What is the function of your vision?
Your vision is what allows you to see the world around you. You have vision thanks to several components within the eye and brain that work together. These parts include the: Lens. Retina. Optic nerve. Each part turns light and electrical signals into images that you can see.
What are the parts of vision?
Vision refers to the parts of your eye and brain that enable to you to see. The main parts of the eye include the cornea, pupil, iris, lens, retina and optic nerve. Coronavirus
What is the pathway of light through the eye?
First, light passes through the cornea (the clear front layer of the eye). The cornea is shaped like a dome and bends light to help the eye focus. Some of this light enters the eye through an opening called the pupil (PYOO-pul).
How do the eyes work together?
How the Eyes Work All the different parts of your eyes work together to help you see. First, light passes through the cornea (the clear front layer of the eye). The cornea is shaped like a dome and bends light to help the eye focus.

What are the 6 steps of vision in order?
Terms in this set (6)Reception. Light enters through the cornea. ... Transduction. Electro-magnetic energy (light) is converted into electro-chemical impulses by the rods and cones. ... Transmission. ... Selection. ... Organisation. ... Interpretation.
What is the process of vision psychology?
Seeing begins when light falls on the eyes, initiating the process of transduction. Once this visual information reaches the visual cortex, it is processed by a variety of neurons that detect colours, shapes, and motion, and that create meaningful perceptions out of the incoming stimuli.
Which is the nervous mechanism of sight?
Retinal is the fundamental structure involved in the transduction of light into visual signals, i.e. nerve impulses in the ocular system of the central nervous system.
What begins the process of vision?
The vision process starts when light rays from the objects you see pass through the cornea, the clear, dome-like structure covering your eyes. These light rays will then enter a black opening called the pupil. The size of your pupil is controlled by the iris, the colorful part of your eyes.
How is vision processed in the brain?
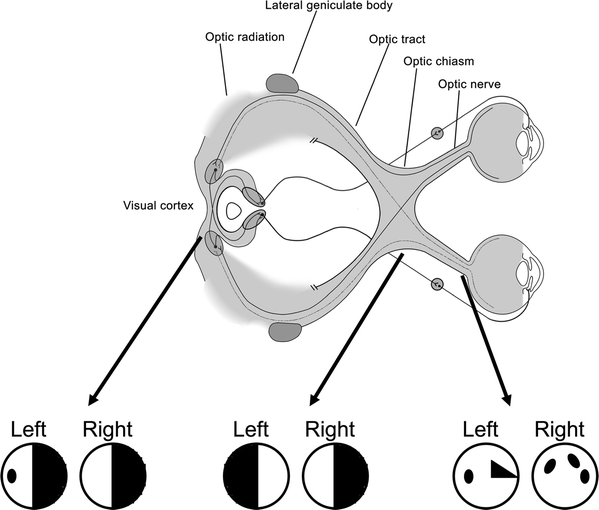
From the eye to the brain The axons of ganglion cells exit the retina to form the optic nerve, which travels to two places: the thalamus (specifically, the lateral geniculate nucleus, or LGN) and the superior colliculus. The LGN is the main relay for visual information from the retina to reach the cortex.
Where is vision processed in the brain?
Visual information from the retina is relayed through the lateral geniculate nucleus of the thalamus to the primary visual cortex — a thin sheet of tissue (less than one-tenth of an inch thick), a bit larger than a half-dollar, which is located in the occipital lobe in the back of the brain.
What is mechanism of vision Class 11?
The function of refracting the light inside the eye is done by the cornea. The light rays having the visible wavelength are focused on the retina of the eye with the help of the cornea and lens of the eye. When the light strikes the retina portion, this generates impulses in the rods and cones in the retina of the eye.
Which of the following is an event in mechanism of vision?
(i) Neural impulses are analyzed and the image formed on the retina is recognized by visual cortex. (ii) Membrane permeability changes. (iii) Ganglion cells are excited. (iv) Bipolar cells are depolarized.
What are the 3 visual pathways?
optic tracts. lateral geniculate body. optic radiation. visual cortex and its cortical projections.
What is the first stage of visual processing?
The optical stage of vision is associated with the optical apparatus of the eye–the front of the eye. This first part of the visual pathway should result in a clear image of the environment on the retina. The pupil is the opening that lets light enter the eye and ultimately reach the retina.
What is visual information processing in psychology?
Visual information processing is the ability to interpret what is seen. It is a vision that directs action. Good visual information processing means being able to quickly and accurately process and analyse what is being seen, and store it in visual memory for later recall.
