How to start on the ketogenic diet?
When you are on the keto diet, we recommend monitoring these four variables:
- How you feel. Once you follow the three steps to starting the keto diet, pay attention to how you feel. ...
- Body composition. In most cases, people use the keto diet to lose fat. ...
- Blood biomarkers. Sometimes how you feel and how much weight you lose don’t reflect what is happening inside your body. ...
- Ketosis. ...
Is it dangerous to exercise while on a ketogenic diet?
Avoid exercise if you experience dizziness or irregular heartbeat while on a ketogenic diet. Both may represent serious conditions like dehydration or electrolyte imbalance. The aim of a ketogenic diet is to burn fat instead of carbohydrates. The human body uses fat as the primary source of energy during extended ketosis.
What are the side effects of a ketogenic diet?
What are the side effects of ketosis?
- Your insulin levels drop. On a normal diet, after eating glucose-containing foods, your insulin levels will be higher. ...
- You're less hungry during the day. Protein is incredibly filling, and because you’re increasing your protein consumption on the keto diet, you’re bound to feel more satiated during the ...
- You can start feeling sick. ...
What to eat and avoid on the ketogenic diet?
There are five types of carbs to avoid on keto:
- Grains
- Beans and legumes
- Most fruits
- Starchy vegetables (including sweet potatoes, potatoes, and most winter squash)
- Sugar (natural, calorie-free sweeteners like stevia and erythritol are OK)
What is the mechanism of action of the keto diet in the human body which is used to reduce weight in obese people?
This diet has a diuretic effect, and some early weight loss is due to water weight loss followed by a fat loss. Interestingly with this diet plan, lean body muscle is largely spared. As a nutritional ketosis state sustains, hunger pangs subside, and an overall reduction in caloric intake helps to further weight loss.
What is the mechanism of the keto diet for epilepsy?
The ketogenic diet has been used to reduce seizures since the 1920s. The mechanism by which the seizures are controlled are poorly understood. Both the low sugar component and high fat component uniquely alters the 'excitability' of the brain, thereby reducing the tendency to generate seizures.
Does the keto diet stop seizures?
Several studies have shown that the ketogenic diet does reduce or prevent seizures in many children whose seizures could not be controlled by medications. Over half of children who go on the diet have at least a 50% reduction in the number of their seizures. Some children, usually 10-15%, even become seizure-free.
Why was the keto diet created?
The ketogenic diet became popular as a therapy for epilepsy in the 1920s and 30s. It was developed to provide an alternative to non-mainstream fasting, which had demonstrated success as an epilepsy therapy. However, the diet was eventually largely abandoned due to the introduction of new anticonvulsant therapies.
How long does it take keto to work for epilepsy?
After an average of 20 weeks of treatment, 50% of the patients had a >90% reduction in seizures.
How does vagus nerve stimulation treat epilepsy?
Vagus nerve stimulator (VNS) therapy is a treatment for epilepsy. The vagus (VAY-gus) nerve runs up the sides of the neck and into the brain. The VNS sends electrical pulses to the nerve, which carries the pulses to the brain. This helps prevent or shorten the length of seizures.
What syndrome's effects may be mitigated by a ketogenic diet?
Bottom Line: Ketogenic diets can improve many aspects of the metabolic syndrome, a major risk factor for obesity, type 2 diabetes, and heart disease.
What is a ketogenic diet and why is it used?
“Ketogenic” is a term for a low-carb diet (like the Atkins diet). The idea is for you to get more calories from protein and fat and less from carbohydrates. You cut back most on the carbs that are easy to digest, like sugar, soda, pastries, and white bread.
What is the keto diet?
The ketogenic diet (KD) is a high-fat, low-carbohydrate, adequate protein diet that has been employed as a treatment for medically-refractory epilepsy for over 90 years.1This “alternative” therapy was originally designed to mimic the biochemical changes associated with fasting, a treatment reported anecdotally over millennia to control seizure activity. The hallmark features of KD treatment are the production of ketone bodies (principally β-hydroxybutyrate, acetoacetate and acetone) – products of fatty acid oxidation in the liver – and reduced blood glucose levels (Figure 1). Ketone bodies provide an alternative substrate to glucose for energy utilization, and, in the developing brain, also constitute essential building blocks for the biosynthesis of cell membranes and lipids.
What is the metabolic pathway of keto?
Metabolic pathways involved in ketogenic diet (KD) treatment. In the liver, fatty acids are ordinarily converted into acetyl-CoA which enters the tri carboxylic acid (TCA) cycle. When fatty acid levels are elevated and exceed the metabolic capacity of (more...)
What are the metabolic changes that are likely related to the KD's anticonvulsant properties?
Metabolic changes likely related to the KD’s anticonvulsant properties include – but are not limited to – ketosis, reduced glucose, elevated fatty acid levels, and enhanced bioenergetic reserves.
What is the mechanism of action of KD?
