Microbial Death Curve, plotted logarithmically, shows this constant death rate as a straight line. Figure 7.1a Rate of Microbial Death Bacterial populations subjected to heat or antimicrobial chemicals die at a constant rate.
What is microbial death?
Microbial Death STUDY Flashcards Learn Write Spell Test PLAY Match Gravity Created by callumscott46 Terms in this set (35) Definition of Microbial Death A permanent loss of reproductive ability under ideal environmental conditions Autolysis Death due to self-degradation via the microbes own enzymes D Value (Viable Cell Count Graph)
What is a bacterial growth curve?
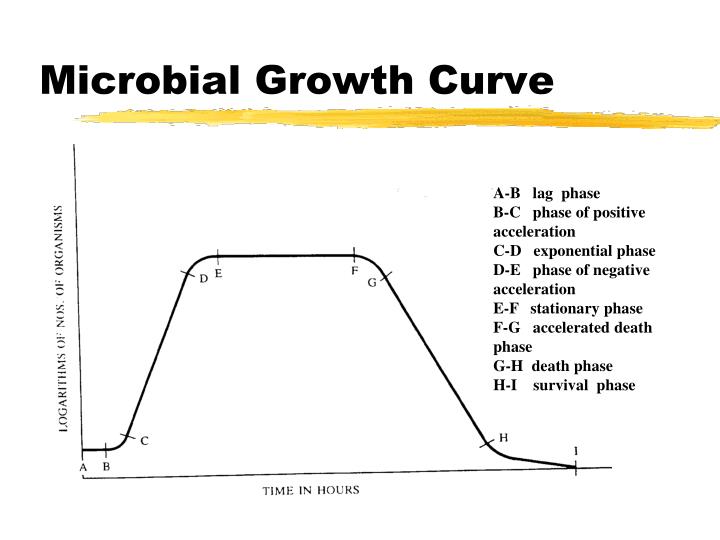
This pattern can be graphically represented as the number of living cells in a population over time and is known as a bacterial growth curve. Bacterial growth cycles in a growth curve consist of four phases: lag, exponential (log), stationary, and death.
What is the death phase of bacteria?
The death phase is characterized by an exponential decrease in the number of living cells. Bacteria require certain conditions for growth, and these conditions are not the same for all bacteria. Factors such as oxygen, pH, temperature, and light influence microbial growth.
Do first-order reaction kinetics explain microbial survival curves?
Reinterpretation of microbial survival curves The heat inactivation of microbial spores and the mortality of vegetative cells exposed to heat or a hostile environment have been traditionally assumed to be governed by first-order reaction kinetics. The concept of thermal death time and the standard methods of calculating the safety of commercial …

What is meant by microbial death?
Microbial Death is defined as the permanent loss of reproductive capacity under ideal environmental conditions. The Microbial Death rate is usually found to be constant over a period of time.
What is microbial curve?
The bacterial growth curve represents the number of live cells in a bacterial population over a period of time. There are four distinct phases of the growth curve: lag, exponential (log), stationary, and death. The initial phase is the lag phase where bacteria are metabolically active but not dividing.
What is the microbial death rate used to measure?
Thermal death time is a concept used to determine how long it takes to kill a specific bacteria at a specific temperature. It was originally developed for food canning and has found applications in cosmetics, and in producing salmonella-free feeds for animals (e.g. poultry, and pharmaceuticals).
What is microbial death quizlet?
Definition of Microbial Death. A permanent loss of reproductive ability under ideal environmental conditions.
What is death phase in bacterial growth?
Death Phase As waste builds up and nutrient rich media is depleted, the death phase is the point where the living cells stop metabolic functions and begin the process of death. As cells lyse and fill the culture with what was once on their insides, the environment changes one last time and exponential decay begins.
What are the 4 phases of the microbial growth curve?
Bacterial colonies progress through four phases of growth: the lag phase, the log phase, the stationary phase, and the death phase. The generation time, which varies among bacteria, is controlled by many environmental conditions and by the nature of the bacterial species.
How do you calculate microbial death?
The formula (log No -- log N)a = kt + C was adapted to linearize these data. No and N are the initial and surviving numbers of organisms at the time t. The death rate is given by k, and C is a constant for a set of data.
What factors affect microbial death?
The rate of growth or death of a particular microbial species is influenced by a variety of physical factors in its environment including temperature, osmotic pressure, pH, and oxygen concentration.
