 Pramlintide can be considered a logical choice when these individuals, despite efforts with optimized insulin treatment, are unable to reach recommended blood glucose targets.
Pramlintide: Mechanism of Action
The human hormone amylin is insoluble and has a tendency to self-aggregate, which makes it difficult to use therapeutically. To overcome this, a soluble, non-aggregating, equipotent analog of human amylin, pramlintide, was formulated ( Figure 2 ). 9, 10
Getting Started With Pramlintide
Pramlintide is a subcutaneous injection given within 15 minutes before the subsequent meal (or snack) that contains at least 250 kcal or 30 g of carbohydrate. 8 When adding pramlintide to the diabetes treatment plan, a number of specific strategies may be helpful.
Managing Potential Side Effects
In clinical trials, there were no pramlintide-induced changes in vital signs, abnormal findings on physical examination, or clinically relevant changes in laboratory tests, including lipid levels. In addition, no changes in cardiac function or clinically relevant changes in electrocardiograms occurred. 21 – 24
Patient Education
Diabetes self-management education is a crucial element of care for all people with diabetes and is necessary to improve patient outcomes. 34 Patients using pramlintide should receive ongoing care under the guidance of a health care professional skilled in the use of insulin and supported by the services of a diabetes educator.
Monitoring Success
After patients have been properly educated about normal physiology and the missing hormones in diabetes that are important to optimal glycemic control and pramlintide has been appropriately titrated in conjunction with suitable adjustments to mealtime insulin therapy, appropriate patient outcomes might include:
What is pramlintide used for?
Pramlintide is used together with insulin to treat type 1 or type 2 diabetes. Pramlintide is usually given after other diabetes medicines have been tried without success. Pramlintide may also be used for purposes not listed in this medication guide.
How should I use pramlintide?
Your doctor may occasionally change your dose to make sure you get the best results. When you first start using pramlintide, your insulin dose will change. Do not use your medicines in larger or smaller amounts or for longer than recommended.
What should I avoid while using pramlintide?
Severe hypoglycemia may impair your thinking or reactions, and may result in an injury if you have an accident. Be careful if you drive, operate machinery, or do anything dangerous that requires you to be alert.
What other drugs will affect pramlintide?
Other drugs may interact with pramlintide, including prescription and over-the-counter medicines, vitamins, and herbal products. Tell each of your health care providers about all medicines you use now and any medicine you start or stop using.
How long after pramlintide injection can you drink?
Take care not to let your blood sugar get too low. Severely low blood sugar (hypoglycemia) may occur within 3 hours after your pramlintide injection. If you have severe hypoglycemia and cannot eat or drink, use a glucagon injection.
How does pramlintide affect blood sugar?
Pramlintide is a man-made form of a hormone that occurs naturally in the body. Pramlintide lowers blood sugar in three ways. It slows the rate that food moves from your stomach to your intestines, which keeps your blood sugar from rising too fast . Pramlintide also lowers the amount of glucose (sugar) your liver produces. Lastly, pramlintide triggers the feeling of fullness after meals to help control your appetite and decrease how much food you eat.
Can you mix pramlintide and insulin?
Do not mix pramlintide and insulin together in the same syringe .
What is pramlintide? What is pramlintide used for?
Pramlintide is an injectable drug that lowers the level of sugar (glucose) in blood. It is used for treating type 1 and type 2 diabetes. Pramlintide is a synthetic (man-made) hormone that resembles human amylin. Amylin is a hormone that is produced by the pancreas and released into the blood after meals where it helps the body to regulate levels of blood glucose. Amylin acts in several ways to control blood glucose. It slows the rate at which food (including glucose) is absorbed from the intestine. Amylin reduces the production of glucose by the liver by inhibiting the action of glucagon, a hormone produced by the pancreas that stimulates the production of glucose by the liver. Amylin also reduces appetite. In studies, pramlintide-treated patients achieved lower blood glucose levels and experienced weight loss. Pramlintide was approved by the FDA in March 2005.
How does amylin affect blood glucose?
Amylin acts in several ways to control blood glucose. It slows the rate at which food (including glucose) is absorbed from the intestine. Amylin reduces the production of glucose by the liver by inhibiting the action of glucagon , a hormone produced by the pancreas that stimulates the production of glucose by the liver.
Can you mix pramlintide and insulin?
Insulin alters the chemical properties of pramlintide. Therefore, pramlintide and insulin should not be mixed in the same syringe.
Does pramlintide cause nausea?
Nausea decreases with continued administration of pramlintide and is less severe when pramlintide is slowly increased to the desired dose. When used with insulin, especially in patients with type 1 diabetes, severe hypoglycemia may occur. If severe hypoglycemia occurs, it usually manifests within 3 hours after receiving pramlintide.
Is pramlintide safe for pregnant women?
There are no adequate studies of pramlintide in pregnant women.
Does pramlintide slow down the absorption of food?
Pramlintide slows the transit of food through the intestine and, therefore, it should not be administered with other drugs that slow down the intestine (for example, atropine) or slow the absorption of food (for example, acarbose [ Precose ]). Pramlintide may interfere with (slow) the absorption of orally administered drugs.