What are the 3 psychological dimensions of vision?
COLOR AND DEPTH PERCEPTION Let's look at how color vision works and how we perceive three dimensions (height, width, and depth).
Why is vision important in psychology?
The visual system constructs a mental representation of the world around us (Figure SAP. 12). This contributes to our ability to successfully navigate through physical space and interact with important individuals and objects in our environments.
What are the three components of vision?
You have vision thanks to several components within your eye and brain that work together....These parts include the:Lens.Retina.Optic nerve.
What is the force that contacts the human chemistry in the recording retina of the eye?
It is known that a force called radiant energy , contacts the human chemistry in the recording retina of the eye. The transformation which follows that reaction sends on a force which so acts on cells in both of the visual centers in the brain, that a conception is formed in the mind. Without the mind the eyes could not function.
How is the retina held against the inner surface of the eyeball?
The retina is held closely against the inner surface of the eyeball walls by the pressure outward of the fluid contained in the eyeball.
What was the undercurrent of a special tension in her mind?
Although always helped by sunlight and methods of relaxation, there was a constant undercurrent of a special tension in her mind which would often hamper and disturb the vision, and was relieved, sometimes in a moment, when the morbid attitude of the mind was overcome by some simple expedient which secured relaxation.
What is the fault of the control center in the brain?
But in the great majority of difficulties with vision, the fault is that the external muscles of the eye act in an abnormal manner and misdirect the rays of light after they enter the eye. This certainly is the fault of the control center in the brain.
Can the left eye see the right half of a card?
Since the eyes cannot see, with the right eye the letters on the left half of the card, nor with the left eye the letters on the right half of the card, such a transposition cannot be effected by the eyes. The fault in the fusion must be in the section of the vision mechanism which is behind the retina.
Is the eye neglected?
The eye alone is being neglected. There is no least effort being made to study, and nurture, and develop and save the functions and power of the mechanism of vision. The higher mental elements of the faculty of vision are being deliberately ignored.
Can a human lens refract light?
The prevailing method of treating visual dysfunctions apparently takes it for granted that the human lens has not the power to use its adaptive function – in other words, that it cannot refract the rays of light properly, and that it cannot recover what power it has lost.
How do the eyes work?
How the Eyes Work. All the different parts of your eyes work together to help you see. First, light passes through the cornea (the clear front layer of the eye). The cornea is shaped like a dome and bends light to help the eye focus. Some of this light enters the eye through an opening called the pupil (PYOO-pul).
What part of the eye controls light?
The iris (the colored part of the eye) controls how much light the pupil lets in. Next, light passes through the lens (a clear inner part of the eye). The lens works together with the cornea to focus light correctly on the retina. When light hits the retina (a light-sensitive layer of tissue at the back of the eye), ...
What cells turn light into electrical signals?
When light hits the retina (a light-sensitive layer of tissue at the back of the eye), special cells called photoreceptors turn the light into electrical signals.
Do eyes need tears?
Your eyes also need tears to work correctly .
What are the conditions that affect vision?
There are many different conditions that can affect your vision. These conditions often interfere with the ability of light to pass from the eye to the brain. Healthcare providers can often prevent or correct many of these conditions.Conditions that affect your vision can include: 1 Aging: As you get older, your risk increases for vision-impairing conditions. Common disorders include cataracts (clouding of the eye lens) and age-related macular degeneration (AMD), a condition that causes loss or distortion of vision. 2 Damage: Injuries may cause a detached retina or a clouding of the cornea or lens. This damage can block light from passing through your eye and cause vision loss. 3 Development disorders: Sight problems such as amblyopia (lazy eye) occur when one or both eyes develop abnormally during childhood. 4 Disease: Diseases like glaucoma (increased fluid pressure in the eye) can damage the optic nerve. As a result, they impair the brain’s ability to turn electrical signals into images. 5 Infection: Infections in any part of the eye can affect your ability to see. 6 Refractive errors: Vision problems can occur when your eye doesn’t bend light properly. This issue may impair your eye’s ability to focus and cause unclear eyesight. Corrective lenses, such as glasses or contact lenses, can often improve your eyes ability to see clearly.
What are the parts of the eye that make up vision?
The main components of your vision include: Cornea: This is the front layer of your eye. The cornea is dome-shaped and it works by bending the light that enters your eye.
Why is my vision unclear?