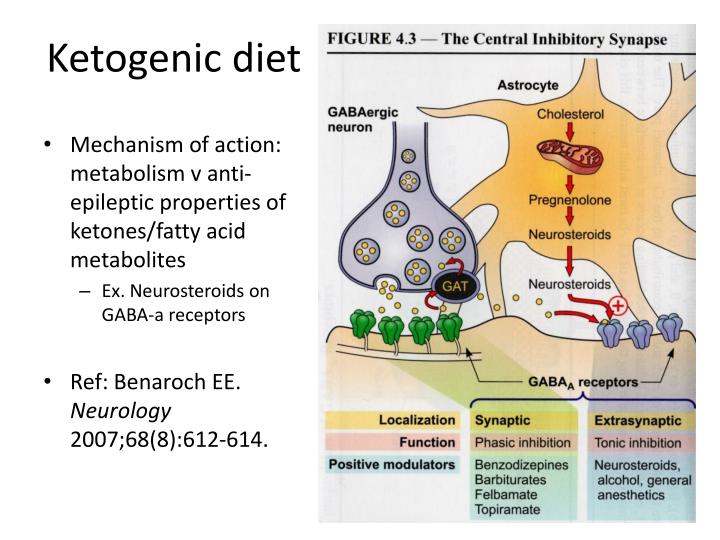
An enduring hypothesis regarding the mechanisms KD action involves enhancement of GABA-mediated inhibition. Facilitation of GABAergic neurotransmission has long been accepted as a critical mechanism of action for a variety of clinically effective antiepileptic drugs, and thus there is an intrinsic appeal to invoking this mechanism. With respect to ketone bodies, however, GABAAreceptors do not appear to be the primary targets in this regard. The indirect evidence comes from acute animal studies in which the KD is found to be most effective against seizures evoked by the GABAergic antagonists (i.e., PTZ, bicuculline, picrotoxin and γ-butyrolactone), whereas it fails to block acute seizures provoked by kainic acid, strychnine (a glycine receptor antagonist), and maximal electroshock (MES; involving voltage-dependent sodium channels).48
Does LGIT cause ketosis?
Interestingly, LGIT does not induce the prominent ketosis seen with classic KDs and the Atkin’s diet.
Do ketones affect KD?
In summary, the available evidence thus far fails to strongly support a primary mechanistic role for ketone bodies in the clinical efficacy of the KD, as no compelling molecular target has been identified and linked to attenuation of spontaneous seizures in a chronic epilepsy model. At this juncture, it is unlikely that there is only one relevant action of any of the primary ketone bodies on neuronal activity. If ketones are indeed fundamentally required for the anticonvulsant efficacy of the KD, they are more likely contributory to other parallel (and possibly synergistic) effects of the diet. Of the various hypotheses proposed, the most likely candidate mechanisms are membrane hyperpolarization through activation of potassium channels, increased GABAergic neurotransmission, or a reduction in vesicular glutamate release. Ketones have been shown to reduce brain glucose consumption,95and reduced glucose is another key hallmark of a KD discussed in more detail below.
Is KD effective in epilepsy?
Comparable to induced models, the KD has also been shown to be effective in genetically-determined epilepsy models. The EL mouse is a seizure-susceptible inbred strain believed to represent a model of multifactorial idiopathic partial epilepsy with secondary generalization.65Environmental stimulation such as repetitive handling can induce seizures in EL mice and facilitate epileptogenesis beginning at P30. Generalized seizures generally manifest by the second postnatal month and persist throughout later life.66When fed a 4.75:1 KD formula over a 10-week period, seizure susceptibility scores were significantly reduced compared to controls after 3 weeks, but this difference disappeared by week 7.67These transient results were similar to what had been reported earlier in the kindling model.44
Does keto diet help with seizures?
Ketogenic diet therapy combines several beneficial mechanisms that provide broad benefits for the treatment of epilepsy with the potential to not only suppress seizures but also to modify the course of the epilepsy.
Is ketogenic diet good for epilepsy?
New insights into the mechanisms of the ketogenic diet. Ketogenic diet therapy combines several beneficial mechanisms that provide broad benefits for the treatment of epilepsy with the potential to not only suppress seizures but also to modify the course of the epilepsy.
How does the keto diet work?
Because the ketogenic diet works when medicines fail, it appears that the diet’s mechanisms of action are different than those of anti-epileptic drugs. AEDs work by targeting neurons, and altering the chemical signals they produce. While the Ketogenic Diet shows efficacy in a spectrum of epilepsy syndromes, specific AEDs are only effective if ...
Who endorsed the keto diet?
The consensus statement was subsequently endorsed by the Practice Committee of the Child Neurology Society, paving the way for broad use of the Ketogenic Diet to treat epilepsy. Among the committee’s conclusions were:
Does ketones help with seizures?