What is pramlintide used for?
Pramlintide is a recombinant DNA produced polypeptide analogue of human amylin that is used in combination with insulin in the therapy of diabetes. Pramlintide has not been associated with serum enzyme elevations during therapy or with instances of clinically apparent liver injury.
Is pramlintide safe for breast milk?
Pramlintide has a high molecular weight, so it is unlikely to pass into breastmilk in clinically important amounts. It also has a short half-life and it is a peptide that is likely digested in the infant's gastrointestinal tract, so it is unlikely to reach the clinically important levels in infant serum.
Does pramlintide slow down digestion?
By mimicking amylin, pramlintide slows gastric emptying, inhibits digestive secretions (gastric acid, pancreatic enzymes, and bile), reduces glucagon secretion, and increases satiety; all of these actions are mediated mostly by glucose -sensitive areas in the brain stem.
Does pramlintide cause hypoglycemia?
The use of pramlintide may cause an increased risk of insulin-induced hypoglycemia. Pramlintide is a recombinant DNA produced polypeptide analogue of human amylin that is used in combination with insulin in the therapy of diabetes.
What is pramlintide acetate?
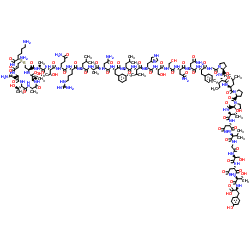
Pramlintide is provided as an acetate salt of the synthetic 37-amino acid polypeptide, which differs in amino acid sequence from human amylin by replacement with proline at positions 25 (alanine), 28 (serine), and 29 (serine). The structural formula of pramlintide acetate is as shown: .
How does amylin affect postprandial glucose?
Amylin affects the rate of postprandial glucose appearance through a variety of mechanisms. Amylin slows gastric emptying (i.e., the rate at which food is released from the stomach to the small intestine) without altering the overall absorption of nutrients. In addition, amylin suppresses glucagon secretion (not normalized by insulin alone), which leads to suppression of endogenous glucose output from the liver. Amylin also regulates food intake due to centrally-mediated modulation of appetite.
How much Symlin is bioavailable?
Pharmacokinetics Absorption. The absolute bioavailability of a single SC dose of SYMLIN is approximately 30 to 40%. Subcutaneous administration of different doses of SYMLIN into the abdominal area or thigh of healthy subjects resulted in dose-proportionate maximum plasma concentrations (Cmax) and overall exposure (expressed as area under the plasma concentration curve or (AUC)) (Table 1).
How long does it take for Symlin to show up?
When severe hypoglycemia associated with SYMLIN use occurs, it is seen within 3 hours following a SYMLIN injection.
What is a symlin pen?
SYMLIN is formulated as a clear , isotonic, sterile solution for subcutaneous (SC) administration. The disposable multidose SymlinPen™ pen-injector contains 1000 mcg/mL of pramlintide (as acetate); SYMLIN vials contain 600 mcg/mL of pramlintide (as acetate). Both formulations contain 2.25 mg/mL of metacresol as a preservative, D-mannitol as a
What is a symlin injection?
SYMLIN® (pramlintide acetate) injection is an antihyperglycemic drug for use in patients with diabetes treated with insulin. Pramlintide is a synthetic analog of human amylin, a naturally occurring neuroendocrine hormone synthesized by pancreatic beta cells that contributes to glucose control during the postprandial period.Pramlintide is provided as an acetate salt of the synthetic 37-amino acid polypeptide, which differs in amino acid sequence from human amylin by replacement with proline at positions 25 (alanine), 28 (serine), and 29 (serine).
What is the role of amylin in insulin?
Amylin also regulates food intake due to centrally-mediated modulation of appetite. In patients with insulin-using type 2 or type 1 diabetes, the pancreatic beta cells are dysfunctional or damaged, resulting in reduced secretion of both insulin and amylin in response to food. Mechanism of Action .
What is pramlintide?
WikiProject Pharmacology may be able to help recruit an expert. (March 2010) Pramlintide (trade name Symlin) is an injectable amylin analogue drug for diabetes (both type 1 and 2) , developed by Amylin Pharmaceuticals (now a wholly owned subsidiary of AstraZeneca ). Pramlintide is sold as an acetate salt.
Is pramlintide an analogue?
Pramlintide (trade name Symlin) is an injectable amylin analogue drug for diabetes (both type 1 and 2), developed by Amylin Pharmaceuticals (now a wholly owned subsidiary of AstraZeneca ). Pramlintide is sold as an acetate salt.
Does pramlintide help with satiety?
In synergy with endogenous amylin, pramlintide aids in the regulation of blood glucose by slowing gastric emptying, promoting satiety via hypothalamic receptors (different receptors than for GLP-1 ), and inhibiting inappropriate secretion of glucagon, a catabolic hormone that opposes the effects of insulin and amylin.
Is pramlintide safe for diabetics?
Pramlintide has been approved by the FDA, for use by type 1 and type 2 diabetic patients who use insulin. Pramlintide allows patients to use less insulin, lowers average blood sugar levels, and substantially reduces what otherwise would be a large unhealthy rise in blood sugar that occurs in diabetics right after eating.