What factors may affect the microbial death rate?
Terms in this set (5)Time.No. Of microbes and composition of population.Temp and oh of environment.Concentration and mode of action of microcidal agent.Presence of organic matter like blood and saliva can decrease effectiveness.
What are endospores used for?
It allows the bacterium to produce a dormant and highly resistant cell to preserve the cell's genetic material in times of extreme stress. Endospores can survive environmental assaults that would normally kill the bacterium.
What is the most widely used physical method of microbial control?
Heat. Heating is one of the most common—and oldest—forms of microbial control. It is used in simple techniques like cooking and canning. Heat can kill microbes by altering their membranes and denaturing proteins.
Which of the following terms is defined as the destruction of vegetative pathogens?
E) Burying human wastes. a. Which of the following terms is defined as the destruction of vegetative pathogens but not bacterial endospores? A) Disinfection.
What is the purpose of a growth curve in microbiology?
Growth curves are also common tools in ecological studies; they are used to track the rise and fall of populations of plants, animals, and other multicellular organisms over time.
What is the purpose of growth curve?
Growth curves are widely used in statistics to determine patterns of growth over time of a quantity—be it linear, exponential, or cubic. Businesses use growth curves to track or predict many factors, including future sales.
How does an antimicrobial work?
Antimicrobials work at a cellular level to continually disrupt and prevent the growth of microorganisms. By creating an inhospitable environment for microorganisms like bacteria, mold and mildew, antimicrobials protect everyday products like countertops, toys, surface coatings, textiles and hospital equipment.
What factors may affect the microbial death rate?
Terms in this set (5)Time.No. Of microbes and composition of population.Temp and oh of environment.Concentration and mode of action of microcidal agent.Presence of organic matter like blood and saliva can decrease effectiveness.
What is the growth curve of bacteria?
The bacterial growth curve represents the number of live cells in a bacterial population over a period of time. There are four distinct phases of the growth curve: lag, exponential (log), stationary, and death. The initial phase is the lag phase where bacteria are metabolically active but not dividing. The exponential or log phase is ...
What is the growth curve of a bacterial population?
The bacterial growth curve represents the number of live cells in a bacterial population over a period of time. Lag Phase: This initial phase is characterized by cellular activity but not growth. A small group of cells are placed in a nutrient rich medium that allows them to synthesize proteins and other molecules necessary for replication.
What is the process of bacterial reproduction?
Geology. Astronomy. Weather & Climate. Bacteria are prokaryotic organisms that most commonly replicate by the asexual process of binary fission. These microbes reproduce rapidly at an exponential rate under favorable conditions. When grown in culture, a predictable pattern of growth in a bacterial population occurs.
What phase do bacteria enter?
These cells increase in size, but no cell division occurs in the phase. Exponential (Log) Phase: After the lag phase, bacterial cells enter the exponential or log phase. This is the time when the cells are dividing by binary fission and doubling in numbers after each generation time. Metabolic activity is high as DNA, RNA, cell wall components, ...
What happens to bacteria during the stationary phase?
Bacterial cell growth reaches a plateau, or stationary phase, where the number of dividing cells equal the number of dying cells. This results in no overall population growth. Under the less favorable conditions, competition for nutrients increases and the cells become less metabolically active.
What are the factors that influence bacteria growth?
Bacteria require certain conditions for growth, and these conditions are not the same for all bacteria. Factors such as oxygen, pH, temperature, and light influence microbial growth. Additional factors include osmotic pressure, atmospheric pressure, and moisture availability.
Where can bacteria be found?
These microbes can be found in locations such as hot springs and in the human body in acidic areas such as the vagina. The majority of bacteria are neutrophiles and grow best in sites with pH values close to 7. Helicobacter pylori is an example of a neutrophile that lives in the acidic environment of the stomach.
What is the death phase of a growth curve?
Death or Decline phase. In the last phase of the growth curve, the death or decline phase, the number of viable cells decreases in a predictable ( or exponential) fashion. The steepness of the slope corresponds to how fast cells are losing viability.
How is microbial growth measured?
While growth for muticelluar organisms is typically measured in terms of the increase in size of a single organism, microbial growth is measured by the increase in population, either by measuring the increase in cell number or the increase in overall mass.
What are the metabolites that are missing from the lag period?
Typically cells in the lag period are synthesizing RNA, enzymes, and essential metabolites that might be missing from their new environment (such as growth factors or macromolecules), as well as adjusting to environmental changes such as changes in temperature, pH, or oxygen availability.