It can be a cure. Since the metabolic shift is not site specific and takes place throughout the brain, the diet can be applied to several epilepsy syndromes. Though the exact mechanisms of action are still being studied, the metabolic theory as well as serum ketones continue to be the most highly supported and studied. The metabolic theory postulates that the seizure control is realized through the restoration of the brain’s natural metabolic state through pathways including enhanced mitochondrial energy metabolism and increased availability of energy to the brain. The diet has also been shown to exert neuroprotective antioxidant effects by reducing reactive oxygen species (ROS) production in mitochondria. Moreover, a reduction in glucose levels in the blood, excitatory neurotransmitters in the brain, and inflammation body-wide may support the anti-seizure effect of the diet.
Is KD a treatment for GLUT-1?
It can be considered the treatment of choice for two distinct disorders of brain metabolism, GLUT-1 deficiency syndrome and PDHD. In the particular epilepsy syndromes of Dravet syndrome, infantile spasms, myoclonic-astatic epilepsy, tuberous sclerosis complex, the KD could be offered earlier.”.
Can ketones cause seizure?
Researchers have also shown that the ketone bodies, beta hydroxybuterate and acetoacetate, might be the cause for the anti-seizure effects. One such paradigm supporting this theory is the fact that seizure control can be lost by consuming carbohydrates, and, thus, falling out of ketosis.
Is ketogenic diet good for epilepsy?
While the Ketogenic Diet shows efficacy in a spectrum of epilepsy syndromes , specific AEDs are only effective if the drug is matched to the condition which is subjective at best. AEDs are known to carry harsh adverse effects, the most common of which are dizziness, drowsiness, and mental slowing, while less common though more severe side effects ...
What is it called when a body is in ketosis?
When ketone bodies accumulate in the blood, this is called ketosis. Healthy individuals naturally experience mild ketosis during periods of fasting (e.g., sleeping overnight) and very strenuous exercise. Proponents of the ketogenic diet state that if the diet is carefully followed, blood levels of ketones should not reach a harmful level (known as “ketoacidosis”) as the brain will use ketones for fuel, and healthy individuals will typically produce enough insulin to prevent excessive ketones from forming. [2] How soon ketosis happens and the number of ketone bodies that accumulate in the blood is variable from person to person and depends on factors such as body fat percentage and resting metabolic rate. [3]
How much protein is in a keto diet?
The findings below have been limited to research specific to the ketogenic diet: the studies listed contain about 70-80% fat, 10-20% protein, and 5-10% carbohydrate. Diets otherwise termed “low carbohydrate” may not include these specific ratios, allowing higher amounts of protein or carbohydrate.
What are the effects of diet?
The Research So Far 1 A satiating effect with decreased food cravings due to the high-fat content of the diet. 2 A decrease in appetite-stimulating hormones, such as insulin and ghrelin, when eating restricted amounts of carbohydrate. 3 A direct hunger-reducing role of ketone bodies—the body’s main fuel source on the diet. 4 Increased calorie expenditure due to the metabolic effects of converting fat and protein to glucose. 5 Promotion of fat loss versus lean body mass, partly due to decreased insulin levels.
How are net carbs calculated?
They are calculated by subtracting the amount of indigestible carbohydrates from the total carbohydrate amount.
When did the low carb diet start?
However, this diet is gaining considerable attention as a potential weight-loss strategy due to the low-carb diet craze, which started in the 1970s with the Atkins diet (a very low-carbohydrate, high-protein diet, which was a commercial success and popularized low-carb diets to a new level). Today, other low-carb diets including ...
What happens to the body when glucose is depleted?
If this continues for 3-4 days and stored glucose is fully depleted, blood levels of a hormone called insulin decrease, and the body begins to use fat as its primary fuel. The liver produces ketone bodies from fat, which can be used in the absence of glucose. [1]
Is ketoacidosis harmful?
Proponents of the ketogenic diet state that if the diet is carefully followed, blood levels of ketones should not reach a harmful level (known as “ketoacidosis”) as the brain will use ketones for fuel, and healthy individuals will typically produce enough insulin to prevent excessive ketones from forming. [2] .
What are the hypotheses of ketogenic diet?
The present discussion will focus on three of them. The gist of all of these hypotheses is that the ketogenic diet makes the brain switch from a glucose-based metabolism to a ketone-based metabolism , and that this change somehow produces anticonvulsant effects.
What is the keto diet?
The ketogenic diet is a high-fat, low-carbohydrate diet used to treat drug-resistant seizures, especially in children. The ketogenic diet was first formulated by Wilder1 in 1921. It lost favor after the invention of phenytoin in 1938, but came back into prominence in the 1990s when it became clear that the diet could control seizures that resist anticonvulsant drugs.2
Does ketogenic diet affect mitochondria?
Bough et al.15 have reported that rats on the ketogenic diet produce more mitochondria than rats on normal rodent chow . Presumably, more mitochondria would also mean more energy for the brain, and, therefore, possibly, fewer seizures. As with the “increased brain energy” hypothesis, the question remains as to whether the epileptic brain is energy deficient, and whether supplying more energy will make the epileptic brain less excitable.