Infection: Infections in any part of the eye can affect your ability to see. Refractive errors: Vision problems can occur when your eye doesn’t bend light properly. This issue may impair your eye’s ability to focus and cause unclear eyesight.
What part of the brain is responsible for forming images?
Optic nerve: This part of your vision works as the connecting element between the retina and the brain. Your optic nerve transmits the electrical signals formed in the retina to the brain. Once there, the brain creates images. Tears: Though they are most commonly thought of in relation to crying, tears are meant to keep your eyes wet ...
What is the part of the eye that allows you to see?
You have vision thanks to several components within t your eye and brain that work together. These parts include the: Lens. Retina. Optic nerve. Each part turns light and electrical signals into images that you can see.
Why is it important to have yearly eye care?
It’s important to schedule yearly eye care appointments, so any developing issues can be cared for as early as possible. Wearing sunglasses: More than just a fashion statement, sunglasses protect your eyes from the sun's damaging rays and can slow down the aging process of your eyes.
How does the cornea work?
The cornea is dome-shaped and it works by bending the light that enters your eye. Pupil: The pupil is the black dot in the center of your eye that acts as a gateway for light. It expands in dim light and shrinks in bright light. It’s controlled by the iris. Iris: This part is typically referred to as your eye color.
What is the reflex process of bringing light rays from an object into perfect focus on the retina?
Accommodation of lens to focus image: Accommodation is a reflex process to bring light rays from object into perfect focus on retina by adjusting the lens. When an object lying less than 6 meter away is viewed, image formed behind retina. But due to accommodation of lens image formed in retina and we can see the object.
Which cells transmit impulses directly from the retina to the brain?
Photoreceptor cells, bipolar cells and ganglion cells transmit impulse directly from retina to brain.
What is convergence of images?
Convergence of image: Human eye have binocular vision, it means although we have two eye, we perceive single image. In binocular vision, two eye ball turns slightly inward to focus a close object so that both image falls on corresponding points on retina at same time. This phenomenon is called convergence.
What muscle contract and lens become thick which causes focus on closer object?
For accommodation to view closer object, ciliary muscle contract and lens become thick which causes focus on closer object.
How many rods are in the retina?
Photo-chemical activity in retina and conversion into neural impulse. 1. Photochemical activity in rods: Each eye contains 125 million rods which are located in neuro-retina. Rods contains light sensitive pigment-rhodopsin.
How many cone cells are there in the human eye?
Each eye contains 7 million cone cells. The neural activity in cone cell is similar to that of rod cell but there are three different types of cone cells and each cone cell contains different photo-pigment and are sensitive to red, green and blue.
How far can the eye see light?
The normal eye is able to accommodate light from object about 25 cm to infinity.
How does the human eye work?
Each human eye captures a 2D image and thus, transfers two versions of an image to the brain. Human eyes have an evolved sense of vision that helps the brain to interpret exact synchronisation. Due to the ability of human eyes which possess foveas, felines, primates, and frontal vision, this accurate synchronisation happens.
What are the two methods of 3D vision?
Allied Mechanisms. Other than the stereoscopic vision process, humans also use a stereogram mechanism for 3D vision. Cross-eye and parallel viewing are the two methods that bring about a stereogram. More information on stereoscopic vision you should check out our detailed study materials.
What is the difference between stereoscopic vision and binocular vision?
This can also be termed as the binocular disparity in animals and retinal disparity in humans. Stereoscopic vision signifies the three-dimensional visual ability of humans with their two eyes. A single eye creates a two-dimensional image of objects. However, the brain merges these two-dimensional images and interprets their difference.
What is stereopsis in 3D vision?
Stereopsis is a process of visual perception in which an in-depth sense of sight creates different perspectives of received information by the horizontal separation of two eyes. This can also be termed as the binocular disparity in animals and retinal disparity in humans.
What are the advantages of stereoscopic vision?
Advantages of Stereoscopic Vision. With the help of stereoscopic vision, humans can manage to handle small objects. It helps to reciprocate threats and react accordingly. Provides a deep sense of perception. It helps to achieve accuracy in various profiles like the manufacturing industry.
Why do we use stereoscopic vision?
Ans. Stereoscopic vision helps to improve the accuracy of depth perception. Nowadays, for animals, this vision helps them to collect food or defend themselves. However, humans now use stereoscopic vision for artistic purposes.
How far is the distance between two eyes?
The distance between two human eyes is about 2 inches. Thus, this retinal disparity helps the brain to process and assess a sense of distance. The brain utilises all these spatial information and brings about precise depth information as stereoscopic vision.