What are the phases of growth in bacteria?
It has been determined that in a closed system or batch culture (no food added, no wastes removed) bacteria will grow in a predictable pattern, resulting in a growth curve composed of four distinct phases of growth: the lag phase, the exponential or log phase, the stationary phase, and the death or decline phase.
What is the exponential phase of cell division?
Exponential or Log phase. Once cells have accumulated all that they need for growth, they proceed into cell division. The exponential or log phase of growth is marked by predictable doublings of the population, where 1 cell become 2 cells, becomes 4, becomes 8 etc. Conditions that are optimal for the cells will result in very rapid growth ...
What is the lag phase of bacteria?
The lag phase is an adaptation period, where the bacteria are adjusting to their new conditions. The length of the lag phase can vary considerably, based on how different the conditions are from the conditions that the bacteria came from, as well as the condition of the bacterial cells themselves. Actively growing cells transferred from one type of media into the same type of media, with the same environmental conditions, will have the shortest lag period. Damaged cells will have a long lag period, since they must repair themselves before they can engage in reproduction.
What is the process of dividing bacteria and archaea?
Bacteria and archaea most commonly engage in a process known as binary fission, where a single cell splits into two equally sized cells.
What is the growth curve of bacteria?
Bacterial growth curve. The term growth is more commonly used to refer to growth in the size of a population. Population growth is often studied by analyzing the growth of microbes in liquid (broth) culture. When microorganisms are cultivated in broth, they usually are grown in a batch culture; that is, they are incubated in a closed culture vessel ...
How to get a growth curve of a species of bacteria?
The bacterial growth curve of a particular species of bacteria can be obtained by the following steps; The growth curve of a population of a particular species can be obtained by growing a pure culture of the organism in a liquid medium at a constant temperature.
What happens to bacteria during the stationary phase?
During the stationary phase, the bacterial cells also produce secondary metabolites or metabolites produced after active growth, such as antibiotics.
What happens during the metabolic phase of a bacterial cell?
During this step the cells start their metabolic activity but don’t divide. In this phase the bacterial cells also synthesis RNA, enzymes, and essential metabolites, as well as adjusting to environmental changes such as changes in temperature, pH, or oxygen availability.
Why do microbes enter stationary phase?
One of the most important reasons is nutrient limitation; if an essential nutrient is severely depleted, population growth will slow and eventually stop. Aerobic organisms often are limited by O2 availability.
What causes bacteria to die?
The depletion of essential nutrients and the accumulation of toxic wastes; such as acids are the main reasons for the Death or Decline phase of growing bacterial cells. It is thought to be under specific conditions the dead cells might be revived, this condition is known as viable but nonculturable (VBNC).
What happens to the population of bacteria during the inoculum phase?
During this phase, the bacterial cells start to increase their size and physiologically they are becoming very active and are synthesizing new protoplasm.
Which model of microbial growth is the most notable?
Most of the models of microbial growth in food are Empirical algebraic, of which the Gompertz model is the most notable, Rate equations, mostly variants of the Verhulst's logistic model, or Population Dynamics models, which can be deterministic and continuous or stochastic and discrete.
Can a model predict non-isothermal growth?
None provides any mechanistic insight or has inherent advantage over the others. In principle, models of all three kinds can predict non-isothermal growth patterns from isothermal data. Thus a modeler should choose the simplest and most convenient model for this purpose.
Lag Phase
Exponential Or Log Phase
- Once cells have accumulated all that they need for growth, they proceed into cell division. The exponential or log phaseof growth is marked by predictable doublings of the population, where 1 cell become 2 cells, becomes 4, becomes 8 etc. Conditions that are optimal for the cells will result in very rapid growth (and a steeper slope on the growth curve), while less than ideal conditions …
Stationary Phase
- All good things must come to an end (otherwise bacteria would equal the mass of the Earth in 7 days!). At some point the bacterial population runs out of an essential nutrient/chemical or its growth is inhibited by its own waste products (it is a closed container, remember?) or lack of physical space, causing the cells to enter into the stationary phase. At this point the number of n…
Death Or Decline Phase
- In the last phase of the growth curve, the death or decline phase, the number of viable cells decreases in a predictable (or exponential) fashion. The steepness of the slope corresponds to how fast cells are losing viability. It is thought that the culture conditions have deteriorated to a point where the cells are irreparably harmed, since cells c...